Add vendor
Specifically because I want to modify a dependency
This commit is contained in:
22
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
22
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
language: go
|
||||
|
||||
os:
|
||||
- linux
|
||||
- osx
|
||||
- windows
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- go1.13.x
|
||||
- go1.x
|
||||
|
||||
services:
|
||||
- xvfb
|
||||
|
||||
before_install:
|
||||
- export DISPLAY=:99.0
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- if [ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "linux" ]; then sudo apt-get install xsel; fi
|
||||
- go test -v .
|
||||
- if [ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "linux" ]; then sudo apt-get install xclip; fi
|
||||
- go test -v .
|
||||
27
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
27
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2013 Ato Araki. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
|
||||
met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
|
||||
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
|
||||
distribution.
|
||||
* Neither the name of @atotto. nor the names of its
|
||||
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
|
||||
this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
|
||||
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
|
||||
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
|
||||
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
|
||||
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
|
||||
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
|
||||
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
48
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
48
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/atotto/clipboard)
|
||||
|
||||
[](http://godoc.org/github.com/atotto/clipboard)
|
||||
|
||||
# Clipboard for Go
|
||||
|
||||
Provide copying and pasting to the Clipboard for Go.
|
||||
|
||||
Build:
|
||||
|
||||
$ go get github.com/atotto/clipboard
|
||||
|
||||
Platforms:
|
||||
|
||||
* OSX
|
||||
* Windows 7 (probably work on other Windows)
|
||||
* Linux, Unix (requires 'xclip' or 'xsel' command to be installed)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Document:
|
||||
|
||||
* http://godoc.org/github.com/atotto/clipboard
|
||||
|
||||
Notes:
|
||||
|
||||
* Text string only
|
||||
* UTF-8 text encoding only (no conversion)
|
||||
|
||||
TODO:
|
||||
|
||||
* Clipboard watcher(?)
|
||||
|
||||
## Commands:
|
||||
|
||||
paste shell command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ go get github.com/atotto/clipboard/cmd/gopaste
|
||||
$ # example:
|
||||
$ gopaste > document.txt
|
||||
|
||||
copy shell command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ go get github.com/atotto/clipboard/cmd/gocopy
|
||||
$ # example:
|
||||
$ cat document.txt | gocopy
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
20
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
20
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2013 @atotto. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package clipboard read/write on clipboard
|
||||
package clipboard
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadAll read string from clipboard
|
||||
func ReadAll() (string, error) {
|
||||
return readAll()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WriteAll write string to clipboard
|
||||
func WriteAll(text string) error {
|
||||
return writeAll(text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Unsupported might be set true during clipboard init, to help callers decide
|
||||
// whether or not to offer clipboard options.
|
||||
var Unsupported bool
|
||||
52
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_darwin.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
52
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_darwin.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2013 @atotto. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build darwin
|
||||
|
||||
package clipboard
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os/exec"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs = "pbpaste"
|
||||
copyCmdArgs = "pbcopy"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func getPasteCommand() *exec.Cmd {
|
||||
return exec.Command(pasteCmdArgs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getCopyCommand() *exec.Cmd {
|
||||
return exec.Command(copyCmdArgs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readAll() (string, error) {
|
||||
pasteCmd := getPasteCommand()
|
||||
out, err := pasteCmd.Output()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return string(out), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeAll(text string) error {
|
||||
copyCmd := getCopyCommand()
|
||||
in, err := copyCmd.StdinPipe()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err := copyCmd.Start(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, err := in.Write([]byte(text)); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := in.Close(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return copyCmd.Wait()
|
||||
}
|
||||
42
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_plan9.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
42
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_plan9.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2013 @atotto. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build plan9
|
||||
|
||||
package clipboard
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func readAll() (string, error) {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open("/dev/snarf")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
str, err := ioutil.ReadAll(f)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return string(str), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeAll(text string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.OpenFile("/dev/snarf", os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
_, err = f.Write([]byte(text))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
149
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
149
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2013 @atotto. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build freebsd linux netbsd openbsd solaris dragonfly
|
||||
|
||||
package clipboard
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/exec"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
xsel = "xsel"
|
||||
xclip = "xclip"
|
||||
powershellExe = "powershell.exe"
|
||||
clipExe = "clip.exe"
|
||||
wlcopy = "wl-copy"
|
||||
wlpaste = "wl-paste"
|
||||
termuxClipboardGet = "termux-clipboard-get"
|
||||
termuxClipboardSet = "termux-clipboard-set"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
Primary bool
|
||||
trimDos bool
|
||||
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs []string
|
||||
copyCmdArgs []string
|
||||
|
||||
xselPasteArgs = []string{xsel, "--output", "--clipboard"}
|
||||
xselCopyArgs = []string{xsel, "--input", "--clipboard"}
|
||||
|
||||
xclipPasteArgs = []string{xclip, "-out", "-selection", "clipboard"}
|
||||
xclipCopyArgs = []string{xclip, "-in", "-selection", "clipboard"}
|
||||
|
||||
powershellExePasteArgs = []string{powershellExe, "Get-Clipboard"}
|
||||
clipExeCopyArgs = []string{clipExe}
|
||||
|
||||
wlpasteArgs = []string{wlpaste, "--no-newline"}
|
||||
wlcopyArgs = []string{wlcopy}
|
||||
|
||||
termuxPasteArgs = []string{termuxClipboardGet}
|
||||
termuxCopyArgs = []string{termuxClipboardSet}
|
||||
|
||||
missingCommands = errors.New("No clipboard utilities available. Please install xsel, xclip, wl-clipboard or Termux:API add-on for termux-clipboard-get/set.")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
if os.Getenv("WAYLAND_DISPLAY") != "" {
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs = wlpasteArgs
|
||||
copyCmdArgs = wlcopyArgs
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(wlcopy); err == nil {
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(wlpaste); err == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs = xclipPasteArgs
|
||||
copyCmdArgs = xclipCopyArgs
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(xclip); err == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs = xselPasteArgs
|
||||
copyCmdArgs = xselCopyArgs
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(xsel); err == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs = termuxPasteArgs
|
||||
copyCmdArgs = termuxCopyArgs
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(termuxClipboardSet); err == nil {
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(termuxClipboardGet); err == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs = powershellExePasteArgs
|
||||
copyCmdArgs = clipExeCopyArgs
|
||||
trimDos = true
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(clipExe); err == nil {
|
||||
if _, err := exec.LookPath(powershellExe); err == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Unsupported = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getPasteCommand() *exec.Cmd {
|
||||
if Primary {
|
||||
pasteCmdArgs = pasteCmdArgs[:1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return exec.Command(pasteCmdArgs[0], pasteCmdArgs[1:]...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getCopyCommand() *exec.Cmd {
|
||||
if Primary {
|
||||
copyCmdArgs = copyCmdArgs[:1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return exec.Command(copyCmdArgs[0], copyCmdArgs[1:]...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readAll() (string, error) {
|
||||
if Unsupported {
|
||||
return "", missingCommands
|
||||
}
|
||||
pasteCmd := getPasteCommand()
|
||||
out, err := pasteCmd.Output()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
result := string(out)
|
||||
if trimDos && len(result) > 1 {
|
||||
result = result[:len(result)-2]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeAll(text string) error {
|
||||
if Unsupported {
|
||||
return missingCommands
|
||||
}
|
||||
copyCmd := getCopyCommand()
|
||||
in, err := copyCmd.StdinPipe()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err := copyCmd.Start(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, err := in.Write([]byte(text)); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := in.Close(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return copyCmd.Wait()
|
||||
}
|
||||
157
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
157
vendor/github.com/atotto/clipboard/clipboard_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2013 @atotto. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build windows
|
||||
|
||||
package clipboard
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"syscall"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
"unsafe"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
cfUnicodetext = 13
|
||||
gmemMoveable = 0x0002
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
user32 = syscall.MustLoadDLL("user32")
|
||||
isClipboardFormatAvailable = user32.MustFindProc("IsClipboardFormatAvailable")
|
||||
openClipboard = user32.MustFindProc("OpenClipboard")
|
||||
closeClipboard = user32.MustFindProc("CloseClipboard")
|
||||
emptyClipboard = user32.MustFindProc("EmptyClipboard")
|
||||
getClipboardData = user32.MustFindProc("GetClipboardData")
|
||||
setClipboardData = user32.MustFindProc("SetClipboardData")
|
||||
|
||||
kernel32 = syscall.NewLazyDLL("kernel32")
|
||||
globalAlloc = kernel32.NewProc("GlobalAlloc")
|
||||
globalFree = kernel32.NewProc("GlobalFree")
|
||||
globalLock = kernel32.NewProc("GlobalLock")
|
||||
globalUnlock = kernel32.NewProc("GlobalUnlock")
|
||||
lstrcpy = kernel32.NewProc("lstrcpyW")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// waitOpenClipboard opens the clipboard, waiting for up to a second to do so.
|
||||
func waitOpenClipboard() error {
|
||||
started := time.Now()
|
||||
limit := started.Add(time.Second)
|
||||
var r uintptr
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
for time.Now().Before(limit) {
|
||||
r, _, err = openClipboard.Call(0)
|
||||
if r != 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readAll() (string, error) {
|
||||
// LockOSThread ensure that the whole method will keep executing on the same thread from begin to end (it actually locks the goroutine thread attribution).
|
||||
// Otherwise if the goroutine switch thread during execution (which is a common practice), the OpenClipboard and CloseClipboard will happen on two different threads, and it will result in a clipboard deadlock.
|
||||
runtime.LockOSThread()
|
||||
defer runtime.UnlockOSThread()
|
||||
if formatAvailable, _, err := isClipboardFormatAvailable.Call(cfUnicodetext); formatAvailable == 0 {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := waitOpenClipboard()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
h, _, err := getClipboardData.Call(cfUnicodetext)
|
||||
if h == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
l, _, err := globalLock.Call(h)
|
||||
if l == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
text := syscall.UTF16ToString((*[1 << 20]uint16)(unsafe.Pointer(l))[:])
|
||||
|
||||
r, _, err := globalUnlock.Call(h)
|
||||
if r == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
closed, _, err := closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
if closed == 0 {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return text, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeAll(text string) error {
|
||||
// LockOSThread ensure that the whole method will keep executing on the same thread from begin to end (it actually locks the goroutine thread attribution).
|
||||
// Otherwise if the goroutine switch thread during execution (which is a common practice), the OpenClipboard and CloseClipboard will happen on two different threads, and it will result in a clipboard deadlock.
|
||||
runtime.LockOSThread()
|
||||
defer runtime.UnlockOSThread()
|
||||
|
||||
err := waitOpenClipboard()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, _, err := emptyClipboard.Call(0)
|
||||
if r == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
data := syscall.StringToUTF16(text)
|
||||
|
||||
// "If the hMem parameter identifies a memory object, the object must have
|
||||
// been allocated using the function with the GMEM_MOVEABLE flag."
|
||||
h, _, err := globalAlloc.Call(gmemMoveable, uintptr(len(data)*int(unsafe.Sizeof(data[0]))))
|
||||
if h == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if h != 0 {
|
||||
globalFree.Call(h)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
l, _, err := globalLock.Call(h)
|
||||
if l == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, _, err = lstrcpy.Call(l, uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&data[0])))
|
||||
if r == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, _, err = globalUnlock.Call(h)
|
||||
if r == 0 {
|
||||
if err.(syscall.Errno) != 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, _, err = setClipboardData.Call(cfUnicodetext, h)
|
||||
if r == 0 {
|
||||
_, _, _ = closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
h = 0 // suppress deferred cleanup
|
||||
closed, _, err := closeClipboard.Call()
|
||||
if closed == 0 {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2022 Ayman Bagabas
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
83
vendor/github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
83
vendor/github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# go-osc52
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/aymanbagabas/go-osc52.svg" alt="Latest Release"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2?tab=doc"><img src="https://godoc.org/github.com/golang/gddo?status.svg" alt="GoDoc"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
A Go library to work with the [ANSI OSC52](https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands) terminal sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
You can use this small library to construct an ANSI OSC52 sequence suitable for
|
||||
your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
s := "Hello World!"
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy `s` to system clipboard
|
||||
osc52.New(s).WriteTo(os.Stderr)
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy `s` to primary clipboard (X11)
|
||||
osc52.New(s).Primary().WriteTo(os.Stderr)
|
||||
|
||||
// Query the clipboard
|
||||
osc52.Query().WriteTo(os.Stderr)
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear system clipboard
|
||||
osc52.Clear().WriteTo(os.Stderr)
|
||||
|
||||
// Use the fmt.Stringer interface to copy `s` to system clipboard
|
||||
fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.New(s))
|
||||
|
||||
// Or to primary clipboard
|
||||
fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.New(s).Primary())
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## SSH Example
|
||||
|
||||
You can use this over SSH using [gliderlabs/ssh](https://github.com/gliderlabs/ssh) for instance:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var sshSession ssh.Session
|
||||
seq := osc52.New("Hello awesome!")
|
||||
// Check if term is screen or tmux
|
||||
pty, _, _ := s.Pty()
|
||||
if pty.Term == "screen" {
|
||||
seq = seq.Screen()
|
||||
} else if isTmux {
|
||||
seq = seq.Tmux()
|
||||
}
|
||||
seq.WriteTo(sshSession.Stderr())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Tmux
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you have `set-clipboard on` in your config, otherwise, tmux won't
|
||||
allow your application to access the clipboard [^1].
|
||||
|
||||
Using the tmux option, `osc52.TmuxMode` or `osc52.New(...).Tmux()`, wraps the
|
||||
OSC52 sequence in a special tmux DCS sequence and pass it to the outer
|
||||
terminal. This requires `allow-passthrough on` in your config.
|
||||
`allow-passthrough` is no longer enabled by default
|
||||
[since tmux 3.3a](https://github.com/tmux/tmux/issues/3218#issuecomment-1153089282) [^2].
|
||||
|
||||
[^1]: See [tmux clipboard](https://github.com/tmux/tmux/wiki/Clipboard)
|
||||
[^2]: [What is allow-passthrough](https://github.com/tmux/tmux/wiki/FAQ#what-is-the-passthrough-escape-sequence-and-how-do-i-use-it)
|
||||
|
||||
## Credits
|
||||
|
||||
* [vim-oscyank](https://github.com/ojroques/vim-oscyank) this is heavily inspired by vim-oscyank.
|
||||
305
vendor/github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2/osc52.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
305
vendor/github.com/aymanbagabas/go-osc52/v2/osc52.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
|
||||
// OSC52 is a terminal escape sequence that allows copying text to the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The sequence consists of the following:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 52 ; Pc ; Pd BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Pc is the clipboard choice:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// c: clipboard
|
||||
// p: primary
|
||||
// q: secondary (not supported)
|
||||
// s: select (not supported)
|
||||
// 0-7: cut-buffers (not supported)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Pd is the data to copy to the clipboard. This string should be encoded in
|
||||
// base64 (RFC-4648).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Pd is "?", the terminal replies to the host with the current contents of
|
||||
// the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Pd is neither a base64 string nor "?", the terminal clears the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
// where Ps = 52 => Manipulate Selection Data.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // copy "hello world" to the system clipboard
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.New("hello world"))
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // copy "hello world" to the primary Clipboard
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.New("hello world").Primary())
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // limit the size of the string to copy 10 bytes
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.New("0123456789").Limit(10))
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // escape the OSC52 sequence for screen using DCS sequences
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.New("hello world").Screen())
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // escape the OSC52 sequence for Tmux
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.New("hello world").Tmux())
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // query the system Clipboard
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.Query())
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // query the primary clipboard
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.Query().Primary())
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // clear the system Clipboard
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.Clear())
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // clear the primary Clipboard
|
||||
// fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, osc52.Clear().Primary())
|
||||
package osc52
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/base64"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Clipboard is the clipboard buffer to use.
|
||||
type Clipboard rune
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// SystemClipboard is the system clipboard buffer.
|
||||
SystemClipboard Clipboard = 'c'
|
||||
// PrimaryClipboard is the primary clipboard buffer (X11).
|
||||
PrimaryClipboard = 'p'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Mode is the mode to use for the OSC52 sequence.
|
||||
type Mode uint
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// DefaultMode is the default OSC52 sequence mode.
|
||||
DefaultMode Mode = iota
|
||||
// ScreenMode escapes the OSC52 sequence for screen using DCS sequences.
|
||||
ScreenMode
|
||||
// TmuxMode escapes the OSC52 sequence for tmux. Not needed if tmux
|
||||
// clipboard is set to `set-clipboard on`
|
||||
TmuxMode
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Operation is the OSC52 operation.
|
||||
type Operation uint
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// SetOperation is the copy operation.
|
||||
SetOperation Operation = iota
|
||||
// QueryOperation is the query operation.
|
||||
QueryOperation
|
||||
// ClearOperation is the clear operation.
|
||||
ClearOperation
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Sequence is the OSC52 sequence.
|
||||
type Sequence struct {
|
||||
str string
|
||||
limit int
|
||||
op Operation
|
||||
mode Mode
|
||||
clipboard Clipboard
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ fmt.Stringer = Sequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ io.WriterTo = Sequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the OSC52 sequence.
|
||||
func (s Sequence) String() string {
|
||||
var seq strings.Builder
|
||||
// mode escape sequences start
|
||||
seq.WriteString(s.seqStart())
|
||||
// actual OSC52 sequence start
|
||||
seq.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("\x1b]52;%c;", s.clipboard))
|
||||
switch s.op {
|
||||
case SetOperation:
|
||||
str := s.str
|
||||
if s.limit > 0 && len(str) > s.limit {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
b64 := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(str))
|
||||
switch s.mode {
|
||||
case ScreenMode:
|
||||
// Screen doesn't support OSC52 but will pass the contents of a DCS
|
||||
// sequence to the outer terminal unchanged.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Here, we split the encoded string into 76 bytes chunks and then
|
||||
// join the chunks with <end-dsc><start-dsc> sequences. Finally,
|
||||
// wrap the whole thing in
|
||||
// <start-dsc><start-osc52><joined-chunks><end-osc52><end-dsc>.
|
||||
// s := strings.SplitN(b64, "", 76)
|
||||
s := make([]string, 0, len(b64)/76+1)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(b64); i += 76 {
|
||||
end := i + 76
|
||||
if end > len(b64) {
|
||||
end = len(b64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = append(s, b64[i:end])
|
||||
}
|
||||
seq.WriteString(strings.Join(s, "\x1b\\\x1bP"))
|
||||
default:
|
||||
seq.WriteString(b64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case QueryOperation:
|
||||
// OSC52 queries the clipboard using "?"
|
||||
seq.WriteString("?")
|
||||
case ClearOperation:
|
||||
// OSC52 clears the clipboard if the data is neither a base64 string nor "?"
|
||||
// we're using "!" as a default
|
||||
seq.WriteString("!")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// actual OSC52 sequence end
|
||||
seq.WriteString("\x07")
|
||||
// mode escape end
|
||||
seq.WriteString(s.seqEnd())
|
||||
return seq.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WriteTo writes the OSC52 sequence to the writer.
|
||||
func (s Sequence) WriteTo(out io.Writer) (int64, error) {
|
||||
n, err := out.Write([]byte(s.String()))
|
||||
return int64(n), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Mode sets the mode for the OSC52 sequence.
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Mode(m Mode) Sequence {
|
||||
s.mode = m
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tmux sets the mode to TmuxMode.
|
||||
// Used to escape the OSC52 sequence for `tmux`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: this is not needed if tmux clipboard is set to `set-clipboard on`. If
|
||||
// TmuxMode is used, tmux must have `allow-passthrough on` set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar for s.Mode(TmuxMode).
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Tmux() Sequence {
|
||||
return s.Mode(TmuxMode)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Screen sets the mode to ScreenMode.
|
||||
// Used to escape the OSC52 sequence for `screen`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar for s.Mode(ScreenMode).
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Screen() Sequence {
|
||||
return s.Mode(ScreenMode)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clipboard sets the clipboard buffer for the OSC52 sequence.
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Clipboard(c Clipboard) Sequence {
|
||||
s.clipboard = c
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Primary sets the clipboard buffer to PrimaryClipboard.
|
||||
// This is the X11 primary clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar for s.Clipboard(PrimaryClipboard).
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Primary() Sequence {
|
||||
return s.Clipboard(PrimaryClipboard)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Limit sets the limit for the OSC52 sequence.
|
||||
// The default limit is 0 (no limit).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Strings longer than the limit get ignored. Settting the limit to 0 or a
|
||||
// negative value disables the limit. Each terminal defines its own escapse
|
||||
// sequence limit.
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Limit(l int) Sequence {
|
||||
if l < 0 {
|
||||
s.limit = 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s.limit = l
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Operation sets the operation for the OSC52 sequence.
|
||||
// The default operation is SetOperation.
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Operation(o Operation) Sequence {
|
||||
s.op = o
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear sets the operation to ClearOperation.
|
||||
// This clears the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar for s.Operation(ClearOperation).
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Clear() Sequence {
|
||||
return s.Operation(ClearOperation)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Query sets the operation to QueryOperation.
|
||||
// This queries the clipboard contents.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar for s.Operation(QueryOperation).
|
||||
func (s Sequence) Query() Sequence {
|
||||
return s.Operation(QueryOperation)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetString sets the string for the OSC52 sequence. Strings are joined with a
|
||||
// space character.
|
||||
func (s Sequence) SetString(strs ...string) Sequence {
|
||||
s.str = strings.Join(strs, " ")
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New creates a new OSC52 sequence with the given string(s). Strings are
|
||||
// joined with a space character.
|
||||
func New(strs ...string) Sequence {
|
||||
s := Sequence{
|
||||
str: strings.Join(strs, " "),
|
||||
limit: 0,
|
||||
mode: DefaultMode,
|
||||
clipboard: SystemClipboard,
|
||||
op: SetOperation,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Query creates a new OSC52 sequence with the QueryOperation.
|
||||
// This returns a new OSC52 sequence to query the clipboard contents.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar for New().Query().
|
||||
func Query() Sequence {
|
||||
return New().Query()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear creates a new OSC52 sequence with the ClearOperation.
|
||||
// This returns a new OSC52 sequence to clear the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar for New().Clear().
|
||||
func Clear() Sequence {
|
||||
return New().Clear()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Sequence) seqStart() string {
|
||||
switch s.mode {
|
||||
case TmuxMode:
|
||||
// Write the start of a tmux escape sequence.
|
||||
return "\x1bPtmux;\x1b"
|
||||
case ScreenMode:
|
||||
// Write the start of a DCS sequence.
|
||||
return "\x1bP"
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Sequence) seqEnd() string {
|
||||
switch s.mode {
|
||||
case TmuxMode:
|
||||
// Terminate the tmux escape sequence.
|
||||
return "\x1b\\"
|
||||
case ScreenMode:
|
||||
// Write the end of a DCS sequence.
|
||||
return "\x1b\x5c"
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2020-2023 Charmbracelet, Inc
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
207
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/cursor/cursor.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
207
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/cursor/cursor.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,207 @@
|
||||
package cursor
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const defaultBlinkSpeed = time.Millisecond * 530
|
||||
|
||||
// initialBlinkMsg initializes cursor blinking.
|
||||
type initialBlinkMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// BlinkMsg signals that the cursor should blink. It contains metadata that
|
||||
// allows us to tell if the blink message is the one we're expecting.
|
||||
type BlinkMsg struct {
|
||||
id int
|
||||
tag int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// blinkCanceled is sent when a blink operation is canceled.
|
||||
type blinkCanceled struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// blinkCtx manages cursor blinking.
|
||||
type blinkCtx struct {
|
||||
ctx context.Context
|
||||
cancel context.CancelFunc
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Mode describes the behavior of the cursor.
|
||||
type Mode int
|
||||
|
||||
// Available cursor modes.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
CursorBlink Mode = iota
|
||||
CursorStatic
|
||||
CursorHide
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the cursor mode in a human-readable format. This method is
|
||||
// provisional and for informational purposes only.
|
||||
func (c Mode) String() string {
|
||||
return [...]string{
|
||||
"blink",
|
||||
"static",
|
||||
"hidden",
|
||||
}[c]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Model is the Bubble Tea model for this cursor element.
|
||||
type Model struct {
|
||||
BlinkSpeed time.Duration
|
||||
// Style for styling the cursor block.
|
||||
Style lipgloss.Style
|
||||
// TextStyle is the style used for the cursor when it is hidden (when blinking).
|
||||
// I.e. displaying normal text.
|
||||
TextStyle lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// char is the character under the cursor
|
||||
char string
|
||||
// The ID of this Model as it relates to other cursors
|
||||
id int
|
||||
// focus indicates whether the containing input is focused
|
||||
focus bool
|
||||
// Cursor Blink state.
|
||||
Blink bool
|
||||
// Used to manage cursor blink
|
||||
blinkCtx *blinkCtx
|
||||
// The ID of the blink message we're expecting to receive.
|
||||
blinkTag int
|
||||
// mode determines the behavior of the cursor
|
||||
mode Mode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New creates a new model with default settings.
|
||||
func New() Model {
|
||||
return Model{
|
||||
BlinkSpeed: defaultBlinkSpeed,
|
||||
|
||||
Blink: true,
|
||||
mode: CursorBlink,
|
||||
|
||||
blinkCtx: &blinkCtx{
|
||||
ctx: context.Background(),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Update updates the cursor.
|
||||
func (m Model) Update(msg tea.Msg) (Model, tea.Cmd) {
|
||||
switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
case initialBlinkMsg:
|
||||
// We accept all initialBlinkMsgs generated by the Blink command.
|
||||
|
||||
if m.mode != CursorBlink || !m.focus {
|
||||
return m, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cmd := m.BlinkCmd()
|
||||
return m, cmd
|
||||
|
||||
case BlinkMsg:
|
||||
// We're choosy about whether to accept blinkMsgs so that our cursor
|
||||
// only exactly when it should.
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this model blink-able?
|
||||
if m.mode != CursorBlink || !m.focus {
|
||||
return m, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Were we expecting this blink message?
|
||||
if msg.id != m.id || msg.tag != m.blinkTag {
|
||||
return m, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var cmd tea.Cmd
|
||||
if m.mode == CursorBlink {
|
||||
m.Blink = !m.Blink
|
||||
cmd = m.BlinkCmd()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m, cmd
|
||||
|
||||
case blinkCanceled: // no-op
|
||||
return m, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Mode returns the model's cursor mode. For available cursor modes, see
|
||||
// type Mode.
|
||||
func (m Model) Mode() Mode {
|
||||
return m.mode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetMode sets the model's cursor mode. This method returns a command.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For available cursor modes, see type CursorMode.
|
||||
func (m *Model) SetMode(mode Mode) tea.Cmd {
|
||||
m.mode = mode
|
||||
m.Blink = m.mode == CursorHide || !m.focus
|
||||
if mode == CursorBlink {
|
||||
return Blink
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BlinkCmd is a command used to manage cursor blinking.
|
||||
func (m *Model) BlinkCmd() tea.Cmd {
|
||||
if m.mode != CursorBlink {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if m.blinkCtx != nil && m.blinkCtx.cancel != nil {
|
||||
m.blinkCtx.cancel()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(m.blinkCtx.ctx, m.BlinkSpeed)
|
||||
m.blinkCtx.cancel = cancel
|
||||
|
||||
m.blinkTag++
|
||||
|
||||
return func() tea.Msg {
|
||||
defer cancel()
|
||||
<-ctx.Done()
|
||||
if ctx.Err() == context.DeadlineExceeded {
|
||||
return BlinkMsg{id: m.id, tag: m.blinkTag}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return blinkCanceled{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Blink is a command used to initialize cursor blinking.
|
||||
func Blink() tea.Msg {
|
||||
return initialBlinkMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Focus focuses the cursor to allow it to blink if desired.
|
||||
func (m *Model) Focus() tea.Cmd {
|
||||
m.focus = true
|
||||
m.Blink = m.mode == CursorHide // show the cursor unless we've explicitly hidden it
|
||||
|
||||
if m.mode == CursorBlink && m.focus {
|
||||
return m.BlinkCmd()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Blur blurs the cursor.
|
||||
func (m *Model) Blur() {
|
||||
m.focus = false
|
||||
m.Blink = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetChar sets the character under the cursor.
|
||||
func (m *Model) SetChar(char string) {
|
||||
m.char = char
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// View displays the cursor.
|
||||
func (m Model) View() string {
|
||||
if m.Blink {
|
||||
return m.TextStyle.Inline(true).Render(m.char)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m.Style.Inline(true).Reverse(true).Render(m.char)
|
||||
}
|
||||
233
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/help/help.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
233
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/help/help.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,233 @@
|
||||
package help
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/key"
|
||||
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// KeyMap is a map of keybindings used to generate help. Since it's an
|
||||
// interface it can be any type, though struct or a map[string][]key.Binding
|
||||
// are likely candidates.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that if a key is disabled (via key.Binding.SetEnabled) it will not be
|
||||
// rendered in the help view, so in theory generated help should self-manage.
|
||||
type KeyMap interface {
|
||||
|
||||
// ShortHelp returns a slice of bindings to be displayed in the short
|
||||
// version of the help. The help bubble will render help in the order in
|
||||
// which the help items are returned here.
|
||||
ShortHelp() []key.Binding
|
||||
|
||||
// FullHelp returns an extended group of help items, grouped by columns.
|
||||
// The help bubble will render the help in the order in which the help
|
||||
// items are returned here.
|
||||
FullHelp() [][]key.Binding
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Styles is a set of available style definitions for the Help bubble.
|
||||
type Styles struct {
|
||||
Ellipsis lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Styling for the short help
|
||||
ShortKey lipgloss.Style
|
||||
ShortDesc lipgloss.Style
|
||||
ShortSeparator lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Styling for the full help
|
||||
FullKey lipgloss.Style
|
||||
FullDesc lipgloss.Style
|
||||
FullSeparator lipgloss.Style
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Model contains the state of the help view.
|
||||
type Model struct {
|
||||
Width int
|
||||
ShowAll bool // if true, render the "full" help menu
|
||||
|
||||
ShortSeparator string
|
||||
FullSeparator string
|
||||
|
||||
// The symbol we use in the short help when help items have been truncated
|
||||
// due to width. Periods of ellipsis by default.
|
||||
Ellipsis string
|
||||
|
||||
Styles Styles
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New creates a new help view with some useful defaults.
|
||||
func New() Model {
|
||||
keyStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{
|
||||
Light: "#909090",
|
||||
Dark: "#626262",
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
descStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{
|
||||
Light: "#B2B2B2",
|
||||
Dark: "#4A4A4A",
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
sepStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{
|
||||
Light: "#DDDADA",
|
||||
Dark: "#3C3C3C",
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return Model{
|
||||
ShortSeparator: " • ",
|
||||
FullSeparator: " ",
|
||||
Ellipsis: "…",
|
||||
Styles: Styles{
|
||||
ShortKey: keyStyle,
|
||||
ShortDesc: descStyle,
|
||||
ShortSeparator: sepStyle,
|
||||
Ellipsis: sepStyle.Copy(),
|
||||
FullKey: keyStyle.Copy(),
|
||||
FullDesc: descStyle.Copy(),
|
||||
FullSeparator: sepStyle.Copy(),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewModel creates a new help view with some useful defaults.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [New] instead.
|
||||
var NewModel = New
|
||||
|
||||
// Update helps satisfy the Bubble Tea Model interface. It's a no-op.
|
||||
func (m Model) Update(_ tea.Msg) (Model, tea.Cmd) {
|
||||
return m, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// View renders the help view's current state.
|
||||
func (m Model) View(k KeyMap) string {
|
||||
if m.ShowAll {
|
||||
return m.FullHelpView(k.FullHelp())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m.ShortHelpView(k.ShortHelp())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShortHelpView renders a single line help view from a slice of keybindings.
|
||||
// If the line is longer than the maximum width it will be gracefully
|
||||
// truncated, showing only as many help items as possible.
|
||||
func (m Model) ShortHelpView(bindings []key.Binding) string {
|
||||
if len(bindings) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
var totalWidth int
|
||||
var separator = m.Styles.ShortSeparator.Inline(true).Render(m.ShortSeparator)
|
||||
|
||||
for i, kb := range bindings {
|
||||
if !kb.Enabled() {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var sep string
|
||||
if totalWidth > 0 && i < len(bindings) {
|
||||
sep = separator
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
str := sep +
|
||||
m.Styles.ShortKey.Inline(true).Render(kb.Help().Key) + " " +
|
||||
m.Styles.ShortDesc.Inline(true).Render(kb.Help().Desc)
|
||||
|
||||
w := lipgloss.Width(str)
|
||||
|
||||
// If adding this help item would go over the available width, stop
|
||||
// drawing.
|
||||
if m.Width > 0 && totalWidth+w > m.Width {
|
||||
// Although if there's room for an ellipsis, print that.
|
||||
tail := " " + m.Styles.Ellipsis.Inline(true).Render(m.Ellipsis)
|
||||
tailWidth := lipgloss.Width(tail)
|
||||
|
||||
if totalWidth+tailWidth < m.Width {
|
||||
b.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
totalWidth += w
|
||||
b.WriteString(str)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FullHelpView renders help columns from a slice of key binding slices. Each
|
||||
// top level slice entry renders into a column.
|
||||
func (m Model) FullHelpView(groups [][]key.Binding) string {
|
||||
if len(groups) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Linter note: at this time we don't think it's worth the additional
|
||||
// code complexity involved in preallocating this slice.
|
||||
//nolint:prealloc
|
||||
var (
|
||||
out []string
|
||||
|
||||
totalWidth int
|
||||
sep = m.Styles.FullSeparator.Render(m.FullSeparator)
|
||||
sepWidth = lipgloss.Width(sep)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Iterate over groups to build columns
|
||||
for i, group := range groups {
|
||||
if group == nil || !shouldRenderColumn(group) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
keys []string
|
||||
descriptions []string
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Separate keys and descriptions into different slices
|
||||
for _, kb := range group {
|
||||
if !kb.Enabled() {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
keys = append(keys, kb.Help().Key)
|
||||
descriptions = append(descriptions, kb.Help().Desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
col := lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Top,
|
||||
m.Styles.FullKey.Render(strings.Join(keys, "\n")),
|
||||
m.Styles.FullKey.Render(" "),
|
||||
m.Styles.FullDesc.Render(strings.Join(descriptions, "\n")),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Column
|
||||
totalWidth += lipgloss.Width(col)
|
||||
if m.Width > 0 && totalWidth > m.Width {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
out = append(out, col)
|
||||
|
||||
// Separator
|
||||
if i < len(group)-1 {
|
||||
totalWidth += sepWidth
|
||||
if m.Width > 0 && totalWidth > m.Width {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
out = append(out, sep)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Top, out...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func shouldRenderColumn(b []key.Binding) (ok bool) {
|
||||
for _, v := range b {
|
||||
if v.Enabled() {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
142
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/key/key.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
142
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/key/key.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
|
||||
// Package key provides some types and functions for generating user-definable
|
||||
// keymappings useful in Bubble Tea components. There are a few different ways
|
||||
// you can define a keymapping with this package. Here's one example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type KeyMap struct {
|
||||
// Up key.Binding
|
||||
// Down key.Binding
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var DefaultKeyMap = KeyMap{
|
||||
// Up: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
// key.WithKeys("k", "up"), // actual keybindings
|
||||
// key.WithHelp("↑/k", "move up"), // corresponding help text
|
||||
// ),
|
||||
// Down: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
// key.WithKeys("j", "down"),
|
||||
// key.WithHelp("↓/j", "move down"),
|
||||
// ),
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func (m Model) Update(msg tea.Msg) (tea.Model, tea.Cmd) {
|
||||
// switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
// case tea.KeyMsg:
|
||||
// switch {
|
||||
// case key.Matches(msg, DefaultKeyMap.Up):
|
||||
// // The user pressed up
|
||||
// case key.Matches(msg, DefaultKeyMap.Down):
|
||||
// // The user pressed down
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // ...
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The help information, which is not used in the example above, can be used
|
||||
// to render help text for keystrokes in your views.
|
||||
package key
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Binding describes a set of keybindings and, optionally, their associated
|
||||
// help text.
|
||||
type Binding struct {
|
||||
keys []string
|
||||
help Help
|
||||
disabled bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BindingOpt is an initialization option for a keybinding. It's used as an
|
||||
// argument to NewBinding.
|
||||
type BindingOpt func(*Binding)
|
||||
|
||||
// NewBinding returns a new keybinding from a set of BindingOpt options.
|
||||
func NewBinding(opts ...BindingOpt) Binding {
|
||||
b := &Binding{}
|
||||
for _, opt := range opts {
|
||||
opt(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return *b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithKeys initializes a keybinding with the given keystrokes.
|
||||
func WithKeys(keys ...string) BindingOpt {
|
||||
return func(b *Binding) {
|
||||
b.keys = keys
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithHelp initializes a keybinding with the given help text.
|
||||
func WithHelp(key, desc string) BindingOpt {
|
||||
return func(b *Binding) {
|
||||
b.help = Help{Key: key, Desc: desc}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithDisabled initializes a disabled keybinding.
|
||||
func WithDisabled() BindingOpt {
|
||||
return func(b *Binding) {
|
||||
b.disabled = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetKeys sets the keys for the keybinding.
|
||||
func (b *Binding) SetKeys(keys ...string) {
|
||||
b.keys = keys
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Keys returns the keys for the keybinding.
|
||||
func (b Binding) Keys() []string {
|
||||
return b.keys
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHelp sets the help text for the keybinding.
|
||||
func (b *Binding) SetHelp(key, desc string) {
|
||||
b.help = Help{Key: key, Desc: desc}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Help returns the Help information for the keybinding.
|
||||
func (b Binding) Help() Help {
|
||||
return b.help
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Enabled returns whether or not the keybinding is enabled. Disabled
|
||||
// keybindings won't be activated and won't show up in help. Keybindings are
|
||||
// enabled by default.
|
||||
func (b Binding) Enabled() bool {
|
||||
return !b.disabled && b.keys != nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetEnabled enables or disables the keybinding.
|
||||
func (b *Binding) SetEnabled(v bool) {
|
||||
b.disabled = !v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Unbind removes the keys and help from this binding, effectively nullifying
|
||||
// it. This is a step beyond disabling it, since applications can enable
|
||||
// or disable key bindings based on application state.
|
||||
func (b *Binding) Unbind() {
|
||||
b.keys = nil
|
||||
b.help = Help{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Help is help information for a given keybinding.
|
||||
type Help struct {
|
||||
Key string
|
||||
Desc string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Matches checks if the given KeyMsg matches the given bindings.
|
||||
func Matches(k tea.KeyMsg, b ...Binding) bool {
|
||||
keys := k.String()
|
||||
for _, binding := range b {
|
||||
for _, v := range binding.keys {
|
||||
if keys == v && binding.Enabled() {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
102
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/runeutil/runeutil.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
102
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/runeutil/runeutil.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
||||
// Package runeutil provides a utility function for use in Bubbles
|
||||
// that can process Key messages containing runes.
|
||||
package runeutil
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Sanitizer is a helper for bubble widgets that want to process
|
||||
// Runes from input key messages.
|
||||
type Sanitizer interface {
|
||||
// Sanitize removes control characters from runes in a KeyRunes
|
||||
// message, and optionally replaces newline/carriage return/tabs by a
|
||||
// specified character.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The rune array is modified in-place if possible. In that case, the
|
||||
// returned slice is the original slice shortened after the control
|
||||
// characters have been removed/translated.
|
||||
Sanitize(runes []rune) []rune
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewSanitizer constructs a rune sanitizer.
|
||||
func NewSanitizer(opts ...Option) Sanitizer {
|
||||
s := sanitizer{
|
||||
replaceNewLine: []rune("\n"),
|
||||
replaceTab: []rune(" "),
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, o := range opts {
|
||||
s = o(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Option is the type of option that can be passed to Sanitize().
|
||||
type Option func(sanitizer) sanitizer
|
||||
|
||||
// ReplaceTabs replaces tabs by the specified string.
|
||||
func ReplaceTabs(tabRepl string) Option {
|
||||
return func(s sanitizer) sanitizer {
|
||||
s.replaceTab = []rune(tabRepl)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReplaceNewlines replaces newline characters by the specified string.
|
||||
func ReplaceNewlines(nlRepl string) Option {
|
||||
return func(s sanitizer) sanitizer {
|
||||
s.replaceNewLine = []rune(nlRepl)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *sanitizer) Sanitize(runes []rune) []rune {
|
||||
// dstrunes are where we are storing the result.
|
||||
dstrunes := runes[:0:len(runes)]
|
||||
// copied indicates whether dstrunes is an alias of runes
|
||||
// or a copy. We need a copy when dst moves past src.
|
||||
// We use this as an optimization to avoid allocating
|
||||
// a new rune slice in the common case where the output
|
||||
// is smaller or equal to the input.
|
||||
copied := false
|
||||
|
||||
for src := 0; src < len(runes); src++ {
|
||||
r := runes[src]
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case r == utf8.RuneError:
|
||||
// skip
|
||||
|
||||
case r == '\r' || r == '\n':
|
||||
if len(dstrunes)+len(s.replaceNewLine) > src && !copied {
|
||||
dst := len(dstrunes)
|
||||
dstrunes = make([]rune, dst, len(runes)+len(s.replaceNewLine))
|
||||
copy(dstrunes, runes[:dst])
|
||||
copied = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
dstrunes = append(dstrunes, s.replaceNewLine...)
|
||||
|
||||
case r == '\t':
|
||||
if len(dstrunes)+len(s.replaceTab) > src && !copied {
|
||||
dst := len(dstrunes)
|
||||
dstrunes = make([]rune, dst, len(runes)+len(s.replaceTab))
|
||||
copy(dstrunes, runes[:dst])
|
||||
copied = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
dstrunes = append(dstrunes, s.replaceTab...)
|
||||
|
||||
case unicode.IsControl(r):
|
||||
// Other control characters: skip.
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// Keep the character.
|
||||
dstrunes = append(dstrunes, runes[src])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dstrunes
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type sanitizer struct {
|
||||
replaceNewLine []rune
|
||||
replaceTab []rune
|
||||
}
|
||||
123
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/textarea/memoization/memoization.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
123
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/textarea/memoization/memoization.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
package memoization
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"container/list"
|
||||
"crypto/sha256"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Hasher is an interface that requires a Hash method. The Hash method is
|
||||
// expected to return a string representation of the hash of the object.
|
||||
type Hasher interface {
|
||||
Hash() string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// entry is a struct that holds a key-value pair. It is used as an element
|
||||
// in the evictionList of the MemoCache.
|
||||
type entry[T any] struct {
|
||||
key string
|
||||
value T
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MemoCache is a struct that represents a cache with a set capacity. It
|
||||
// uses an LRU (Least Recently Used) eviction policy. It is safe for
|
||||
// concurrent use.
|
||||
type MemoCache[H Hasher, T any] struct {
|
||||
capacity int
|
||||
mutex sync.Mutex
|
||||
cache map[string]*list.Element // The cache holding the results
|
||||
evictionList *list.List // A list to keep track of the order for LRU
|
||||
hashableItems map[string]T // This map keeps track of the original hashable items (optional)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMemoCache is a function that creates a new MemoCache with a given
|
||||
// capacity. It returns a pointer to the created MemoCache.
|
||||
func NewMemoCache[H Hasher, T any](capacity int) *MemoCache[H, T] {
|
||||
return &MemoCache[H, T]{
|
||||
capacity: capacity,
|
||||
cache: make(map[string]*list.Element),
|
||||
evictionList: list.New(),
|
||||
hashableItems: make(map[string]T),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Capacity is a method that returns the capacity of the MemoCache.
|
||||
func (m *MemoCache[H, T]) Capacity() int {
|
||||
return m.capacity
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Size is a method that returns the current size of the MemoCache. It is
|
||||
// the number of items currently stored in the cache.
|
||||
func (m *MemoCache[H, T]) Size() int {
|
||||
m.mutex.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mutex.Unlock()
|
||||
return m.evictionList.Len()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Get is a method that returns the value associated with the given
|
||||
// hashable item in the MemoCache. If there is no corresponding value, the
|
||||
// method returns nil.
|
||||
func (m *MemoCache[H, T]) Get(h H) (T, bool) {
|
||||
m.mutex.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mutex.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
hashedKey := h.Hash()
|
||||
if element, found := m.cache[hashedKey]; found {
|
||||
m.evictionList.MoveToFront(element)
|
||||
return element.Value.(*entry[T]).value, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
var result T
|
||||
return result, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set is a method that sets the value for the given hashable item in the
|
||||
// MemoCache. If the cache is at capacity, it evicts the least recently
|
||||
// used item before adding the new item.
|
||||
func (m *MemoCache[H, T]) Set(h H, value T) {
|
||||
m.mutex.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mutex.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
hashedKey := h.Hash()
|
||||
if element, found := m.cache[hashedKey]; found {
|
||||
m.evictionList.MoveToFront(element)
|
||||
element.Value.(*entry[T]).value = value
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if the cache is at capacity
|
||||
if m.evictionList.Len() >= m.capacity {
|
||||
// Evict the least recently used item from the cache
|
||||
toEvict := m.evictionList.Back()
|
||||
if toEvict != nil {
|
||||
evictedEntry := m.evictionList.Remove(toEvict).(*entry[T])
|
||||
delete(m.cache, evictedEntry.key)
|
||||
delete(m.hashableItems, evictedEntry.key) // if you're keeping track of original items
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the value to the cache and the evictionList
|
||||
newEntry := &entry[T]{
|
||||
key: hashedKey,
|
||||
value: value,
|
||||
}
|
||||
element := m.evictionList.PushFront(newEntry)
|
||||
m.cache[hashedKey] = element
|
||||
m.hashableItems[hashedKey] = value // if you're keeping track of original items
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HString is a type that implements the Hasher interface for strings.
|
||||
type HString string
|
||||
|
||||
// Hash is a method that returns the hash of the string.
|
||||
func (h HString) Hash() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%x", sha256.Sum256([]byte(h)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HInt is a type that implements the Hasher interface for integers.
|
||||
type HInt int
|
||||
|
||||
// Hash is a method that returns the hash of the integer.
|
||||
func (h HInt) Hash() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%x", sha256.Sum256([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("%d", h))))
|
||||
}
|
||||
1390
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/textarea/textarea.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
1390
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/textarea/textarea.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
48
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/viewport/keymap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
48
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/viewport/keymap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
package viewport
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/key"
|
||||
|
||||
const spacebar = " "
|
||||
|
||||
// KeyMap defines the keybindings for the viewport. Note that you don't
|
||||
// necessary need to use keybindings at all; the viewport can be controlled
|
||||
// programmatically with methods like Model.LineDown(1). See the GoDocs for
|
||||
// details.
|
||||
type KeyMap struct {
|
||||
PageDown key.Binding
|
||||
PageUp key.Binding
|
||||
HalfPageUp key.Binding
|
||||
HalfPageDown key.Binding
|
||||
Down key.Binding
|
||||
Up key.Binding
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultKeyMap returns a set of pager-like default keybindings.
|
||||
func DefaultKeyMap() KeyMap {
|
||||
return KeyMap{
|
||||
PageDown: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
key.WithKeys("pgdown", spacebar, "f"),
|
||||
key.WithHelp("f/pgdn", "page down"),
|
||||
),
|
||||
PageUp: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
key.WithKeys("pgup", "b"),
|
||||
key.WithHelp("b/pgup", "page up"),
|
||||
),
|
||||
HalfPageUp: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
key.WithKeys("u", "ctrl+u"),
|
||||
key.WithHelp("u", "½ page up"),
|
||||
),
|
||||
HalfPageDown: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
key.WithKeys("d", "ctrl+d"),
|
||||
key.WithHelp("d", "½ page down"),
|
||||
),
|
||||
Up: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
key.WithKeys("up", "k"),
|
||||
key.WithHelp("↑/k", "up"),
|
||||
),
|
||||
Down: key.NewBinding(
|
||||
key.WithKeys("down", "j"),
|
||||
key.WithHelp("↓/j", "down"),
|
||||
),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
405
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/viewport/viewport.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
405
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/viewport/viewport.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,405 @@
|
||||
package viewport
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/key"
|
||||
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// New returns a new model with the given width and height as well as default
|
||||
// key mappings.
|
||||
func New(width, height int) (m Model) {
|
||||
m.Width = width
|
||||
m.Height = height
|
||||
m.setInitialValues()
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Model is the Bubble Tea model for this viewport element.
|
||||
type Model struct {
|
||||
Width int
|
||||
Height int
|
||||
KeyMap KeyMap
|
||||
|
||||
// Whether or not to respond to the mouse. The mouse must be enabled in
|
||||
// Bubble Tea for this to work. For details, see the Bubble Tea docs.
|
||||
MouseWheelEnabled bool
|
||||
|
||||
// The number of lines the mouse wheel will scroll. By default, this is 3.
|
||||
MouseWheelDelta int
|
||||
|
||||
// YOffset is the vertical scroll position.
|
||||
YOffset int
|
||||
|
||||
// YPosition is the position of the viewport in relation to the terminal
|
||||
// window. It's used in high performance rendering only.
|
||||
YPosition int
|
||||
|
||||
// Style applies a lipgloss style to the viewport. Realistically, it's most
|
||||
// useful for setting borders, margins and padding.
|
||||
Style lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// HighPerformanceRendering bypasses the normal Bubble Tea renderer to
|
||||
// provide higher performance rendering. Most of the time the normal Bubble
|
||||
// Tea rendering methods will suffice, but if you're passing content with
|
||||
// a lot of ANSI escape codes you may see improved rendering in certain
|
||||
// terminals with this enabled.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This should only be used in program occupying the entire terminal,
|
||||
// which is usually via the alternate screen buffer.
|
||||
HighPerformanceRendering bool
|
||||
|
||||
initialized bool
|
||||
lines []string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Model) setInitialValues() {
|
||||
m.KeyMap = DefaultKeyMap()
|
||||
m.MouseWheelEnabled = true
|
||||
m.MouseWheelDelta = 3
|
||||
m.initialized = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Init exists to satisfy the tea.Model interface for composability purposes.
|
||||
func (m Model) Init() tea.Cmd {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AtTop returns whether or not the viewport is at the very top position.
|
||||
func (m Model) AtTop() bool {
|
||||
return m.YOffset <= 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AtBottom returns whether or not the viewport is at or past the very bottom
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
func (m Model) AtBottom() bool {
|
||||
return m.YOffset >= m.maxYOffset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PastBottom returns whether or not the viewport is scrolled beyond the last
|
||||
// line. This can happen when adjusting the viewport height.
|
||||
func (m Model) PastBottom() bool {
|
||||
return m.YOffset > m.maxYOffset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollPercent returns the amount scrolled as a float between 0 and 1.
|
||||
func (m Model) ScrollPercent() float64 {
|
||||
if m.Height >= len(m.lines) {
|
||||
return 1.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
y := float64(m.YOffset)
|
||||
h := float64(m.Height)
|
||||
t := float64(len(m.lines) - 1)
|
||||
v := y / (t - h)
|
||||
return math.Max(0.0, math.Min(1.0, v))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetContent set the pager's text content. For high performance rendering the
|
||||
// Sync command should also be called.
|
||||
func (m *Model) SetContent(s string) {
|
||||
s = strings.ReplaceAll(s, "\r\n", "\n") // normalize line endings
|
||||
m.lines = strings.Split(s, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
if m.YOffset > len(m.lines)-1 {
|
||||
m.GotoBottom()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// maxYOffset returns the maximum possible value of the y-offset based on the
|
||||
// viewport's content and set height.
|
||||
func (m Model) maxYOffset() int {
|
||||
return max(0, len(m.lines)-m.Height)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// visibleLines returns the lines that should currently be visible in the
|
||||
// viewport.
|
||||
func (m Model) visibleLines() (lines []string) {
|
||||
if len(m.lines) > 0 {
|
||||
top := max(0, m.YOffset)
|
||||
bottom := clamp(m.YOffset+m.Height, top, len(m.lines))
|
||||
lines = m.lines[top:bottom]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lines
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// scrollArea returns the scrollable boundaries for high performance rendering.
|
||||
func (m Model) scrollArea() (top, bottom int) {
|
||||
top = max(0, m.YPosition)
|
||||
bottom = max(top, top+m.Height)
|
||||
if top > 0 && bottom > top {
|
||||
bottom--
|
||||
}
|
||||
return top, bottom
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetYOffset sets the Y offset.
|
||||
func (m *Model) SetYOffset(n int) {
|
||||
m.YOffset = clamp(n, 0, m.maxYOffset())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ViewDown moves the view down by the number of lines in the viewport.
|
||||
// Basically, "page down".
|
||||
func (m *Model) ViewDown() []string {
|
||||
if m.AtBottom() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m.LineDown(m.Height)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ViewUp moves the view up by one height of the viewport. Basically, "page up".
|
||||
func (m *Model) ViewUp() []string {
|
||||
if m.AtTop() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m.LineUp(m.Height)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HalfViewDown moves the view down by half the height of the viewport.
|
||||
func (m *Model) HalfViewDown() (lines []string) {
|
||||
if m.AtBottom() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m.LineDown(m.Height / 2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HalfViewUp moves the view up by half the height of the viewport.
|
||||
func (m *Model) HalfViewUp() (lines []string) {
|
||||
if m.AtTop() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m.LineUp(m.Height / 2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LineDown moves the view down by the given number of lines.
|
||||
func (m *Model) LineDown(n int) (lines []string) {
|
||||
if m.AtBottom() || n == 0 || len(m.lines) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make sure the number of lines by which we're going to scroll isn't
|
||||
// greater than the number of lines we actually have left before we reach
|
||||
// the bottom.
|
||||
m.SetYOffset(m.YOffset + n)
|
||||
|
||||
// Gather lines to send off for performance scrolling.
|
||||
bottom := clamp(m.YOffset+m.Height, 0, len(m.lines))
|
||||
top := clamp(m.YOffset+m.Height-n, 0, bottom)
|
||||
return m.lines[top:bottom]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LineUp moves the view down by the given number of lines. Returns the new
|
||||
// lines to show.
|
||||
func (m *Model) LineUp(n int) (lines []string) {
|
||||
if m.AtTop() || n == 0 || len(m.lines) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make sure the number of lines by which we're going to scroll isn't
|
||||
// greater than the number of lines we are from the top.
|
||||
m.SetYOffset(m.YOffset - n)
|
||||
|
||||
// Gather lines to send off for performance scrolling.
|
||||
top := max(0, m.YOffset)
|
||||
bottom := clamp(m.YOffset+n, 0, m.maxYOffset())
|
||||
return m.lines[top:bottom]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TotalLineCount returns the total number of lines (both hidden and visible) within the viewport.
|
||||
func (m Model) TotalLineCount() int {
|
||||
return len(m.lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VisibleLineCount returns the number of the visible lines within the viewport.
|
||||
func (m Model) VisibleLineCount() int {
|
||||
return len(m.visibleLines())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GotoTop sets the viewport to the top position.
|
||||
func (m *Model) GotoTop() (lines []string) {
|
||||
if m.AtTop() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m.SetYOffset(0)
|
||||
return m.visibleLines()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GotoBottom sets the viewport to the bottom position.
|
||||
func (m *Model) GotoBottom() (lines []string) {
|
||||
m.SetYOffset(m.maxYOffset())
|
||||
return m.visibleLines()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sync tells the renderer where the viewport will be located and requests
|
||||
// a render of the current state of the viewport. It should be called for the
|
||||
// first render and after a window resize.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For high performance rendering only.
|
||||
func Sync(m Model) tea.Cmd {
|
||||
if len(m.lines) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
top, bottom := m.scrollArea()
|
||||
return tea.SyncScrollArea(m.visibleLines(), top, bottom)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ViewDown is a high performance command that moves the viewport up by a given
|
||||
// number of lines. Use Model.ViewDown to get the lines that should be rendered.
|
||||
// For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// lines := model.ViewDown(1)
|
||||
// cmd := ViewDown(m, lines)
|
||||
func ViewDown(m Model, lines []string) tea.Cmd {
|
||||
if len(lines) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
top, bottom := m.scrollArea()
|
||||
return tea.ScrollDown(lines, top, bottom)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ViewUp is a high performance command the moves the viewport down by a given
|
||||
// number of lines height. Use Model.ViewUp to get the lines that should be
|
||||
// rendered.
|
||||
func ViewUp(m Model, lines []string) tea.Cmd {
|
||||
if len(lines) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
top, bottom := m.scrollArea()
|
||||
return tea.ScrollUp(lines, top, bottom)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Update handles standard message-based viewport updates.
|
||||
func (m Model) Update(msg tea.Msg) (Model, tea.Cmd) {
|
||||
var cmd tea.Cmd
|
||||
m, cmd = m.updateAsModel(msg)
|
||||
return m, cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Author's note: this method has been broken out to make it easier to
|
||||
// potentially transition Update to satisfy tea.Model.
|
||||
func (m Model) updateAsModel(msg tea.Msg) (Model, tea.Cmd) {
|
||||
if !m.initialized {
|
||||
m.setInitialValues()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var cmd tea.Cmd
|
||||
|
||||
switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
case tea.KeyMsg:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case key.Matches(msg, m.KeyMap.PageDown):
|
||||
lines := m.ViewDown()
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewDown(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case key.Matches(msg, m.KeyMap.PageUp):
|
||||
lines := m.ViewUp()
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewUp(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case key.Matches(msg, m.KeyMap.HalfPageDown):
|
||||
lines := m.HalfViewDown()
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewDown(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case key.Matches(msg, m.KeyMap.HalfPageUp):
|
||||
lines := m.HalfViewUp()
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewUp(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case key.Matches(msg, m.KeyMap.Down):
|
||||
lines := m.LineDown(1)
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewDown(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case key.Matches(msg, m.KeyMap.Up):
|
||||
lines := m.LineUp(1)
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewUp(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case tea.MouseMsg:
|
||||
if !m.MouseWheelEnabled || msg.Action != tea.MouseActionPress {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch msg.Button {
|
||||
case tea.MouseButtonWheelUp:
|
||||
lines := m.LineUp(m.MouseWheelDelta)
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewUp(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case tea.MouseButtonWheelDown:
|
||||
lines := m.LineDown(m.MouseWheelDelta)
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
cmd = ViewDown(m, lines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m, cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// View renders the viewport into a string.
|
||||
func (m Model) View() string {
|
||||
if m.HighPerformanceRendering {
|
||||
// Just send newlines since we're going to be rendering the actual
|
||||
// content separately. We still need to send something that equals the
|
||||
// height of this view so that the Bubble Tea standard renderer can
|
||||
// position anything below this view properly.
|
||||
return strings.Repeat("\n", max(0, m.Height-1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
w, h := m.Width, m.Height
|
||||
if sw := m.Style.GetWidth(); sw != 0 {
|
||||
w = min(w, sw)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if sh := m.Style.GetHeight(); sh != 0 {
|
||||
h = min(h, sh)
|
||||
}
|
||||
contentWidth := w - m.Style.GetHorizontalFrameSize()
|
||||
contentHeight := h - m.Style.GetVerticalFrameSize()
|
||||
contents := lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Width(contentWidth). // pad to width.
|
||||
Height(contentHeight). // pad to height.
|
||||
MaxHeight(contentHeight). // truncate height if taller.
|
||||
MaxWidth(contentWidth). // truncate width if wider.
|
||||
Render(strings.Join(m.visibleLines(), "\n"))
|
||||
return m.Style.Copy().
|
||||
UnsetWidth().UnsetHeight(). // Style size already applied in contents.
|
||||
Render(contents)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func clamp(v, low, high int) int {
|
||||
if high < low {
|
||||
low, high = high, low
|
||||
}
|
||||
return min(high, max(low, v))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a > b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
1
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.gitattributes
generated
vendored
Normal file
1
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.gitattributes
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
*.golden -text
|
||||
22
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
22
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.envrc
|
||||
|
||||
examples/fullscreen/fullscreen
|
||||
examples/help/help
|
||||
examples/http/http
|
||||
examples/list-default/list-default
|
||||
examples/list-fancy/list-fancy
|
||||
examples/list-simple/list-simple
|
||||
examples/mouse/mouse
|
||||
examples/pager/pager
|
||||
examples/progress-download/color_vortex.blend
|
||||
examples/progress-download/progress-download
|
||||
examples/simple/simple
|
||||
examples/spinner/spinner
|
||||
examples/textinput/textinput
|
||||
examples/textinputs/textinputs
|
||||
examples/views/views
|
||||
tutorials/basics/basics
|
||||
tutorials/commands/commands
|
||||
.idea
|
||||
coverage.txt
|
||||
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
run:
|
||||
tests: false
|
||||
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- EXC0001
|
||||
- EXC0005
|
||||
- EXC0011
|
||||
- EXC0012
|
||||
- EXC0013
|
||||
|
||||
max-issues-per-linter: 0
|
||||
max-same-issues: 0
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
# - dupl
|
||||
- exhaustive
|
||||
# - exhaustivestruct
|
||||
- goconst
|
||||
- godot
|
||||
- godox
|
||||
- gomnd
|
||||
- gomoddirectives
|
||||
- goprintffuncname
|
||||
# - lll
|
||||
- misspell
|
||||
- nakedret
|
||||
- nestif
|
||||
- noctx
|
||||
- nolintlint
|
||||
- prealloc
|
||||
- wrapcheck
|
||||
|
||||
# disable default linters, they are already enabled in .golangci.yml
|
||||
disable:
|
||||
- deadcode
|
||||
- errcheck
|
||||
- gosimple
|
||||
- govet
|
||||
- ineffassign
|
||||
- staticcheck
|
||||
- structcheck
|
||||
- typecheck
|
||||
- unused
|
||||
- varcheck
|
||||
30
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
30
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
run:
|
||||
tests: false
|
||||
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- EXC0001
|
||||
- EXC0005
|
||||
- EXC0011
|
||||
- EXC0012
|
||||
- EXC0013
|
||||
|
||||
max-issues-per-linter: 0
|
||||
max-same-issues: 0
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
- bodyclose
|
||||
- exportloopref
|
||||
- gofumpt
|
||||
- goimports
|
||||
- gosec
|
||||
- nilerr
|
||||
- predeclared
|
||||
- revive
|
||||
- rowserrcheck
|
||||
- sqlclosecheck
|
||||
- tparallel
|
||||
- unconvert
|
||||
- unparam
|
||||
- whitespace
|
||||
6
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
6
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
includes:
|
||||
- from_url:
|
||||
url: charmbracelet/meta/main/goreleaser-lib.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://goreleaser.com/static/schema-pro.json
|
||||
|
||||
13
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/CONTRIBUTING.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
13
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/CONTRIBUTING.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
# Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
Pull requests are welcome for any changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider opening an issue for larger changes to get feedback on the idea from the team.
|
||||
|
||||
If your change touches parts of the Bubble Tea renderer or internals, make sure
|
||||
that all the examples in the `examples/` folder continue to run correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
For commit messages, please use conventional commits[^1] to make it easier to
|
||||
generate release notes.
|
||||
|
||||
[^1]: https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2020-2023 Charmbracelet, Inc
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
451
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
451
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,451 @@
|
||||
# Bubble Tea
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<a href="https://stuff.charm.sh/bubbletea/bubbletea-4k.png"><img src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/assets/25087/108d4fdb-d554-4910-abed-2a5f5586a60e" width="313" alt="Bubble Tea Title Treatment"></a><br>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/charmbracelet/bubbletea.svg" alt="Latest Release"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea?tab=doc"><img src="https://godoc.org/github.com/golang/gddo?status.svg" alt="GoDoc"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/actions"><img src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/workflows/build/badge.svg" alt="Build Status"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://www.phorm.ai/query?projectId=a0e324b6-b706-4546-b951-6671ea60c13f"><img src="https://stuff.charm.sh/misc/phorm-badge.svg" alt="phorm.ai"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The fun, functional and stateful way to build terminal apps. A Go framework
|
||||
based on [The Elm Architecture][elm]. Bubble Tea is well-suited for simple and
|
||||
complex terminal applications, either inline, full-window, or a mix of both.
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<img src="https://stuff.charm.sh/bubbletea/bubbletea-example.gif" width="100%" alt="Bubble Tea Example">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Bubble Tea is in use in production and includes a number of features and
|
||||
performance optimizations we’ve added along the way. Among those is a standard
|
||||
framerate-based renderer, a renderer for high-performance scrollable
|
||||
regions which works alongside the main renderer, and mouse support.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, see the tutorial below, the [examples][examples], the
|
||||
[docs][docs], the [video tutorials][youtube] and some common [resources](#libraries-we-use-with-bubble-tea).
|
||||
|
||||
[youtube]: https://charm.sh/yt
|
||||
|
||||
## By the way
|
||||
|
||||
Be sure to check out [Bubbles][bubbles], a library of common UI components for Bubble Tea.
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles"><img src="https://stuff.charm.sh/bubbles/bubbles-badge.png" width="174" alt="Bubbles Badge"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles"><img src="https://stuff.charm.sh/bubbles-examples/textinput.gif" width="400" alt="Text Input Example from Bubbles"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
## Tutorial
|
||||
|
||||
Bubble Tea is based on the functional design paradigms of [The Elm
|
||||
Architecture][elm], which happens to work nicely with Go. It's a delightful way
|
||||
to build applications.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial assumes you have a working knowledge of Go.
|
||||
|
||||
By the way, the non-annotated source code for this program is available
|
||||
[on GitHub][tut-source].
|
||||
|
||||
[elm]: https://guide.elm-lang.org/architecture/
|
||||
[tut-source]:https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tree/master/tutorials/basics
|
||||
|
||||
### Enough! Let's get to it.
|
||||
|
||||
For this tutorial, we're making a shopping list.
|
||||
|
||||
To start we'll define our package and import some libraries. Our only external
|
||||
import will be the Bubble Tea library, which we'll call `tea` for short.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
|
||||
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Bubble Tea programs are comprised of a **model** that describes the application
|
||||
state and three simple methods on that model:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Init**, a function that returns an initial command for the application to run.
|
||||
* **Update**, a function that handles incoming events and updates the model accordingly.
|
||||
* **View**, a function that renders the UI based on the data in the model.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Model
|
||||
|
||||
So let's start by defining our model which will store our application's state.
|
||||
It can be any type, but a `struct` usually makes the most sense.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type model struct {
|
||||
choices []string // items on the to-do list
|
||||
cursor int // which to-do list item our cursor is pointing at
|
||||
selected map[int]struct{} // which to-do items are selected
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Initialization
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we’ll define our application’s initial state. In this case, we’re defining
|
||||
a function to return our initial model, however, we could just as easily define
|
||||
the initial model as a variable elsewhere, too.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func initialModel() model {
|
||||
return model{
|
||||
// Our to-do list is a grocery list
|
||||
choices: []string{"Buy carrots", "Buy celery", "Buy kohlrabi"},
|
||||
|
||||
// A map which indicates which choices are selected. We're using
|
||||
// the map like a mathematical set. The keys refer to the indexes
|
||||
// of the `choices` slice, above.
|
||||
selected: make(map[int]struct{}),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we define the `Init` method. `Init` can return a `Cmd` that could perform
|
||||
some initial I/O. For now, we don't need to do any I/O, so for the command,
|
||||
we'll just return `nil`, which translates to "no command."
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (m model) Init() tea.Cmd {
|
||||
// Just return `nil`, which means "no I/O right now, please."
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### The Update Method
|
||||
|
||||
Next up is the update method. The update function is called when ”things
|
||||
happen.” Its job is to look at what has happened and return an updated model in
|
||||
response. It can also return a `Cmd` to make more things happen, but for now
|
||||
don't worry about that part.
|
||||
|
||||
In our case, when a user presses the down arrow, `Update`’s job is to notice
|
||||
that the down arrow was pressed and move the cursor accordingly (or not).
|
||||
|
||||
The “something happened” comes in the form of a `Msg`, which can be any type.
|
||||
Messages are the result of some I/O that took place, such as a keypress, timer
|
||||
tick, or a response from a server.
|
||||
|
||||
We usually figure out which type of `Msg` we received with a type switch, but
|
||||
you could also use a type assertion.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, we'll just deal with `tea.KeyMsg` messages, which are automatically
|
||||
sent to the update function when keys are pressed.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (m model) Update(msg tea.Msg) (tea.Model, tea.Cmd) {
|
||||
switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Is it a key press?
|
||||
case tea.KeyMsg:
|
||||
|
||||
// Cool, what was the actual key pressed?
|
||||
switch msg.String() {
|
||||
|
||||
// These keys should exit the program.
|
||||
case "ctrl+c", "q":
|
||||
return m, tea.Quit
|
||||
|
||||
// The "up" and "k" keys move the cursor up
|
||||
case "up", "k":
|
||||
if m.cursor > 0 {
|
||||
m.cursor--
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The "down" and "j" keys move the cursor down
|
||||
case "down", "j":
|
||||
if m.cursor < len(m.choices)-1 {
|
||||
m.cursor++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The "enter" key and the spacebar (a literal space) toggle
|
||||
// the selected state for the item that the cursor is pointing at.
|
||||
case "enter", " ":
|
||||
_, ok := m.selected[m.cursor]
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
delete(m.selected, m.cursor)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
m.selected[m.cursor] = struct{}{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the updated model to the Bubble Tea runtime for processing.
|
||||
// Note that we're not returning a command.
|
||||
return m, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You may have noticed that <kbd>ctrl+c</kbd> and <kbd>q</kbd> above return
|
||||
a `tea.Quit` command with the model. That’s a special command which instructs
|
||||
the Bubble Tea runtime to quit, exiting the program.
|
||||
|
||||
### The View Method
|
||||
|
||||
At last, it’s time to render our UI. Of all the methods, the view is the
|
||||
simplest. We look at the model in its current state and use it to return
|
||||
a `string`. That string is our UI!
|
||||
|
||||
Because the view describes the entire UI of your application, you don’t have to
|
||||
worry about redrawing logic and stuff like that. Bubble Tea takes care of it
|
||||
for you.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (m model) View() string {
|
||||
// The header
|
||||
s := "What should we buy at the market?\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
// Iterate over our choices
|
||||
for i, choice := range m.choices {
|
||||
|
||||
// Is the cursor pointing at this choice?
|
||||
cursor := " " // no cursor
|
||||
if m.cursor == i {
|
||||
cursor = ">" // cursor!
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this choice selected?
|
||||
checked := " " // not selected
|
||||
if _, ok := m.selected[i]; ok {
|
||||
checked = "x" // selected!
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render the row
|
||||
s += fmt.Sprintf("%s [%s] %s\n", cursor, checked, choice)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The footer
|
||||
s += "\nPress q to quit.\n"
|
||||
|
||||
// Send the UI for rendering
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### All Together Now
|
||||
|
||||
The last step is to simply run our program. We pass our initial model to
|
||||
`tea.NewProgram` and let it rip:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
p := tea.NewProgram(initialModel())
|
||||
if _, err := p.Run(); err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Printf("Alas, there's been an error: %v", err)
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## What’s Next?
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial covers the basics of building an interactive terminal UI, but
|
||||
in the real world you'll also need to perform I/O. To learn about that have a
|
||||
look at the [Command Tutorial][cmd]. It's pretty simple.
|
||||
|
||||
There are also several [Bubble Tea examples][examples] available and, of course,
|
||||
there are [Go Docs][docs].
|
||||
|
||||
[cmd]: http://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tree/master/tutorials/commands/
|
||||
[examples]: http://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tree/master/examples
|
||||
[docs]: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea?tab=doc
|
||||
|
||||
## Debugging
|
||||
|
||||
### Debugging with Delve
|
||||
|
||||
Since Bubble Tea apps assume control of stdin and stdout, you’ll need to run
|
||||
delve in headless mode and then connect to it:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Start the debugger
|
||||
$ dlv debug --headless --api-version=2 --listen=127.0.0.1:43000 .
|
||||
API server listening at: 127.0.0.1:43000
|
||||
|
||||
# Connect to it from another terminal
|
||||
$ dlv connect 127.0.0.1:43000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not explicitly supply the `--listen` flag, the port used will vary
|
||||
per run, so passing this in makes the debugger easier to use from a script
|
||||
or your IDE of choice.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, we pass in `--api-version=2` because delve defaults to version 1
|
||||
for backwards compatibility reasons. However, delve recommends using version 2
|
||||
for all new development and some clients may no longer work with version 1.
|
||||
For more information, see the [Delve documentation](https://github.com/go-delve/delve/tree/master/Documentation/api).
|
||||
|
||||
### Logging Stuff
|
||||
|
||||
You can’t really log to stdout with Bubble Tea because your TUI is busy
|
||||
occupying that! You can, however, log to a file by including something like
|
||||
the following prior to starting your Bubble Tea program:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
if len(os.Getenv("DEBUG")) > 0 {
|
||||
f, err := tea.LogToFile("debug.log", "debug")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("fatal:", err)
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To see what’s being logged in real time, run `tail -f debug.log` while you run
|
||||
your program in another window.
|
||||
|
||||
## Libraries we use with Bubble Tea
|
||||
|
||||
* [Bubbles][bubbles]: Common Bubble Tea components such as text inputs, viewports, spinners and so on
|
||||
* [Lip Gloss][lipgloss]: Style, format and layout tools for terminal applications
|
||||
* [Harmonica][harmonica]: A spring animation library for smooth, natural motion
|
||||
* [BubbleZone][bubblezone]: Easy mouse event tracking for Bubble Tea components
|
||||
* [ntcharts][ntcharts]: A terminal charting library built for Bubble Tea and [Lip Gloss][lipgloss]
|
||||
* [Termenv][termenv]: Advanced ANSI styling for terminal applications
|
||||
* [Reflow][reflow]: Advanced ANSI-aware methods for working with text
|
||||
|
||||
[bubbles]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles
|
||||
[lipgloss]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss
|
||||
[harmonica]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/harmonica
|
||||
[bubblezone]: https://github.com/lrstanley/bubblezone
|
||||
[ntcharts]: https://github.com/NimbleMarkets/ntcharts
|
||||
[termenv]: https://github.com/muesli/termenv
|
||||
[reflow]: https://github.com/muesli/reflow
|
||||
|
||||
## Bubble Tea in the Wild
|
||||
|
||||
For some Bubble Tea programs in production, see:
|
||||
|
||||
* [ASCII Movie](https://github.com/gabe565/ascii-movie): a Star Wars ASCII art movie player
|
||||
* [AT CLI](https://github.com/daskycodes/at_cli): execute AT Commands via serial port connections
|
||||
* [Aztify](https://github.com/Azure/aztfy): bring Microsoft Azure resources under Terraform
|
||||
* [brows](https://github.com/rubysolo/brows): a GitHub release browser
|
||||
* [Canard](https://github.com/mrusme/canard): an RSS client
|
||||
* [charm](https://github.com/charmbracelet/charm): the official Charm user account manager
|
||||
* [chatgpt-cli](https://github.com/j178/chatgpt): a CLI for ChatGPT
|
||||
* [chatgpt-tui](https://github.com/tearingItUp786/chatgpt-tui): a TUI for ChatGPT with SQLite sessions
|
||||
* [ChatGPTUI](https://github.com/dwisiswant0/chatgptui): a TUI for ChatGPT
|
||||
* [chezmoi](https://github.com/twpayne/chezmoi): securely manage your dotfiles across multiple machines
|
||||
* [chip-8](https://github.com/braheezy/chip-8): a CHIP-8 interpreter
|
||||
* [chtop](https://github.com/chhetripradeep/chtop): monitor your ClickHouse node without leaving the terminal
|
||||
* [circumflex](https://github.com/bensadeh/circumflex): read Hacker News in the terminal
|
||||
* [clidle](https://github.com/ajeetdsouza/clidle): a Wordle clone
|
||||
* [cLive](https://github.com/koki-develop/clive): automate terminal operations and view them live in a browser
|
||||
* [container-canary](https://github.com/NVIDIA/container-canary): a container validator
|
||||
* [countdown](https://github.com/aldernero/countdown): a multi-event countdown timer
|
||||
* [CRT](https://github.com/BigJk/crt): a simple terminal emulator for running Bubble Tea in a dedicated window, with optional shaders
|
||||
* [cueitup](https://github.com/dhth/cueitup): inspect messages in an AWS SQS queue in a simple and deliberate manner
|
||||
* [Daytona](https://github.com/daytonaio/daytona): an development environment manager
|
||||
* [dns53](https://github.com/purpleclay/dns53): dynamic DNS with Amazon Route53; expose your EC2 quickly, securely and privately
|
||||
* [eks-node-viewer](https://github.com/awslabs/eks-node-viewer): a tool for visualizing dynamic node usage within an EKS cluster
|
||||
* [End Of Eden](https://github.com/BigJk/end_of_eden): a "Slay the Spire"-like, roguelike deck-builder game
|
||||
* [enola](https://github.com/sherlock-project/enola): find social media accounts by username across social networks
|
||||
* [flapioca](https://github.com/kbrgl/flapioca): Flappy Bird on the CLI!
|
||||
* [fm](https://github.com/knipferrc/fm): a terminal-based file manager
|
||||
* [fork-cleaner](https://github.com/caarlos0/fork-cleaner): clean up old and inactive forks in your GitHub account
|
||||
* [fractals-cli](https://github.com/MicheleFiladelfia/fractals-cli): a multiplatform terminal fractal explorer
|
||||
* [fztea](https://github.com/jon4hz/fztea): a Flipper Zero TUI
|
||||
* [gama](https://github.com/termkit/gama): manage GitHub Actions from the terminal
|
||||
* [gambit](https://github.com/maaslalani/gambit): chess in the terminal
|
||||
* [gembro](https://git.sr.ht/~rafael/gembro): a mouse-driven Gemini browser
|
||||
* [gh-b](https://github.com/joaom00/gh-b): a GitHub CLI extension for managing branches
|
||||
* [gh-dash](https://www.github.com/dlvhdr/gh-dash): a GitHub CLI extension for PRs and issues
|
||||
* [gitflow-toolkit](https://github.com/mritd/gitflow-toolkit): a GitFlow submission tool
|
||||
* [Glow](https://github.com/charmbracelet/glow): a markdown reader, browser, and online markdown stash
|
||||
* [go-sweep](https://github.com/maxpaulus43/go-sweep): Minesweeper in the terminal
|
||||
* [gocovsh](https://github.com/orlangure/gocovsh): explore Go coverage reports from the CLI
|
||||
* [got](https://github.com/fedeztk/got): a simple translator and text-to-speech app built on simplytranslate's APIs
|
||||
* [gum](https://github.com/charmbracelet/gum): interactivity and styling for shells and shell scripts
|
||||
* [hiSHtory](https://github.com/ddworken/hishtory): your shell history in context: synced, and queryable
|
||||
* [httpit](https://github.com/gonetx/httpit): a rapid http(s) benchmark tool
|
||||
* [Huh?](https://github.com/charmbracelet/huh): an interactive prompt and form toolkit
|
||||
* [IDNT](https://github.com/r-darwish/idnt): a batch software uninstaller
|
||||
* [json-log-viewer](https://github.com/hedhyw/json-log-viewer): an interactive JSON log viewer
|
||||
* [kboard](https://github.com/CamiloGarciaLaRotta/kboard): a typing game
|
||||
* [kplay](https://github.com/dhth/kplay): inspect messages in a Kafka topic
|
||||
* [laboon](https://github.com/arisnacg/laboon): a Docker-desktop-style container manager
|
||||
* [mc](https://github.com/minio/mc): the official [MinIO](https://min.io) client
|
||||
* [mergestat](https://github.com/mergestat/mergestat): run SQL queries on git repositories
|
||||
* [meteor](https://github.com/stefanlogue/meteor): a highly customizable conventional commit message tool
|
||||
* [mods](https://github.com/charmbracelet/mods): AI on the CLI, built for pipelines
|
||||
* [nachrichten](https://github.com/zMoooooritz/nachrichten): access up-to-date news in German provided by the [Tagesschau](https://www.tagesschau.de/)
|
||||
* [Neon Modem Overdrive](https://github.com/mrusme/neonmodem): a BBS-style TUI client for Discourse, Lemmy, Lobste.rs and Hacker News
|
||||
* [nom](https://github.com/guyfedwards/nom): an RSS reader and manager
|
||||
* [Noted](https://github.com/torbratsberg/noted): a note viewer and manager
|
||||
* [outtasync](https://github.com/dhth/outtasync): identify CloudFormation stacks that are out of sync with their template files
|
||||
* [pathos](https://github.com/chip/pathos): a PATH environment variable editor
|
||||
* [Plandex](https://github.com/plandex-ai/plandex): a terminal-based AI coding engine for complex tasks
|
||||
* [portal](https://github.com/ZinoKader/portal): secure transfers between computers
|
||||
* [prs](https://github.com/dhth/prs): stay up to date with your PRs
|
||||
* [puffin](https://github.com/siddhantac/puffin): a TUI for hledger to manage your finances
|
||||
* [pug](https://github.com/leg100/pug): terraform task manager
|
||||
* [punchout](https://github.com/dhth/punchout): takes the suck out of logging time on JIRA
|
||||
* [redis-viewer](https://github.com/SaltFishPr/redis-viewer): a Redis database browser
|
||||
* [redis_tui](https://github.com/mat2cc/redis_tui): a Redis database browser
|
||||
* [schemas](https://github.com/dhth/schemas): lets you inspect postgres schemas in the terminal
|
||||
* [scrabbler](https://github.com/wI2L/scrabbler): an automatic draw tool for your duplicate Scrabble games
|
||||
* [sku](https://github.com/fedeztk/sku): Sudoku on the CLI
|
||||
* [Slides](https://github.com/maaslalani/slides): a markdown-based presentation tool
|
||||
* [SlurmCommander](https://github.com/CLIP-HPC/SlurmCommander): a Slurm workload manager
|
||||
* [Soft Serve](https://github.com/charmbracelet/soft-serve): a command-line-first Git server that runs a TUI over SSH
|
||||
* [solitaire-tui](https://github.com/brianstrauch/solitaire-tui): Klondike Solitaire for the terminal
|
||||
* [StormForge Optimize Controller](https://github.com/thestormforge/optimize-controller): a tool for experimenting with application configurations in Kubernetes
|
||||
* [Storydb](https://github.com/grrlopes/storydb): an improved bash/zsh-style ctrl+r command history finder
|
||||
* [STTG](https://github.com/wille1101/sttg): a teletext client for SVT, Sweden’s national public television station
|
||||
* [sttr](https://github.com/abhimanyu003/sttr): a general-purpose text transformer
|
||||
* [superfile](https://github.com/MHNightCat/superfile) a fancy, modern terminal-based file manager
|
||||
* [tasktimer](https://github.com/caarlos0/tasktimer): a dead-simple task timer
|
||||
* [termdbms](https://github.com/mathaou/termdbms): a keyboard and mouse driven database browser
|
||||
* [tgpt](https://github.com/aandrew-me/tgpt): conversational AI for the CLI; no API keys necessary
|
||||
* [ticker](https://github.com/achannarasappa/ticker): a terminal stock viewer and stock position tracker
|
||||
* [trainer](https://github.com/rusinikita/trainer): a Go concurrency coding interview simulator with learning materials
|
||||
* [tran](https://github.com/abdfnx/tran): securely transfer stuff between computers (based on [portal](https://github.com/ZinoKader/portal))
|
||||
* [Trufflehog](https://github.com/trufflesecurity/trufflehog): find leaked credentials
|
||||
* [Typer](https://github.com/maaslalani/typer): a typing test
|
||||
* [typioca](https://github.com/bloznelis/typioca): a typing test
|
||||
* [tz](https://github.com/oz/tz): a scheduling aid for people in multiple time zones
|
||||
* [ugm](https://github.com/ariasmn/ugm): a unix user and group browser
|
||||
* [walk](https://github.com/antonmedv/walk): a terminal navigator
|
||||
* [wander](https://github.com/robinovitch61/wander): a HashiCorp Nomad terminal client
|
||||
* [WG Commander](https://github.com/AndrianBdn/wg-cmd): a TUI for a simple WireGuard VPN setup
|
||||
* [wishlist](https://github.com/charmbracelet/wishlist): an SSH directory
|
||||
|
||||
## Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
We'd love to hear your thoughts on this project. Feel free to drop us a note!
|
||||
|
||||
* [Twitter](https://twitter.com/charmcli)
|
||||
* [The Fediverse](https://mastodon.social/@charmcli)
|
||||
* [Discord](https://charm.sh/chat)
|
||||
|
||||
## Acknowledgments
|
||||
|
||||
Bubble Tea is based on the paradigms of [The Elm Architecture][elm] by Evan
|
||||
Czaplicki et alia and the excellent [go-tea][gotea] by TJ Holowaychuk. It’s
|
||||
inspired by the many great [_Zeichenorientierte Benutzerschnittstellen_][zb]
|
||||
of days past.
|
||||
|
||||
[elm]: https://guide.elm-lang.org/architecture/
|
||||
[gotea]: https://github.com/tj/go-tea
|
||||
[zb]: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zeichenorientierte_Benutzerschnittstelle
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
[MIT](https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/raw/master/LICENSE)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
Part of [Charm](https://charm.sh).
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://charm.sh/"><img alt="The Charm logo" src="https://stuff.charm.sh/charm-badge.jpg" width="400"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Charm热爱开源 • Charm loves open source • نحنُ نحب المصادر المفتوحة
|
||||
216
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/commands.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
216
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/commands.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,216 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Batch performs a bunch of commands concurrently with no ordering guarantees
|
||||
// about the results. Use a Batch to return several commands.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func (m model) Init() Cmd {
|
||||
// return tea.Batch(someCommand, someOtherCommand)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func Batch(cmds ...Cmd) Cmd {
|
||||
var validCmds []Cmd //nolint:prealloc
|
||||
for _, c := range cmds {
|
||||
if c == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
validCmds = append(validCmds, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch len(validCmds) {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
return validCmds[0]
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return BatchMsg(validCmds)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BatchMsg is a message used to perform a bunch of commands concurrently with
|
||||
// no ordering guarantees. You can send a BatchMsg with Batch.
|
||||
type BatchMsg []Cmd
|
||||
|
||||
// Sequence runs the given commands one at a time, in order. Contrast this with
|
||||
// Batch, which runs commands concurrently.
|
||||
func Sequence(cmds ...Cmd) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return sequenceMsg(cmds)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// sequenceMsg is used internally to run the given commands in order.
|
||||
type sequenceMsg []Cmd
|
||||
|
||||
// Every is a command that ticks in sync with the system clock. So, if you
|
||||
// wanted to tick with the system clock every second, minute or hour you
|
||||
// could use this. It's also handy for having different things tick in sync.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because we're ticking with the system clock the tick will likely not run for
|
||||
// the entire specified duration. For example, if we're ticking for one minute
|
||||
// and the clock is at 12:34:20 then the next tick will happen at 12:35:00, 40
|
||||
// seconds later.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To produce the command, pass a duration and a function which returns
|
||||
// a message containing the time at which the tick occurred.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type TickMsg time.Time
|
||||
//
|
||||
// cmd := Every(time.Second, func(t time.Time) Msg {
|
||||
// return TickMsg(t)
|
||||
// })
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Beginners' note: Every sends a single message and won't automatically
|
||||
// dispatch messages at an interval. To do that, you'll want to return another
|
||||
// Every command after receiving your tick message. For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type TickMsg time.Time
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Send a message every second.
|
||||
// func tickEvery() Cmd {
|
||||
// return Every(time.Second, func(t time.Time) Msg {
|
||||
// return TickMsg(t)
|
||||
// })
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func (m model) Init() Cmd {
|
||||
// // Start ticking.
|
||||
// return tickEvery()
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func (m model) Update(msg Msg) (Model, Cmd) {
|
||||
// switch msg.(type) {
|
||||
// case TickMsg:
|
||||
// // Return your Every command again to loop.
|
||||
// return m, tickEvery()
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// return m, nil
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Every is analogous to Tick in the Elm Architecture.
|
||||
func Every(duration time.Duration, fn func(time.Time) Msg) Cmd {
|
||||
n := time.Now()
|
||||
d := n.Truncate(duration).Add(duration).Sub(n)
|
||||
t := time.NewTimer(d)
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
ts := <-t.C
|
||||
t.Stop()
|
||||
for len(t.C) > 0 {
|
||||
<-t.C
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fn(ts)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tick produces a command at an interval independent of the system clock at
|
||||
// the given duration. That is, the timer begins precisely when invoked,
|
||||
// and runs for its entire duration.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To produce the command, pass a duration and a function which returns
|
||||
// a message containing the time at which the tick occurred.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type TickMsg time.Time
|
||||
//
|
||||
// cmd := Tick(time.Second, func(t time.Time) Msg {
|
||||
// return TickMsg(t)
|
||||
// })
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Beginners' note: Tick sends a single message and won't automatically
|
||||
// dispatch messages at an interval. To do that, you'll want to return another
|
||||
// Tick command after receiving your tick message. For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type TickMsg time.Time
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func doTick() Cmd {
|
||||
// return Tick(time.Second, func(t time.Time) Msg {
|
||||
// return TickMsg(t)
|
||||
// })
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func (m model) Init() Cmd {
|
||||
// // Start ticking.
|
||||
// return doTick()
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func (m model) Update(msg Msg) (Model, Cmd) {
|
||||
// switch msg.(type) {
|
||||
// case TickMsg:
|
||||
// // Return your Tick command again to loop.
|
||||
// return m, doTick()
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// return m, nil
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func Tick(d time.Duration, fn func(time.Time) Msg) Cmd {
|
||||
t := time.NewTimer(d)
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
ts := <-t.C
|
||||
t.Stop()
|
||||
for len(t.C) > 0 {
|
||||
<-t.C
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fn(ts)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sequentially produces a command that sequentially executes the given
|
||||
// commands.
|
||||
// The Msg returned is the first non-nil message returned by a Cmd.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func saveStateCmd() Msg {
|
||||
// if err := save(); err != nil {
|
||||
// return errMsg{err}
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// return nil
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// cmd := Sequentially(saveStateCmd, Quit)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use Sequence instead.
|
||||
func Sequentially(cmds ...Cmd) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
for _, cmd := range cmds {
|
||||
if cmd == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if msg := cmd(); msg != nil {
|
||||
return msg
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setWindowTitleMsg is an internal message used to set the window title.
|
||||
type setWindowTitleMsg string
|
||||
|
||||
// SetWindowTitle produces a command that sets the terminal title.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func (m model) Init() Cmd {
|
||||
// // Set title.
|
||||
// return tea.SetWindowTitle("My App")
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func SetWindowTitle(title string) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return setWindowTitleMsg(title)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type windowSizeMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// WindowSize is a command that queries the terminal for its current size. It
|
||||
// delivers the results to Update via a [WindowSizeMsg]. Keep in mind that
|
||||
// WindowSizeMsgs will automatically be delivered to Update when the [Program]
|
||||
// starts and when the window dimensions change so in many cases you will not
|
||||
// need to explicitly invoke this command.
|
||||
func WindowSize() Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return windowSizeMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
129
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/exec.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
129
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/exec.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/exec"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// execMsg is used internally to run an ExecCommand sent with Exec.
|
||||
type execMsg struct {
|
||||
cmd ExecCommand
|
||||
fn ExecCallback
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Exec is used to perform arbitrary I/O in a blocking fashion, effectively
|
||||
// pausing the Program while execution is running and resuming it when
|
||||
// execution has completed.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Most of the time you'll want to use ExecProcess, which runs an exec.Cmd.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For non-interactive i/o you should use a Cmd (that is, a tea.Cmd).
|
||||
func Exec(c ExecCommand, fn ExecCallback) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return execMsg{cmd: c, fn: fn}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExecProcess runs the given *exec.Cmd in a blocking fashion, effectively
|
||||
// pausing the Program while the command is running. After the *exec.Cmd exists
|
||||
// the Program resumes. It's useful for spawning other interactive applications
|
||||
// such as editors and shells from within a Program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To produce the command, pass an *exec.Cmd and a function which returns
|
||||
// a message containing the error which may have occurred when running the
|
||||
// ExecCommand.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type VimFinishedMsg struct { err error }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// c := exec.Command("vim", "file.txt")
|
||||
//
|
||||
// cmd := ExecProcess(c, func(err error) Msg {
|
||||
// return VimFinishedMsg{err: err}
|
||||
// })
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Or, if you don't care about errors, you could simply:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// cmd := ExecProcess(exec.Command("vim", "file.txt"), nil)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For non-interactive i/o you should use a Cmd (that is, a tea.Cmd).
|
||||
func ExecProcess(c *exec.Cmd, fn ExecCallback) Cmd {
|
||||
return Exec(wrapExecCommand(c), fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExecCallback is used when executing an *exec.Command to return a message
|
||||
// with an error, which may or may not be nil.
|
||||
type ExecCallback func(error) Msg
|
||||
|
||||
// ExecCommand can be implemented to execute things in a blocking fashion in
|
||||
// the current terminal.
|
||||
type ExecCommand interface {
|
||||
Run() error
|
||||
SetStdin(io.Reader)
|
||||
SetStdout(io.Writer)
|
||||
SetStderr(io.Writer)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// wrapExecCommand wraps an exec.Cmd so that it satisfies the ExecCommand
|
||||
// interface so it can be used with Exec.
|
||||
func wrapExecCommand(c *exec.Cmd) ExecCommand {
|
||||
return &osExecCommand{Cmd: c}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// osExecCommand is a layer over an exec.Cmd that satisfies the ExecCommand
|
||||
// interface.
|
||||
type osExecCommand struct{ *exec.Cmd }
|
||||
|
||||
// SetStdin sets stdin on underlying exec.Cmd to the given io.Reader.
|
||||
func (c *osExecCommand) SetStdin(r io.Reader) {
|
||||
// If unset, have the command use the same input as the terminal.
|
||||
if c.Stdin == nil {
|
||||
c.Stdin = r
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetStdout sets stdout on underlying exec.Cmd to the given io.Writer.
|
||||
func (c *osExecCommand) SetStdout(w io.Writer) {
|
||||
// If unset, have the command use the same output as the terminal.
|
||||
if c.Stdout == nil {
|
||||
c.Stdout = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetStderr sets stderr on the underlying exec.Cmd to the given io.Writer.
|
||||
func (c *osExecCommand) SetStderr(w io.Writer) {
|
||||
// If unset, use stderr for the command's stderr
|
||||
if c.Stderr == nil {
|
||||
c.Stderr = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// exec runs an ExecCommand and delivers the results to the program as a Msg.
|
||||
func (p *Program) exec(c ExecCommand, fn ExecCallback) {
|
||||
if err := p.ReleaseTerminal(); err != nil {
|
||||
// If we can't release input, abort.
|
||||
if fn != nil {
|
||||
go p.Send(fn(err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
c.SetStdin(p.input)
|
||||
c.SetStdout(p.output)
|
||||
c.SetStderr(os.Stderr)
|
||||
|
||||
// Execute system command.
|
||||
if err := c.Run(); err != nil {
|
||||
_ = p.RestoreTerminal() // also try to restore the terminal.
|
||||
if fn != nil {
|
||||
go p.Send(fn(err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Have the program re-capture input.
|
||||
err := p.RestoreTerminal()
|
||||
if fn != nil {
|
||||
go p.Send(fn(err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
14
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/inputreader_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
14
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/inputreader_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
//go:build !windows
|
||||
// +build !windows
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/cancelreader"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func newInputReader(r io.Reader) (cancelreader.CancelReader, error) {
|
||||
return cancelreader.NewReader(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
107
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/inputreader_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
107
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/inputreader_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
//go:build windows
|
||||
// +build windows
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/term"
|
||||
"github.com/erikgeiser/coninput"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/cancelreader"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/sys/windows"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type conInputReader struct {
|
||||
cancelMixin
|
||||
|
||||
conin windows.Handle
|
||||
|
||||
originalMode uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ cancelreader.CancelReader = &conInputReader{}
|
||||
|
||||
func newInputReader(r io.Reader) (cancelreader.CancelReader, error) {
|
||||
fallback := func(io.Reader) (cancelreader.CancelReader, error) {
|
||||
return cancelreader.NewReader(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f, ok := r.(term.File); !ok || f.Fd() != os.Stdin.Fd() {
|
||||
return fallback(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
conin, err := coninput.NewStdinHandle()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fallback(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
originalMode, err := prepareConsole(conin,
|
||||
windows.ENABLE_MOUSE_INPUT,
|
||||
windows.ENABLE_WINDOW_INPUT,
|
||||
windows.ENABLE_EXTENDED_FLAGS,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to prepare console input: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return &conInputReader{
|
||||
conin: conin,
|
||||
originalMode: originalMode,
|
||||
}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cancel implements cancelreader.CancelReader.
|
||||
func (r *conInputReader) Cancel() bool {
|
||||
r.setCanceled()
|
||||
|
||||
return windows.CancelIo(r.conin) == nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Close implements cancelreader.CancelReader.
|
||||
func (r *conInputReader) Close() error {
|
||||
if r.originalMode != 0 {
|
||||
err := windows.SetConsoleMode(r.conin, r.originalMode)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("reset console mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read implements cancelreader.CancelReader.
|
||||
func (*conInputReader) Read(_ []byte) (n int, err error) {
|
||||
return 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func prepareConsole(input windows.Handle, modes ...uint32) (originalMode uint32, err error) {
|
||||
err = windows.GetConsoleMode(input, &originalMode)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, fmt.Errorf("get console mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
newMode := coninput.AddInputModes(0, modes...)
|
||||
|
||||
err = windows.SetConsoleMode(input, newMode)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, fmt.Errorf("set console mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return originalMode, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cancelMixin represents a goroutine-safe cancelation status.
|
||||
type cancelMixin struct {
|
||||
unsafeCanceled bool
|
||||
lock sync.Mutex
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *cancelMixin) setCanceled() {
|
||||
c.lock.Lock()
|
||||
defer c.lock.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
c.unsafeCanceled = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
708
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
708
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,708 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"regexp"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// KeyMsg contains information about a keypress. KeyMsgs are always sent to
|
||||
// the program's update function. There are a couple general patterns you could
|
||||
// use to check for keypresses:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Switch on the string representation of the key (shorter)
|
||||
// switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
// case KeyMsg:
|
||||
// switch msg.String() {
|
||||
// case "enter":
|
||||
// fmt.Println("you pressed enter!")
|
||||
// case "a":
|
||||
// fmt.Println("you pressed a!")
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Switch on the key type (more foolproof)
|
||||
// switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
// case KeyMsg:
|
||||
// switch msg.Type {
|
||||
// case KeyEnter:
|
||||
// fmt.Println("you pressed enter!")
|
||||
// case KeyRunes:
|
||||
// switch string(msg.Runes) {
|
||||
// case "a":
|
||||
// fmt.Println("you pressed a!")
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that Key.Runes will always contain at least one character, so you can
|
||||
// always safely call Key.Runes[0]. In most cases Key.Runes will only contain
|
||||
// one character, though certain input method editors (most notably Chinese
|
||||
// IMEs) can input multiple runes at once.
|
||||
type KeyMsg Key
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation for a key message. It's safe (and
|
||||
// encouraged) for use in key comparison.
|
||||
func (k KeyMsg) String() (str string) {
|
||||
return Key(k).String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Key contains information about a keypress.
|
||||
type Key struct {
|
||||
Type KeyType
|
||||
Runes []rune
|
||||
Alt bool
|
||||
Paste bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a friendly string representation for a key. It's safe (and
|
||||
// encouraged) for use in key comparison.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// k := Key{Type: KeyEnter}
|
||||
// fmt.Println(k)
|
||||
// // Output: enter
|
||||
func (k Key) String() (str string) {
|
||||
var buf strings.Builder
|
||||
if k.Alt {
|
||||
buf.WriteString("alt+")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if k.Type == KeyRunes {
|
||||
if k.Paste {
|
||||
// Note: bubbles/keys bindings currently do string compares to
|
||||
// recognize shortcuts. Since pasted text should never activate
|
||||
// shortcuts, we need to ensure that the binding code doesn't
|
||||
// match Key events that result from pastes. We achieve this
|
||||
// here by enclosing pastes in '[...]' so that the string
|
||||
// comparison in Matches() fails in that case.
|
||||
buf.WriteByte('[')
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf.WriteString(string(k.Runes))
|
||||
if k.Paste {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(']')
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
} else if s, ok := keyNames[k.Type]; ok {
|
||||
buf.WriteString(s)
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// KeyType indicates the key pressed, such as KeyEnter or KeyBreak or KeyCtrlC.
|
||||
// All other keys will be type KeyRunes. To get the rune value, check the Rune
|
||||
// method on a Key struct, or use the Key.String() method:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// k := Key{Type: KeyRunes, Runes: []rune{'a'}, Alt: true}
|
||||
// if k.Type == KeyRunes {
|
||||
//
|
||||
// fmt.Println(k.Runes)
|
||||
// // Output: a
|
||||
//
|
||||
// fmt.Println(k.String())
|
||||
// // Output: alt+a
|
||||
//
|
||||
// }
|
||||
type KeyType int
|
||||
|
||||
func (k KeyType) String() (str string) {
|
||||
if s, ok := keyNames[k]; ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Control keys. We could do this with an iota, but the values are very
|
||||
// specific, so we set the values explicitly to avoid any confusion.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See also:
|
||||
// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C0_and_C1_control_codes
|
||||
const (
|
||||
keyNUL KeyType = 0 // null, \0
|
||||
keySOH KeyType = 1 // start of heading
|
||||
keySTX KeyType = 2 // start of text
|
||||
keyETX KeyType = 3 // break, ctrl+c
|
||||
keyEOT KeyType = 4 // end of transmission
|
||||
keyENQ KeyType = 5 // enquiry
|
||||
keyACK KeyType = 6 // acknowledge
|
||||
keyBEL KeyType = 7 // bell, \a
|
||||
keyBS KeyType = 8 // backspace
|
||||
keyHT KeyType = 9 // horizontal tabulation, \t
|
||||
keyLF KeyType = 10 // line feed, \n
|
||||
keyVT KeyType = 11 // vertical tabulation \v
|
||||
keyFF KeyType = 12 // form feed \f
|
||||
keyCR KeyType = 13 // carriage return, \r
|
||||
keySO KeyType = 14 // shift out
|
||||
keySI KeyType = 15 // shift in
|
||||
keyDLE KeyType = 16 // data link escape
|
||||
keyDC1 KeyType = 17 // device control one
|
||||
keyDC2 KeyType = 18 // device control two
|
||||
keyDC3 KeyType = 19 // device control three
|
||||
keyDC4 KeyType = 20 // device control four
|
||||
keyNAK KeyType = 21 // negative acknowledge
|
||||
keySYN KeyType = 22 // synchronous idle
|
||||
keyETB KeyType = 23 // end of transmission block
|
||||
keyCAN KeyType = 24 // cancel
|
||||
keyEM KeyType = 25 // end of medium
|
||||
keySUB KeyType = 26 // substitution
|
||||
keyESC KeyType = 27 // escape, \e
|
||||
keyFS KeyType = 28 // file separator
|
||||
keyGS KeyType = 29 // group separator
|
||||
keyRS KeyType = 30 // record separator
|
||||
keyUS KeyType = 31 // unit separator
|
||||
keyDEL KeyType = 127 // delete. on most systems this is mapped to backspace, I hear
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Control key aliases.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
KeyNull KeyType = keyNUL
|
||||
KeyBreak KeyType = keyETX
|
||||
KeyEnter KeyType = keyCR
|
||||
KeyBackspace KeyType = keyDEL
|
||||
KeyTab KeyType = keyHT
|
||||
KeyEsc KeyType = keyESC
|
||||
KeyEscape KeyType = keyESC
|
||||
|
||||
KeyCtrlAt KeyType = keyNUL // ctrl+@
|
||||
KeyCtrlA KeyType = keySOH
|
||||
KeyCtrlB KeyType = keySTX
|
||||
KeyCtrlC KeyType = keyETX
|
||||
KeyCtrlD KeyType = keyEOT
|
||||
KeyCtrlE KeyType = keyENQ
|
||||
KeyCtrlF KeyType = keyACK
|
||||
KeyCtrlG KeyType = keyBEL
|
||||
KeyCtrlH KeyType = keyBS
|
||||
KeyCtrlI KeyType = keyHT
|
||||
KeyCtrlJ KeyType = keyLF
|
||||
KeyCtrlK KeyType = keyVT
|
||||
KeyCtrlL KeyType = keyFF
|
||||
KeyCtrlM KeyType = keyCR
|
||||
KeyCtrlN KeyType = keySO
|
||||
KeyCtrlO KeyType = keySI
|
||||
KeyCtrlP KeyType = keyDLE
|
||||
KeyCtrlQ KeyType = keyDC1
|
||||
KeyCtrlR KeyType = keyDC2
|
||||
KeyCtrlS KeyType = keyDC3
|
||||
KeyCtrlT KeyType = keyDC4
|
||||
KeyCtrlU KeyType = keyNAK
|
||||
KeyCtrlV KeyType = keySYN
|
||||
KeyCtrlW KeyType = keyETB
|
||||
KeyCtrlX KeyType = keyCAN
|
||||
KeyCtrlY KeyType = keyEM
|
||||
KeyCtrlZ KeyType = keySUB
|
||||
KeyCtrlOpenBracket KeyType = keyESC // ctrl+[
|
||||
KeyCtrlBackslash KeyType = keyFS // ctrl+\
|
||||
KeyCtrlCloseBracket KeyType = keyGS // ctrl+]
|
||||
KeyCtrlCaret KeyType = keyRS // ctrl+^
|
||||
KeyCtrlUnderscore KeyType = keyUS // ctrl+_
|
||||
KeyCtrlQuestionMark KeyType = keyDEL // ctrl+?
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Other keys.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
KeyRunes KeyType = -(iota + 1)
|
||||
KeyUp
|
||||
KeyDown
|
||||
KeyRight
|
||||
KeyLeft
|
||||
KeyShiftTab
|
||||
KeyHome
|
||||
KeyEnd
|
||||
KeyPgUp
|
||||
KeyPgDown
|
||||
KeyCtrlPgUp
|
||||
KeyCtrlPgDown
|
||||
KeyDelete
|
||||
KeyInsert
|
||||
KeySpace
|
||||
KeyCtrlUp
|
||||
KeyCtrlDown
|
||||
KeyCtrlRight
|
||||
KeyCtrlLeft
|
||||
KeyCtrlHome
|
||||
KeyCtrlEnd
|
||||
KeyShiftUp
|
||||
KeyShiftDown
|
||||
KeyShiftRight
|
||||
KeyShiftLeft
|
||||
KeyShiftHome
|
||||
KeyShiftEnd
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftUp
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftDown
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftLeft
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftRight
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftHome
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftEnd
|
||||
KeyF1
|
||||
KeyF2
|
||||
KeyF3
|
||||
KeyF4
|
||||
KeyF5
|
||||
KeyF6
|
||||
KeyF7
|
||||
KeyF8
|
||||
KeyF9
|
||||
KeyF10
|
||||
KeyF11
|
||||
KeyF12
|
||||
KeyF13
|
||||
KeyF14
|
||||
KeyF15
|
||||
KeyF16
|
||||
KeyF17
|
||||
KeyF18
|
||||
KeyF19
|
||||
KeyF20
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Mappings for control keys and other special keys to friendly consts.
|
||||
var keyNames = map[KeyType]string{
|
||||
// Control keys.
|
||||
keyNUL: "ctrl+@", // also ctrl+` (that's ctrl+backtick)
|
||||
keySOH: "ctrl+a",
|
||||
keySTX: "ctrl+b",
|
||||
keyETX: "ctrl+c",
|
||||
keyEOT: "ctrl+d",
|
||||
keyENQ: "ctrl+e",
|
||||
keyACK: "ctrl+f",
|
||||
keyBEL: "ctrl+g",
|
||||
keyBS: "ctrl+h",
|
||||
keyHT: "tab", // also ctrl+i
|
||||
keyLF: "ctrl+j",
|
||||
keyVT: "ctrl+k",
|
||||
keyFF: "ctrl+l",
|
||||
keyCR: "enter",
|
||||
keySO: "ctrl+n",
|
||||
keySI: "ctrl+o",
|
||||
keyDLE: "ctrl+p",
|
||||
keyDC1: "ctrl+q",
|
||||
keyDC2: "ctrl+r",
|
||||
keyDC3: "ctrl+s",
|
||||
keyDC4: "ctrl+t",
|
||||
keyNAK: "ctrl+u",
|
||||
keySYN: "ctrl+v",
|
||||
keyETB: "ctrl+w",
|
||||
keyCAN: "ctrl+x",
|
||||
keyEM: "ctrl+y",
|
||||
keySUB: "ctrl+z",
|
||||
keyESC: "esc",
|
||||
keyFS: "ctrl+\\",
|
||||
keyGS: "ctrl+]",
|
||||
keyRS: "ctrl+^",
|
||||
keyUS: "ctrl+_",
|
||||
keyDEL: "backspace",
|
||||
|
||||
// Other keys.
|
||||
KeyRunes: "runes",
|
||||
KeyUp: "up",
|
||||
KeyDown: "down",
|
||||
KeyRight: "right",
|
||||
KeySpace: " ", // for backwards compatibility
|
||||
KeyLeft: "left",
|
||||
KeyShiftTab: "shift+tab",
|
||||
KeyHome: "home",
|
||||
KeyEnd: "end",
|
||||
KeyCtrlHome: "ctrl+home",
|
||||
KeyCtrlEnd: "ctrl+end",
|
||||
KeyShiftHome: "shift+home",
|
||||
KeyShiftEnd: "shift+end",
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftHome: "ctrl+shift+home",
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftEnd: "ctrl+shift+end",
|
||||
KeyPgUp: "pgup",
|
||||
KeyPgDown: "pgdown",
|
||||
KeyCtrlPgUp: "ctrl+pgup",
|
||||
KeyCtrlPgDown: "ctrl+pgdown",
|
||||
KeyDelete: "delete",
|
||||
KeyInsert: "insert",
|
||||
KeyCtrlUp: "ctrl+up",
|
||||
KeyCtrlDown: "ctrl+down",
|
||||
KeyCtrlRight: "ctrl+right",
|
||||
KeyCtrlLeft: "ctrl+left",
|
||||
KeyShiftUp: "shift+up",
|
||||
KeyShiftDown: "shift+down",
|
||||
KeyShiftRight: "shift+right",
|
||||
KeyShiftLeft: "shift+left",
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftUp: "ctrl+shift+up",
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftDown: "ctrl+shift+down",
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftLeft: "ctrl+shift+left",
|
||||
KeyCtrlShiftRight: "ctrl+shift+right",
|
||||
KeyF1: "f1",
|
||||
KeyF2: "f2",
|
||||
KeyF3: "f3",
|
||||
KeyF4: "f4",
|
||||
KeyF5: "f5",
|
||||
KeyF6: "f6",
|
||||
KeyF7: "f7",
|
||||
KeyF8: "f8",
|
||||
KeyF9: "f9",
|
||||
KeyF10: "f10",
|
||||
KeyF11: "f11",
|
||||
KeyF12: "f12",
|
||||
KeyF13: "f13",
|
||||
KeyF14: "f14",
|
||||
KeyF15: "f15",
|
||||
KeyF16: "f16",
|
||||
KeyF17: "f17",
|
||||
KeyF18: "f18",
|
||||
KeyF19: "f19",
|
||||
KeyF20: "f20",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sequence mappings.
|
||||
var sequences = map[string]Key{
|
||||
// Arrow keys
|
||||
"\x1b[A": {Type: KeyUp},
|
||||
"\x1b[B": {Type: KeyDown},
|
||||
"\x1b[C": {Type: KeyRight},
|
||||
"\x1b[D": {Type: KeyLeft},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2A": {Type: KeyShiftUp},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2B": {Type: KeyShiftDown},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2C": {Type: KeyShiftRight},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2D": {Type: KeyShiftLeft},
|
||||
"\x1b[OA": {Type: KeyShiftUp}, // DECCKM
|
||||
"\x1b[OB": {Type: KeyShiftDown}, // DECCKM
|
||||
"\x1b[OC": {Type: KeyShiftRight}, // DECCKM
|
||||
"\x1b[OD": {Type: KeyShiftLeft}, // DECCKM
|
||||
"\x1b[a": {Type: KeyShiftUp}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[b": {Type: KeyShiftDown}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[c": {Type: KeyShiftRight}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[d": {Type: KeyShiftLeft}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3A": {Type: KeyUp, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3B": {Type: KeyDown, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3C": {Type: KeyRight, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3D": {Type: KeyLeft, Alt: true},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[1;4A": {Type: KeyShiftUp, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;4B": {Type: KeyShiftDown, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;4C": {Type: KeyShiftRight, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;4D": {Type: KeyShiftLeft, Alt: true},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[1;5A": {Type: KeyCtrlUp},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;5B": {Type: KeyCtrlDown},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;5C": {Type: KeyCtrlRight},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;5D": {Type: KeyCtrlLeft},
|
||||
"\x1b[Oa": {Type: KeyCtrlUp, Alt: true}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[Ob": {Type: KeyCtrlDown, Alt: true}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[Oc": {Type: KeyCtrlRight, Alt: true}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[Od": {Type: KeyCtrlLeft, Alt: true}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[1;6A": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftUp},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;6B": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftDown},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;6C": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftRight},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;6D": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftLeft},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;7A": {Type: KeyCtrlUp, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;7B": {Type: KeyCtrlDown, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;7C": {Type: KeyCtrlRight, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;7D": {Type: KeyCtrlLeft, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;8A": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftUp, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;8B": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftDown, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;8C": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftRight, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;8D": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftLeft, Alt: true},
|
||||
|
||||
// Miscellaneous keys
|
||||
"\x1b[Z": {Type: KeyShiftTab},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[2~": {Type: KeyInsert},
|
||||
"\x1b[3;2~": {Type: KeyInsert, Alt: true},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[3~": {Type: KeyDelete},
|
||||
"\x1b[3;3~": {Type: KeyDelete, Alt: true},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[5~": {Type: KeyPgUp},
|
||||
"\x1b[5;3~": {Type: KeyPgUp, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[5;5~": {Type: KeyCtrlPgUp},
|
||||
"\x1b[5^": {Type: KeyCtrlPgUp}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[5;7~": {Type: KeyCtrlPgUp, Alt: true},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[6~": {Type: KeyPgDown},
|
||||
"\x1b[6;3~": {Type: KeyPgDown, Alt: true},
|
||||
"\x1b[6;5~": {Type: KeyCtrlPgDown},
|
||||
"\x1b[6^": {Type: KeyCtrlPgDown}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[6;7~": {Type: KeyCtrlPgDown, Alt: true},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[1~": {Type: KeyHome},
|
||||
"\x1b[H": {Type: KeyHome}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3H": {Type: KeyHome, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;5H": {Type: KeyCtrlHome}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;7H": {Type: KeyCtrlHome, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2H": {Type: KeyShiftHome}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;4H": {Type: KeyShiftHome, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;6H": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftHome}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;8H": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftHome, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[4~": {Type: KeyEnd},
|
||||
"\x1b[F": {Type: KeyEnd}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3F": {Type: KeyEnd, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;5F": {Type: KeyCtrlEnd}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;7F": {Type: KeyCtrlEnd, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2F": {Type: KeyShiftEnd}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;4F": {Type: KeyShiftEnd, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;6F": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftEnd}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;8F": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftEnd, Alt: true}, // xterm, lxterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[7~": {Type: KeyHome}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[7^": {Type: KeyCtrlHome}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[7$": {Type: KeyShiftHome}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[7@": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftHome}, // urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[8~": {Type: KeyEnd}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[8^": {Type: KeyCtrlEnd}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[8$": {Type: KeyShiftEnd}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[8@": {Type: KeyCtrlShiftEnd}, // urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
// Function keys, Linux console
|
||||
"\x1b[[A": {Type: KeyF1}, // linux console
|
||||
"\x1b[[B": {Type: KeyF2}, // linux console
|
||||
"\x1b[[C": {Type: KeyF3}, // linux console
|
||||
"\x1b[[D": {Type: KeyF4}, // linux console
|
||||
"\x1b[[E": {Type: KeyF5}, // linux console
|
||||
|
||||
// Function keys, X11
|
||||
"\x1bOP": {Type: KeyF1}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1bOQ": {Type: KeyF2}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1bOR": {Type: KeyF3}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1bOS": {Type: KeyF4}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3P": {Type: KeyF1, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3Q": {Type: KeyF2, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3R": {Type: KeyF3, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[1;3S": {Type: KeyF4, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[11~": {Type: KeyF1}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[12~": {Type: KeyF2}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[13~": {Type: KeyF3}, // urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[14~": {Type: KeyF4}, // urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[15~": {Type: KeyF5}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[15;3~": {Type: KeyF5, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[17~": {Type: KeyF6}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[18~": {Type: KeyF7}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[19~": {Type: KeyF8}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[20~": {Type: KeyF9}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[21~": {Type: KeyF10}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[17;3~": {Type: KeyF6, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[18;3~": {Type: KeyF7, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[19;3~": {Type: KeyF8, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[20;3~": {Type: KeyF9, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[21;3~": {Type: KeyF10, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[23~": {Type: KeyF11}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[24~": {Type: KeyF12}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[23;3~": {Type: KeyF11, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[24;3~": {Type: KeyF12, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2P": {Type: KeyF13},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2Q": {Type: KeyF14},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[25~": {Type: KeyF13}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[26~": {Type: KeyF14}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[25;3~": {Type: KeyF13, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[26;3~": {Type: KeyF14, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2R": {Type: KeyF15},
|
||||
"\x1b[1;2S": {Type: KeyF16},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[28~": {Type: KeyF15}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
"\x1b[29~": {Type: KeyF16}, // vt100, xterm, also urxvt
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[28;3~": {Type: KeyF15, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
"\x1b[29;3~": {Type: KeyF16, Alt: true}, // vt100, xterm
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[15;2~": {Type: KeyF17},
|
||||
"\x1b[17;2~": {Type: KeyF18},
|
||||
"\x1b[18;2~": {Type: KeyF19},
|
||||
"\x1b[19;2~": {Type: KeyF20},
|
||||
|
||||
"\x1b[31~": {Type: KeyF17},
|
||||
"\x1b[32~": {Type: KeyF18},
|
||||
"\x1b[33~": {Type: KeyF19},
|
||||
"\x1b[34~": {Type: KeyF20},
|
||||
|
||||
// Powershell sequences.
|
||||
"\x1bOA": {Type: KeyUp, Alt: false},
|
||||
"\x1bOB": {Type: KeyDown, Alt: false},
|
||||
"\x1bOC": {Type: KeyRight, Alt: false},
|
||||
"\x1bOD": {Type: KeyLeft, Alt: false},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unknownInputByteMsg is reported by the input reader when an invalid
|
||||
// utf-8 byte is detected on the input. Currently, it is not handled
|
||||
// further by bubbletea. However, having this event makes it possible
|
||||
// to troubleshoot invalid inputs.
|
||||
type unknownInputByteMsg byte
|
||||
|
||||
func (u unknownInputByteMsg) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("?%#02x?", int(u))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unknownCSISequenceMsg is reported by the input reader when an
|
||||
// unrecognized CSI sequence is detected on the input. Currently, it
|
||||
// is not handled further by bubbletea. However, having this event
|
||||
// makes it possible to troubleshoot invalid inputs.
|
||||
type unknownCSISequenceMsg []byte
|
||||
|
||||
func (u unknownCSISequenceMsg) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("?CSI%+v?", []byte(u)[2:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var spaceRunes = []rune{' '}
|
||||
|
||||
// readAnsiInputs reads keypress and mouse inputs from a TTY and produces messages
|
||||
// containing information about the key or mouse events accordingly.
|
||||
func readAnsiInputs(ctx context.Context, msgs chan<- Msg, input io.Reader) error {
|
||||
var buf [256]byte
|
||||
|
||||
var leftOverFromPrevIteration []byte
|
||||
loop:
|
||||
for {
|
||||
// Read and block.
|
||||
numBytes, err := input.Read(buf[:])
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error reading input: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
b := buf[:numBytes]
|
||||
if leftOverFromPrevIteration != nil {
|
||||
b = append(leftOverFromPrevIteration, b...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If we had a short read (numBytes < len(buf)), we're sure that
|
||||
// the end of this read is an event boundary, so there is no doubt
|
||||
// if we are encountering the end of the buffer while parsing a message.
|
||||
// However, if we've succeeded in filling up the buffer, there may
|
||||
// be more data in the OS buffer ready to be read in, to complete
|
||||
// the last message in the input. In that case, we will retry with
|
||||
// the left over data in the next iteration.
|
||||
canHaveMoreData := numBytes == len(buf)
|
||||
|
||||
var i, w int
|
||||
for i, w = 0, 0; i < len(b); i += w {
|
||||
var msg Msg
|
||||
w, msg = detectOneMsg(b[i:], canHaveMoreData)
|
||||
if w == 0 {
|
||||
// Expecting more bytes beyond the current buffer. Try waiting
|
||||
// for more input.
|
||||
leftOverFromPrevIteration = make([]byte, 0, len(b[i:])+len(buf))
|
||||
leftOverFromPrevIteration = append(leftOverFromPrevIteration, b[i:]...)
|
||||
continue loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case msgs <- msg:
|
||||
case <-ctx.Done():
|
||||
err := ctx.Err()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
err = fmt.Errorf("found context error while reading input: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
leftOverFromPrevIteration = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
unknownCSIRe = regexp.MustCompile(`^\x1b\[[\x30-\x3f]*[\x20-\x2f]*[\x40-\x7e]`)
|
||||
mouseSGRRegex = regexp.MustCompile(`(\d+);(\d+);(\d+)([Mm])`)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func detectOneMsg(b []byte, canHaveMoreData bool) (w int, msg Msg) {
|
||||
// Detect mouse events.
|
||||
// X10 mouse events have a length of 6 bytes
|
||||
const mouseEventX10Len = 6
|
||||
if len(b) >= mouseEventX10Len && b[0] == '\x1b' && b[1] == '[' {
|
||||
switch b[2] {
|
||||
case 'M':
|
||||
return mouseEventX10Len, MouseMsg(parseX10MouseEvent(b))
|
||||
case '<':
|
||||
if matchIndices := mouseSGRRegex.FindSubmatchIndex(b[3:]); matchIndices != nil {
|
||||
// SGR mouse events length is the length of the match plus the length of the escape sequence
|
||||
mouseEventSGRLen := matchIndices[1] + 3 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
return mouseEventSGRLen, MouseMsg(parseSGRMouseEvent(b))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Detect bracketed paste.
|
||||
var foundbp bool
|
||||
foundbp, w, msg = detectBracketedPaste(b)
|
||||
if foundbp {
|
||||
return w, msg
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Detect escape sequence and control characters other than NUL,
|
||||
// possibly with an escape character in front to mark the Alt
|
||||
// modifier.
|
||||
var foundSeq bool
|
||||
foundSeq, w, msg = detectSequence(b)
|
||||
if foundSeq {
|
||||
return w, msg
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// No non-NUL control character or escape sequence.
|
||||
// If we are seeing at least an escape character, remember it for later below.
|
||||
alt := false
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
if b[0] == '\x1b' {
|
||||
alt = true
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Are we seeing a standalone NUL? This is not handled by detectSequence().
|
||||
if i < len(b) && b[i] == 0 {
|
||||
return i + 1, KeyMsg{Type: keyNUL, Alt: alt}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the longest sequence of runes that are not control
|
||||
// characters from this point.
|
||||
var runes []rune
|
||||
for rw := 0; i < len(b); i += rw {
|
||||
var r rune
|
||||
r, rw = utf8.DecodeRune(b[i:])
|
||||
if r == utf8.RuneError || r <= rune(keyUS) || r == rune(keyDEL) || r == ' ' {
|
||||
// Rune errors are handled below; control characters and spaces will
|
||||
// be handled by detectSequence in the next call to detectOneMsg.
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
runes = append(runes, r)
|
||||
if alt {
|
||||
// We only support a single rune after an escape alt modifier.
|
||||
i += rw
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= len(b) && canHaveMoreData {
|
||||
// We have encountered the end of the input buffer. Alas, we can't
|
||||
// be sure whether the data in the remainder of the buffer is
|
||||
// complete (maybe there was a short read). Instead of sending anything
|
||||
// dumb to the message channel, do a short read. The outer loop will
|
||||
// handle this case by extending the buffer as necessary.
|
||||
return 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If we found at least one rune, we report the bunch of them as
|
||||
// a single KeyRunes or KeySpace event.
|
||||
if len(runes) > 0 {
|
||||
k := Key{Type: KeyRunes, Runes: runes, Alt: alt}
|
||||
if len(runes) == 1 && runes[0] == ' ' {
|
||||
k.Type = KeySpace
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i, KeyMsg(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We didn't find an escape sequence, nor a valid rune. Was this a
|
||||
// lone escape character at the end of the input?
|
||||
if alt && len(b) == 1 {
|
||||
return 1, KeyMsg(Key{Type: KeyEscape})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The character at the current position is neither an escape
|
||||
// sequence, a valid rune start or a sole escape character. Report
|
||||
// it as an invalid byte.
|
||||
return 1, unknownInputByteMsg(b[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
13
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
13
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
//go:build !windows
|
||||
// +build !windows
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func readInputs(ctx context.Context, msgs chan<- Msg, input io.Reader) error {
|
||||
return readAnsiInputs(ctx, msgs, input)
|
||||
}
|
||||
119
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key_sequences.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
119
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key_sequences.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// extSequences is used by the map-based algorithm below. It contains
|
||||
// the sequences plus their alternatives with an escape character
|
||||
// prefixed, plus the control chars, plus the space.
|
||||
// It does not contain the NUL character, which is handled specially
|
||||
// by detectOneMsg.
|
||||
var extSequences = func() map[string]Key {
|
||||
s := map[string]Key{}
|
||||
for seq, key := range sequences {
|
||||
key := key
|
||||
s[seq] = key
|
||||
if !key.Alt {
|
||||
key.Alt = true
|
||||
s["\x1b"+seq] = key
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := keyNUL + 1; i <= keyDEL; i++ {
|
||||
if i == keyESC {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
s[string([]byte{byte(i)})] = Key{Type: i}
|
||||
s[string([]byte{'\x1b', byte(i)})] = Key{Type: i, Alt: true}
|
||||
if i == keyUS {
|
||||
i = keyDEL - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s[" "] = Key{Type: KeySpace, Runes: spaceRunes}
|
||||
s["\x1b "] = Key{Type: KeySpace, Alt: true, Runes: spaceRunes}
|
||||
s["\x1b\x1b"] = Key{Type: KeyEscape, Alt: true}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
// seqLengths is the sizes of valid sequences, starting with the
|
||||
// largest size.
|
||||
var seqLengths = func() []int {
|
||||
sizes := map[int]struct{}{}
|
||||
for seq := range extSequences {
|
||||
sizes[len(seq)] = struct{}{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
lsizes := make([]int, 0, len(sizes))
|
||||
for sz := range sizes {
|
||||
lsizes = append(lsizes, sz)
|
||||
}
|
||||
sort.Slice(lsizes, func(i, j int) bool { return lsizes[i] > lsizes[j] })
|
||||
return lsizes
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
// detectSequence uses a longest prefix match over the input
|
||||
// sequence and a hash map.
|
||||
func detectSequence(input []byte) (hasSeq bool, width int, msg Msg) {
|
||||
seqs := extSequences
|
||||
for _, sz := range seqLengths {
|
||||
if sz > len(input) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
prefix := input[:sz]
|
||||
key, ok := seqs[string(prefix)]
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
return true, sz, KeyMsg(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Is this an unknown CSI sequence?
|
||||
if loc := unknownCSIRe.FindIndex(input); loc != nil {
|
||||
return true, loc[1], unknownCSISequenceMsg(input[:loc[1]])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// detectBracketedPaste detects an input pasted while bracketed
|
||||
// paste mode was enabled.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: this function is a no-op if bracketed paste was not enabled
|
||||
// on the terminal, since in that case we'd never see this
|
||||
// particular escape sequence.
|
||||
func detectBracketedPaste(input []byte) (hasBp bool, width int, msg Msg) {
|
||||
// Detect the start sequence.
|
||||
const bpStart = "\x1b[200~"
|
||||
if len(input) < len(bpStart) || string(input[:len(bpStart)]) != bpStart {
|
||||
return false, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Skip over the start sequence.
|
||||
input = input[len(bpStart):]
|
||||
|
||||
// If we saw the start sequence, then we must have an end sequence
|
||||
// as well. Find it.
|
||||
const bpEnd = "\x1b[201~"
|
||||
idx := bytes.Index(input, []byte(bpEnd))
|
||||
inputLen := len(bpStart) + idx + len(bpEnd)
|
||||
if idx == -1 {
|
||||
// We have encountered the end of the input buffer without seeing
|
||||
// the marker for the end of the bracketed paste.
|
||||
// Tell the outer loop we have done a short read and we want more.
|
||||
return true, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The paste is everything in-between.
|
||||
paste := input[:idx]
|
||||
|
||||
// All there is in-between is runes, not to be interpreted further.
|
||||
k := Key{Type: KeyRunes, Paste: true}
|
||||
for len(paste) > 0 {
|
||||
r, w := utf8.DecodeRune(paste)
|
||||
if r != utf8.RuneError {
|
||||
k.Runes = append(k.Runes, r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
paste = paste[w:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true, inputLen, KeyMsg(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
351
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
351
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/key_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,351 @@
|
||||
//go:build windows
|
||||
// +build windows
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/erikgeiser/coninput"
|
||||
localereader "github.com/mattn/go-localereader"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/sys/windows"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func readInputs(ctx context.Context, msgs chan<- Msg, input io.Reader) error {
|
||||
if coninReader, ok := input.(*conInputReader); ok {
|
||||
return readConInputs(ctx, msgs, coninReader.conin)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return readAnsiInputs(ctx, msgs, localereader.NewReader(input))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readConInputs(ctx context.Context, msgsch chan<- Msg, con windows.Handle) error {
|
||||
var ps coninput.ButtonState // keep track of previous mouse state
|
||||
var ws coninput.WindowBufferSizeEventRecord // keep track of the last window size event
|
||||
for {
|
||||
events, err := coninput.ReadNConsoleInputs(con, 16)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("read coninput events: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, event := range events {
|
||||
var msgs []Msg
|
||||
switch e := event.Unwrap().(type) {
|
||||
case coninput.KeyEventRecord:
|
||||
if !e.KeyDown || e.VirtualKeyCode == coninput.VK_SHIFT {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < int(e.RepeatCount); i++ {
|
||||
eventKeyType := keyType(e)
|
||||
var runes []rune
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the character only if the key type is an actual character and not a control sequence.
|
||||
// This mimics the behavior in readAnsiInputs where the character is also removed.
|
||||
// We don't need to handle KeySpace here. See the comment in keyType().
|
||||
if eventKeyType == KeyRunes {
|
||||
runes = []rune{e.Char}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
msgs = append(msgs, KeyMsg{
|
||||
Type: eventKeyType,
|
||||
Runes: runes,
|
||||
Alt: e.ControlKeyState.Contains(coninput.LEFT_ALT_PRESSED | coninput.RIGHT_ALT_PRESSED),
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.WindowBufferSizeEventRecord:
|
||||
if e != ws {
|
||||
ws = e
|
||||
msgs = append(msgs, WindowSizeMsg{
|
||||
Width: int(e.Size.X),
|
||||
Height: int(e.Size.Y),
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.MouseEventRecord:
|
||||
event := mouseEvent(ps, e)
|
||||
if event.Type != MouseUnknown {
|
||||
msgs = append(msgs, event)
|
||||
}
|
||||
ps = e.ButtonState
|
||||
case coninput.FocusEventRecord, coninput.MenuEventRecord:
|
||||
// ignore
|
||||
default: // unknown event
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Send all messages to the channel
|
||||
for _, msg := range msgs {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case msgsch <- msg:
|
||||
case <-ctx.Done():
|
||||
err := ctx.Err()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("coninput context error: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func mouseEventButton(p, s coninput.ButtonState) (button MouseButton, action MouseAction) {
|
||||
btn := p ^ s
|
||||
action = MouseActionPress
|
||||
if btn&s == 0 {
|
||||
action = MouseActionRelease
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if btn == 0 {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case s&coninput.FROM_LEFT_1ST_BUTTON_PRESSED > 0:
|
||||
button = MouseButtonLeft
|
||||
case s&coninput.FROM_LEFT_2ND_BUTTON_PRESSED > 0:
|
||||
button = MouseButtonMiddle
|
||||
case s&coninput.RIGHTMOST_BUTTON_PRESSED > 0:
|
||||
button = MouseButtonRight
|
||||
case s&coninput.FROM_LEFT_3RD_BUTTON_PRESSED > 0:
|
||||
button = MouseButtonBackward
|
||||
case s&coninput.FROM_LEFT_4TH_BUTTON_PRESSED > 0:
|
||||
button = MouseButtonForward
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case btn == coninput.FROM_LEFT_1ST_BUTTON_PRESSED: // left button
|
||||
button = MouseButtonLeft
|
||||
case btn == coninput.RIGHTMOST_BUTTON_PRESSED: // right button
|
||||
button = MouseButtonRight
|
||||
case btn == coninput.FROM_LEFT_2ND_BUTTON_PRESSED: // middle button
|
||||
button = MouseButtonMiddle
|
||||
case btn == coninput.FROM_LEFT_3RD_BUTTON_PRESSED: // unknown (possibly mouse backward)
|
||||
button = MouseButtonBackward
|
||||
case btn == coninput.FROM_LEFT_4TH_BUTTON_PRESSED: // unknown (possibly mouse forward)
|
||||
button = MouseButtonForward
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return button, action
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func mouseEvent(p coninput.ButtonState, e coninput.MouseEventRecord) MouseMsg {
|
||||
ev := MouseMsg{
|
||||
X: int(e.MousePositon.X),
|
||||
Y: int(e.MousePositon.Y),
|
||||
Alt: e.ControlKeyState.Contains(coninput.LEFT_ALT_PRESSED | coninput.RIGHT_ALT_PRESSED),
|
||||
Ctrl: e.ControlKeyState.Contains(coninput.LEFT_CTRL_PRESSED | coninput.RIGHT_CTRL_PRESSED),
|
||||
Shift: e.ControlKeyState.Contains(coninput.SHIFT_PRESSED),
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch e.EventFlags {
|
||||
case coninput.CLICK, coninput.DOUBLE_CLICK:
|
||||
ev.Button, ev.Action = mouseEventButton(p, e.ButtonState)
|
||||
if ev.Action == MouseActionRelease {
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseRelease
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch ev.Button {
|
||||
case MouseButtonLeft:
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseLeft
|
||||
case MouseButtonMiddle:
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseMiddle
|
||||
case MouseButtonRight:
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseRight
|
||||
case MouseButtonBackward:
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseBackward
|
||||
case MouseButtonForward:
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseForward
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.MOUSE_WHEELED:
|
||||
if e.WheelDirection > 0 {
|
||||
ev.Button = MouseButtonWheelUp
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseWheelUp
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ev.Button = MouseButtonWheelDown
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseWheelDown
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.MOUSE_HWHEELED:
|
||||
if e.WheelDirection > 0 {
|
||||
ev.Button = MouseButtonWheelRight
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseWheelRight
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ev.Button = MouseButtonWheelLeft
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseWheelLeft
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.MOUSE_MOVED:
|
||||
ev.Button, _ = mouseEventButton(p, e.ButtonState)
|
||||
ev.Action = MouseActionMotion
|
||||
ev.Type = MouseMotion
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ev
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func keyType(e coninput.KeyEventRecord) KeyType {
|
||||
code := e.VirtualKeyCode
|
||||
|
||||
shiftPressed := e.ControlKeyState.Contains(coninput.SHIFT_PRESSED)
|
||||
ctrlPressed := e.ControlKeyState.Contains(coninput.LEFT_CTRL_PRESSED | coninput.RIGHT_CTRL_PRESSED)
|
||||
|
||||
switch code {
|
||||
case coninput.VK_RETURN:
|
||||
return KeyEnter
|
||||
case coninput.VK_BACK:
|
||||
return KeyBackspace
|
||||
case coninput.VK_TAB:
|
||||
if shiftPressed {
|
||||
return KeyShiftTab
|
||||
}
|
||||
return KeyTab
|
||||
case coninput.VK_SPACE:
|
||||
return KeyRunes // this could be KeySpace but on unix space also produces KeyRunes
|
||||
case coninput.VK_ESCAPE:
|
||||
return KeyEscape
|
||||
case coninput.VK_UP:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case shiftPressed && ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlShiftUp
|
||||
case shiftPressed:
|
||||
return KeyShiftUp
|
||||
case ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlUp
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return KeyUp
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.VK_DOWN:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case shiftPressed && ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlShiftDown
|
||||
case shiftPressed:
|
||||
return KeyShiftDown
|
||||
case ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlDown
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return KeyDown
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.VK_RIGHT:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case shiftPressed && ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlShiftRight
|
||||
case shiftPressed:
|
||||
return KeyShiftRight
|
||||
case ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlRight
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return KeyRight
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.VK_LEFT:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case shiftPressed && ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlShiftLeft
|
||||
case shiftPressed:
|
||||
return KeyShiftLeft
|
||||
case ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlLeft
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return KeyLeft
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.VK_HOME:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case shiftPressed && ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlShiftHome
|
||||
case shiftPressed:
|
||||
return KeyShiftHome
|
||||
case ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlHome
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return KeyHome
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.VK_END:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case shiftPressed && ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlShiftEnd
|
||||
case shiftPressed:
|
||||
return KeyShiftEnd
|
||||
case ctrlPressed:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlEnd
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return KeyEnd
|
||||
}
|
||||
case coninput.VK_PRIOR:
|
||||
return KeyPgUp
|
||||
case coninput.VK_NEXT:
|
||||
return KeyPgDown
|
||||
case coninput.VK_DELETE:
|
||||
return KeyDelete
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if e.ControlKeyState&(coninput.LEFT_CTRL_PRESSED|coninput.RIGHT_CTRL_PRESSED) == 0 {
|
||||
return KeyRunes
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch e.Char {
|
||||
case '@':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlAt
|
||||
case '\x01':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlA
|
||||
case '\x02':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlB
|
||||
case '\x03':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlC
|
||||
case '\x04':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlD
|
||||
case '\x05':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlE
|
||||
case '\x06':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlF
|
||||
case '\a':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlG
|
||||
case '\b':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlH
|
||||
case '\t':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlI
|
||||
case '\n':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlJ
|
||||
case '\v':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlK
|
||||
case '\f':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlL
|
||||
case '\r':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlM
|
||||
case '\x0e':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlN
|
||||
case '\x0f':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlO
|
||||
case '\x10':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlP
|
||||
case '\x11':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlQ
|
||||
case '\x12':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlR
|
||||
case '\x13':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlS
|
||||
case '\x14':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlT
|
||||
case '\x15':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlU
|
||||
case '\x16':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlV
|
||||
case '\x17':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlW
|
||||
case '\x18':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlX
|
||||
case '\x19':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlY
|
||||
case '\x1a':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlZ
|
||||
case '\x1b':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlCloseBracket
|
||||
case '\x1c':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlBackslash
|
||||
case '\x1f':
|
||||
return KeyCtrlUnderscore
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch code {
|
||||
case coninput.VK_OEM_4:
|
||||
return KeyCtrlOpenBracket
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return KeyRunes
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
53
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/logging.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
53
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/logging.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// LogToFile sets up default logging to log to a file. This is helpful as we
|
||||
// can't print to the terminal since our TUI is occupying it. If the file
|
||||
// doesn't exist it will be created.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Don't forget to close the file when you're done with it.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// f, err := LogToFile("debug.log", "debug")
|
||||
// if err != nil {
|
||||
// fmt.Println("fatal:", err)
|
||||
// os.Exit(1)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// defer f.Close()
|
||||
func LogToFile(path string, prefix string) (*os.File, error) {
|
||||
return LogToFileWith(path, prefix, log.Default())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LogOptionsSetter is an interface implemented by stdlib's log and charm's log
|
||||
// libraries.
|
||||
type LogOptionsSetter interface {
|
||||
SetOutput(io.Writer)
|
||||
SetPrefix(string)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LogToFileWith does allows to call LogToFile with a custom LogOptionsSetter.
|
||||
func LogToFileWith(path string, prefix string, log LogOptionsSetter) (*os.File, error) {
|
||||
f, err := os.OpenFile(path, os.O_WRONLY|os.O_CREATE|os.O_APPEND, 0o600) //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error opening file for logging: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
log.SetOutput(f)
|
||||
|
||||
// Add a space after the prefix if a prefix is being specified and it
|
||||
// doesn't already have a trailing space.
|
||||
if len(prefix) > 0 {
|
||||
finalChar := prefix[len(prefix)-1]
|
||||
if !unicode.IsSpace(rune(finalChar)) {
|
||||
prefix += " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
log.SetPrefix(prefix)
|
||||
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
308
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/mouse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
308
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/mouse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,308 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// MouseMsg contains information about a mouse event and are sent to a programs
|
||||
// update function when mouse activity occurs. Note that the mouse must first
|
||||
// be enabled in order for the mouse events to be received.
|
||||
type MouseMsg MouseEvent
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of a mouse event.
|
||||
func (m MouseMsg) String() string {
|
||||
return MouseEvent(m).String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MouseEvent represents a mouse event, which could be a click, a scroll wheel
|
||||
// movement, a cursor movement, or a combination.
|
||||
type MouseEvent struct {
|
||||
X int
|
||||
Y int
|
||||
Shift bool
|
||||
Alt bool
|
||||
Ctrl bool
|
||||
Action MouseAction
|
||||
Button MouseButton
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use MouseAction & MouseButton instead.
|
||||
Type MouseEventType
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsWheel returns true if the mouse event is a wheel event.
|
||||
func (m MouseEvent) IsWheel() bool {
|
||||
return m.Button == MouseButtonWheelUp || m.Button == MouseButtonWheelDown ||
|
||||
m.Button == MouseButtonWheelLeft || m.Button == MouseButtonWheelRight
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of a mouse event.
|
||||
func (m MouseEvent) String() (s string) {
|
||||
if m.Ctrl {
|
||||
s += "ctrl+"
|
||||
}
|
||||
if m.Alt {
|
||||
s += "alt+"
|
||||
}
|
||||
if m.Shift {
|
||||
s += "shift+"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if m.Button == MouseButtonNone { //nolint:nestif
|
||||
if m.Action == MouseActionMotion || m.Action == MouseActionRelease {
|
||||
s += mouseActions[m.Action]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s += "unknown"
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if m.IsWheel() {
|
||||
s += mouseButtons[m.Button]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
btn := mouseButtons[m.Button]
|
||||
if btn != "" {
|
||||
s += btn
|
||||
}
|
||||
act := mouseActions[m.Action]
|
||||
if act != "" {
|
||||
s += " " + act
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MouseAction represents the action that occurred during a mouse event.
|
||||
type MouseAction int
|
||||
|
||||
// Mouse event actions.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseActionPress MouseAction = iota
|
||||
MouseActionRelease
|
||||
MouseActionMotion
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var mouseActions = map[MouseAction]string{
|
||||
MouseActionPress: "press",
|
||||
MouseActionRelease: "release",
|
||||
MouseActionMotion: "motion",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MouseButton represents the button that was pressed during a mouse event.
|
||||
type MouseButton int
|
||||
|
||||
// Mouse event buttons
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is based on X11 mouse button codes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1 = left button
|
||||
// 2 = middle button (pressing the scroll wheel)
|
||||
// 3 = right button
|
||||
// 4 = turn scroll wheel up
|
||||
// 5 = turn scroll wheel down
|
||||
// 6 = push scroll wheel left
|
||||
// 7 = push scroll wheel right
|
||||
// 8 = 4th button (aka browser backward button)
|
||||
// 9 = 5th button (aka browser forward button)
|
||||
// 10
|
||||
// 11
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Other buttons are not supported.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseButtonNone MouseButton = iota
|
||||
MouseButtonLeft
|
||||
MouseButtonMiddle
|
||||
MouseButtonRight
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelUp
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelDown
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelLeft
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelRight
|
||||
MouseButtonBackward
|
||||
MouseButtonForward
|
||||
MouseButton10
|
||||
MouseButton11
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var mouseButtons = map[MouseButton]string{
|
||||
MouseButtonNone: "none",
|
||||
MouseButtonLeft: "left",
|
||||
MouseButtonMiddle: "middle",
|
||||
MouseButtonRight: "right",
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelUp: "wheel up",
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelDown: "wheel down",
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelLeft: "wheel left",
|
||||
MouseButtonWheelRight: "wheel right",
|
||||
MouseButtonBackward: "backward",
|
||||
MouseButtonForward: "forward",
|
||||
MouseButton10: "button 10",
|
||||
MouseButton11: "button 11",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MouseEventType indicates the type of mouse event occurring.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use MouseAction & MouseButton instead.
|
||||
type MouseEventType int
|
||||
|
||||
// Mouse event types.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use MouseAction & MouseButton instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseUnknown MouseEventType = iota
|
||||
MouseLeft
|
||||
MouseRight
|
||||
MouseMiddle
|
||||
MouseRelease // mouse button release (X10 only)
|
||||
MouseWheelUp
|
||||
MouseWheelDown
|
||||
MouseWheelLeft
|
||||
MouseWheelRight
|
||||
MouseBackward
|
||||
MouseForward
|
||||
MouseMotion
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse SGR-encoded mouse events; SGR extended mouse events. SGR mouse events
|
||||
// look like:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC [ < Cb ; Cx ; Cy (M or m)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// where:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Cb is the encoded button code
|
||||
// Cx is the x-coordinate of the mouse
|
||||
// Cy is the y-coordinate of the mouse
|
||||
// M is for button press, m is for button release
|
||||
//
|
||||
// https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Extended-coordinates
|
||||
func parseSGRMouseEvent(buf []byte) MouseEvent {
|
||||
str := string(buf[3:])
|
||||
matches := mouseSGRRegex.FindStringSubmatch(str)
|
||||
if len(matches) != 5 { //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
// Unreachable, we already checked the regex in `detectOneMsg`.
|
||||
panic("invalid mouse event")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b, _ := strconv.Atoi(matches[1])
|
||||
px := matches[2]
|
||||
py := matches[3]
|
||||
release := matches[4] == "m"
|
||||
m := parseMouseButton(b, true)
|
||||
|
||||
// Wheel buttons don't have release events
|
||||
// Motion can be reported as a release event in some terminals (Windows Terminal)
|
||||
if m.Action != MouseActionMotion && !m.IsWheel() && release {
|
||||
m.Action = MouseActionRelease
|
||||
m.Type = MouseRelease
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
x, _ := strconv.Atoi(px)
|
||||
y, _ := strconv.Atoi(py)
|
||||
|
||||
// (1,1) is the upper left. We subtract 1 to normalize it to (0,0).
|
||||
m.X = x - 1
|
||||
m.Y = y - 1
|
||||
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const x10MouseByteOffset = 32
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse X10-encoded mouse events; the simplest kind. The last release of X10
|
||||
// was December 1986, by the way. The original X10 mouse protocol limits the Cx
|
||||
// and Cy coordinates to 223 (=255-032).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// X10 mouse events look like:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC [M Cb Cx Cy
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: http://www.xfree86.org/current/ctlseqs.html#Mouse%20Tracking
|
||||
func parseX10MouseEvent(buf []byte) MouseEvent {
|
||||
v := buf[3:6]
|
||||
m := parseMouseButton(int(v[0]), false)
|
||||
|
||||
// (1,1) is the upper left. We subtract 1 to normalize it to (0,0).
|
||||
m.X = int(v[1]) - x10MouseByteOffset - 1
|
||||
m.Y = int(v[2]) - x10MouseByteOffset - 1
|
||||
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Extended-coordinates
|
||||
func parseMouseButton(b int, isSGR bool) MouseEvent {
|
||||
var m MouseEvent
|
||||
e := b
|
||||
if !isSGR {
|
||||
e -= x10MouseByteOffset
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
bitShift = 0b0000_0100
|
||||
bitAlt = 0b0000_1000
|
||||
bitCtrl = 0b0001_0000
|
||||
bitMotion = 0b0010_0000
|
||||
bitWheel = 0b0100_0000
|
||||
bitAdd = 0b1000_0000 // additional buttons 8-11
|
||||
|
||||
bitsMask = 0b0000_0011
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if e&bitAdd != 0 {
|
||||
m.Button = MouseButtonBackward + MouseButton(e&bitsMask)
|
||||
} else if e&bitWheel != 0 {
|
||||
m.Button = MouseButtonWheelUp + MouseButton(e&bitsMask)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
m.Button = MouseButtonLeft + MouseButton(e&bitsMask)
|
||||
// X10 reports a button release as 0b0000_0011 (3)
|
||||
if e&bitsMask == bitsMask {
|
||||
m.Action = MouseActionRelease
|
||||
m.Button = MouseButtonNone
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Motion bit doesn't get reported for wheel events.
|
||||
if e&bitMotion != 0 && !m.IsWheel() {
|
||||
m.Action = MouseActionMotion
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Modifiers
|
||||
m.Alt = e&bitAlt != 0
|
||||
m.Ctrl = e&bitCtrl != 0
|
||||
m.Shift = e&bitShift != 0
|
||||
|
||||
// backward compatibility
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonLeft && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseLeft
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonMiddle && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseMiddle
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonRight && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseRight
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonNone && m.Action == MouseActionRelease:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseRelease
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonWheelUp && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseWheelUp
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonWheelDown && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseWheelDown
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonWheelLeft && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseWheelLeft
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonWheelRight && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseWheelRight
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonBackward && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseBackward
|
||||
case m.Button == MouseButtonForward && m.Action == MouseActionPress:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseForward
|
||||
case m.Action == MouseActionMotion:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseMotion
|
||||
switch m.Button { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case MouseButtonLeft:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseLeft
|
||||
case MouseButtonMiddle:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseMiddle
|
||||
case MouseButtonRight:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseRight
|
||||
case MouseButtonBackward:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseBackward
|
||||
case MouseButtonForward:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseForward
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
m.Type = MouseUnknown
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
25
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/nil_renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
25
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/nil_renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
type nilRenderer struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) start() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) stop() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) kill() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) write(_ string) {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) repaint() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) clearScreen() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) altScreen() bool { return false }
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) enterAltScreen() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) exitAltScreen() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) showCursor() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) hideCursor() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) enableMouseCellMotion() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) disableMouseCellMotion() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) enableMouseAllMotion() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) disableMouseAllMotion() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) enableBracketedPaste() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) disableBracketedPaste() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) enableMouseSGRMode() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) disableMouseSGRMode() {}
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) bracketedPasteActive() bool { return false }
|
||||
func (n nilRenderer) setWindowTitle(_ string) {}
|
||||
236
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/options.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
236
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/options.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"sync/atomic"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ProgramOption is used to set options when initializing a Program. Program can
|
||||
// accept a variable number of options.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// p := NewProgram(model, WithInput(someInput), WithOutput(someOutput))
|
||||
type ProgramOption func(*Program)
|
||||
|
||||
// WithContext lets you specify a context in which to run the Program. This is
|
||||
// useful if you want to cancel the execution from outside. When a Program gets
|
||||
// cancelled it will exit with an error ErrProgramKilled.
|
||||
func WithContext(ctx context.Context) ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.ctx = ctx
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithOutput sets the output which, by default, is stdout. In most cases you
|
||||
// won't need to use this.
|
||||
func WithOutput(output io.Writer) ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.output = output
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithInput sets the input which, by default, is stdin. In most cases you
|
||||
// won't need to use this. To disable input entirely pass nil.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// p := NewProgram(model, WithInput(nil))
|
||||
func WithInput(input io.Reader) ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.input = input
|
||||
p.inputType = customInput
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithInputTTY opens a new TTY for input (or console input device on Windows).
|
||||
func WithInputTTY() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.inputType = ttyInput
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithEnvironment sets the environment variables that the program will use.
|
||||
// This useful when the program is running in a remote session (e.g. SSH) and
|
||||
// you want to pass the environment variables from the remote session to the
|
||||
// program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var sess ssh.Session // ssh.Session is a type from the github.com/charmbracelet/ssh package
|
||||
// pty, _, _ := sess.Pty()
|
||||
// environ := append(sess.Environ(), "TERM="+pty.Term)
|
||||
// p := tea.NewProgram(model, tea.WithEnvironment(environ)
|
||||
func WithEnvironment(env []string) ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.environ = env
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithoutSignalHandler disables the signal handler that Bubble Tea sets up for
|
||||
// Programs. This is useful if you want to handle signals yourself.
|
||||
func WithoutSignalHandler() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withoutSignalHandler
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithoutCatchPanics disables the panic catching that Bubble Tea does by
|
||||
// default. If panic catching is disabled the terminal will be in a fairly
|
||||
// unusable state after a panic because Bubble Tea will not perform its usual
|
||||
// cleanup on exit.
|
||||
func WithoutCatchPanics() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withoutCatchPanics
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithoutSignals will ignore OS signals.
|
||||
// This is mainly useful for testing.
|
||||
func WithoutSignals() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
atomic.StoreUint32(&p.ignoreSignals, 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithAltScreen starts the program with the alternate screen buffer enabled
|
||||
// (i.e. the program starts in full window mode). Note that the altscreen will
|
||||
// be automatically exited when the program quits.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// p := tea.NewProgram(Model{}, tea.WithAltScreen())
|
||||
// if _, err := p.Run(); err != nil {
|
||||
// fmt.Println("Error running program:", err)
|
||||
// os.Exit(1)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To enter the altscreen once the program has already started running use the
|
||||
// EnterAltScreen command.
|
||||
func WithAltScreen() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withAltScreen
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithoutBracketedPaste starts the program with bracketed paste disabled.
|
||||
func WithoutBracketedPaste() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withoutBracketedPaste
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithMouseCellMotion starts the program with the mouse enabled in "cell
|
||||
// motion" mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Cell motion mode enables mouse click, release, and wheel events. Mouse
|
||||
// movement events are also captured if a mouse button is pressed (i.e., drag
|
||||
// events). Cell motion mode is better supported than all motion mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This will try to enable the mouse in extended mode (SGR), if that is not
|
||||
// supported by the terminal it will fall back to normal mode (X10).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To enable mouse cell motion once the program has already started running use
|
||||
// the EnableMouseCellMotion command. To disable the mouse when the program is
|
||||
// running use the DisableMouse command.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The mouse will be automatically disabled when the program exits.
|
||||
func WithMouseCellMotion() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withMouseCellMotion // set
|
||||
p.startupOptions &^= withMouseAllMotion // clear
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithMouseAllMotion starts the program with the mouse enabled in "all motion"
|
||||
// mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// EnableMouseAllMotion is a special command that enables mouse click, release,
|
||||
// wheel, and motion events, which are delivered regardless of whether a mouse
|
||||
// button is pressed, effectively enabling support for hover interactions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This will try to enable the mouse in extended mode (SGR), if that is not
|
||||
// supported by the terminal it will fall back to normal mode (X10).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Many modern terminals support this, but not all. If in doubt, use
|
||||
// EnableMouseCellMotion instead.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To enable the mouse once the program has already started running use the
|
||||
// EnableMouseAllMotion command. To disable the mouse when the program is
|
||||
// running use the DisableMouse command.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The mouse will be automatically disabled when the program exits.
|
||||
func WithMouseAllMotion() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withMouseAllMotion // set
|
||||
p.startupOptions &^= withMouseCellMotion // clear
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithoutRenderer disables the renderer. When this is set output and log
|
||||
// statements will be plainly sent to stdout (or another output if one is set)
|
||||
// without any rendering and redrawing logic. In other words, printing and
|
||||
// logging will behave the same way it would in a non-TUI commandline tool.
|
||||
// This can be useful if you want to use the Bubble Tea framework for a non-TUI
|
||||
// application, or to provide an additional non-TUI mode to your Bubble Tea
|
||||
// programs. For example, your program could behave like a daemon if output is
|
||||
// not a TTY.
|
||||
func WithoutRenderer() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.renderer = &nilRenderer{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithANSICompressor removes redundant ANSI sequences to produce potentially
|
||||
// smaller output, at the cost of some processing overhead.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This feature is provisional, and may be changed or removed in a future version
|
||||
// of this package.
|
||||
func WithANSICompressor() ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withANSICompressor
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithFilter supplies an event filter that will be invoked before Bubble Tea
|
||||
// processes a tea.Msg. The event filter can return any tea.Msg which will then
|
||||
// get handled by Bubble Tea instead of the original event. If the event filter
|
||||
// returns nil, the event will be ignored and Bubble Tea will not process it.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// As an example, this could be used to prevent a program from shutting down if
|
||||
// there are unsaved changes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func filter(m tea.Model, msg tea.Msg) tea.Msg {
|
||||
// if _, ok := msg.(tea.QuitMsg); !ok {
|
||||
// return msg
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// model := m.(myModel)
|
||||
// if model.hasChanges {
|
||||
// return nil
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// return msg
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// p := tea.NewProgram(Model{}, tea.WithFilter(filter));
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if _,err := p.Run(); err != nil {
|
||||
// fmt.Println("Error running program:", err)
|
||||
// os.Exit(1)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func WithFilter(filter func(Model, Msg) Msg) ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.filter = filter
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithFPS sets a custom maximum FPS at which the renderer should run. If
|
||||
// less than 1, the default value of 60 will be used. If over 120, the FPS
|
||||
// will be capped at 120.
|
||||
func WithFPS(fps int) ProgramOption {
|
||||
return func(p *Program) {
|
||||
p.fps = fps
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
76
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
76
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
// renderer is the interface for Bubble Tea renderers.
|
||||
type renderer interface {
|
||||
// Start the renderer.
|
||||
start()
|
||||
|
||||
// Stop the renderer, but render the final frame in the buffer, if any.
|
||||
stop()
|
||||
|
||||
// Stop the renderer without doing any final rendering.
|
||||
kill()
|
||||
|
||||
// Write a frame to the renderer. The renderer can write this data to
|
||||
// output at its discretion.
|
||||
write(string)
|
||||
|
||||
// Request a full re-render. Note that this will not trigger a render
|
||||
// immediately. Rather, this method causes the next render to be a full
|
||||
// repaint. Because of this, it's safe to call this method multiple times
|
||||
// in succession.
|
||||
repaint()
|
||||
|
||||
// Clears the terminal.
|
||||
clearScreen()
|
||||
|
||||
// Whether or not the alternate screen buffer is enabled.
|
||||
altScreen() bool
|
||||
// Enable the alternate screen buffer.
|
||||
enterAltScreen()
|
||||
// Disable the alternate screen buffer.
|
||||
exitAltScreen()
|
||||
|
||||
// Show the cursor.
|
||||
showCursor()
|
||||
// Hide the cursor.
|
||||
hideCursor()
|
||||
|
||||
// enableMouseCellMotion enables mouse click, release, wheel and motion
|
||||
// events if a mouse button is pressed (i.e., drag events).
|
||||
enableMouseCellMotion()
|
||||
|
||||
// disableMouseCellMotion disables Mouse Cell Motion tracking.
|
||||
disableMouseCellMotion()
|
||||
|
||||
// enableMouseAllMotion enables mouse click, release, wheel and motion
|
||||
// events, regardless of whether a mouse button is pressed. Many modern
|
||||
// terminals support this, but not all.
|
||||
enableMouseAllMotion()
|
||||
|
||||
// disableMouseAllMotion disables All Motion mouse tracking.
|
||||
disableMouseAllMotion()
|
||||
|
||||
// enableMouseSGRMode enables mouse extended mode (SGR).
|
||||
enableMouseSGRMode()
|
||||
|
||||
// disableMouseSGRMode disables mouse extended mode (SGR).
|
||||
disableMouseSGRMode()
|
||||
|
||||
// enableBracketedPaste enables bracketed paste, where characters
|
||||
// inside the input are not interpreted when pasted as a whole.
|
||||
enableBracketedPaste()
|
||||
|
||||
// disableBracketedPaste disables bracketed paste.
|
||||
disableBracketedPaste()
|
||||
|
||||
// bracketedPasteActive reports whether bracketed paste mode is
|
||||
// currently enabled.
|
||||
bracketedPasteActive() bool
|
||||
|
||||
// setWindowTitle sets the terminal window title.
|
||||
setWindowTitle(string)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// repaintMsg forces a full repaint.
|
||||
type repaintMsg struct{}
|
||||
228
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/screen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
228
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/screen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
// WindowSizeMsg is used to report the terminal size. It's sent to Update once
|
||||
// initially and then on every terminal resize. Note that Windows does not
|
||||
// have support for reporting when resizes occur as it does not support the
|
||||
// SIGWINCH signal.
|
||||
type WindowSizeMsg struct {
|
||||
Width int
|
||||
Height int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearScreen is a special command that tells the program to clear the screen
|
||||
// before the next update. This can be used to move the cursor to the top left
|
||||
// of the screen and clear visual clutter when the alt screen is not in use.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that it should never be necessary to call ClearScreen() for regular
|
||||
// redraws.
|
||||
func ClearScreen() Msg {
|
||||
return clearScreenMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clearScreenMsg is an internal message that signals to clear the screen.
|
||||
// You can send a clearScreenMsg with ClearScreen.
|
||||
type clearScreenMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// EnterAltScreen is a special command that tells the Bubble Tea program to
|
||||
// enter the alternate screen buffer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because commands run asynchronously, this command should not be used in your
|
||||
// model's Init function. To initialize your program with the altscreen enabled
|
||||
// use the WithAltScreen ProgramOption instead.
|
||||
func EnterAltScreen() Msg {
|
||||
return enterAltScreenMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// enterAltScreenMsg in an internal message signals that the program should
|
||||
// enter alternate screen buffer. You can send a enterAltScreenMsg with
|
||||
// EnterAltScreen.
|
||||
type enterAltScreenMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExitAltScreen is a special command that tells the Bubble Tea program to exit
|
||||
// the alternate screen buffer. This command should be used to exit the
|
||||
// alternate screen buffer while the program is running.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the alternate screen buffer will be automatically exited when the
|
||||
// program quits.
|
||||
func ExitAltScreen() Msg {
|
||||
return exitAltScreenMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// exitAltScreenMsg in an internal message signals that the program should exit
|
||||
// alternate screen buffer. You can send a exitAltScreenMsg with ExitAltScreen.
|
||||
type exitAltScreenMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableMouseCellMotion is a special command that enables mouse click,
|
||||
// release, and wheel events. Mouse movement events are also captured if
|
||||
// a mouse button is pressed (i.e., drag events).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because commands run asynchronously, this command should not be used in your
|
||||
// model's Init function. Use the WithMouseCellMotion ProgramOption instead.
|
||||
func EnableMouseCellMotion() Msg {
|
||||
return enableMouseCellMotionMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// enableMouseCellMotionMsg is a special command that signals to start
|
||||
// listening for "cell motion" type mouse events (ESC[?1002l). To send an
|
||||
// enableMouseCellMotionMsg, use the EnableMouseCellMotion command.
|
||||
type enableMouseCellMotionMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableMouseAllMotion is a special command that enables mouse click, release,
|
||||
// wheel, and motion events, which are delivered regardless of whether a mouse
|
||||
// button is pressed, effectively enabling support for hover interactions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Many modern terminals support this, but not all. If in doubt, use
|
||||
// EnableMouseCellMotion instead.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because commands run asynchronously, this command should not be used in your
|
||||
// model's Init function. Use the WithMouseAllMotion ProgramOption instead.
|
||||
func EnableMouseAllMotion() Msg {
|
||||
return enableMouseAllMotionMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// enableMouseAllMotionMsg is a special command that signals to start listening
|
||||
// for "all motion" type mouse events (ESC[?1003l). To send an
|
||||
// enableMouseAllMotionMsg, use the EnableMouseAllMotion command.
|
||||
type enableMouseAllMotionMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableMouse is a special command that stops listening for mouse events.
|
||||
func DisableMouse() Msg {
|
||||
return disableMouseMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// disableMouseMsg is an internal message that signals to stop listening
|
||||
// for mouse events. To send a disableMouseMsg, use the DisableMouse command.
|
||||
type disableMouseMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// HideCursor is a special command for manually instructing Bubble Tea to hide
|
||||
// the cursor. In some rare cases, certain operations will cause the terminal
|
||||
// to show the cursor, which is normally hidden for the duration of a Bubble
|
||||
// Tea program's lifetime. You will most likely not need to use this command.
|
||||
func HideCursor() Msg {
|
||||
return hideCursorMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hideCursorMsg is an internal command used to hide the cursor. You can send
|
||||
// this message with HideCursor.
|
||||
type hideCursorMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowCursor is a special command for manually instructing Bubble Tea to show
|
||||
// the cursor.
|
||||
func ShowCursor() Msg {
|
||||
return showCursorMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// showCursorMsg is an internal command used to show the cursor. You can send
|
||||
// this message with ShowCursor.
|
||||
type showCursorMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableBracketedPaste is a special command that tells the Bubble Tea program
|
||||
// to accept bracketed paste input.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that bracketed paste will be automatically disabled when the
|
||||
// program quits.
|
||||
func EnableBracketedPaste() Msg {
|
||||
return enableBracketedPasteMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// enableBracketedPasteMsg in an internal message signals that
|
||||
// bracketed paste should be enabled. You can send an
|
||||
// enableBracketedPasteMsg with EnableBracketedPaste.
|
||||
type enableBracketedPasteMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableBracketedPaste is a special command that tells the Bubble Tea program
|
||||
// to accept bracketed paste input.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that bracketed paste will be automatically disabled when the
|
||||
// program quits.
|
||||
func DisableBracketedPaste() Msg {
|
||||
return disableBracketedPasteMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// disableBracketedPasteMsg in an internal message signals that
|
||||
// bracketed paste should be disabled. You can send an
|
||||
// disableBracketedPasteMsg with DisableBracketedPaste.
|
||||
type disableBracketedPasteMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// EnterAltScreen enters the alternate screen buffer, which consumes the entire
|
||||
// terminal window. ExitAltScreen will return the terminal to its former state.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use the WithAltScreen ProgramOption instead.
|
||||
func (p *Program) EnterAltScreen() {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.enterAltScreen()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withAltScreen
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExitAltScreen exits the alternate screen buffer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: The altscreen will exited automatically when the program exits.
|
||||
func (p *Program) ExitAltScreen() {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.exitAltScreen()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.startupOptions &^= withAltScreen
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableMouseCellMotion enables mouse click, release, wheel and motion events
|
||||
// if a mouse button is pressed (i.e., drag events).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use the WithMouseCellMotion ProgramOption instead.
|
||||
func (p *Program) EnableMouseCellMotion() {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseCellMotion()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withMouseCellMotion
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableMouseCellMotion disables Mouse Cell Motion tracking. This will be
|
||||
// called automatically when exiting a Bubble Tea program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: The mouse will automatically be disabled when the program exits.
|
||||
func (p *Program) DisableMouseCellMotion() {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.disableMouseCellMotion()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.startupOptions &^= withMouseCellMotion
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableMouseAllMotion enables mouse click, release, wheel and motion events,
|
||||
// regardless of whether a mouse button is pressed. Many modern terminals
|
||||
// support this, but not all.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use the WithMouseAllMotion ProgramOption instead.
|
||||
func (p *Program) EnableMouseAllMotion() {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseAllMotion()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.startupOptions |= withMouseAllMotion
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableMouseAllMotion disables All Motion mouse tracking. This will be
|
||||
// called automatically when exiting a Bubble Tea program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: The mouse will automatically be disabled when the program exits.
|
||||
func (p *Program) DisableMouseAllMotion() {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.disableMouseAllMotion()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.startupOptions &^= withMouseAllMotion
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetWindowTitle sets the terminal window title.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use the SetWindowTitle command instead.
|
||||
func (p *Program) SetWindowTitle(title string) {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.setWindowTitle(title)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.startupTitle = title
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
33
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/signals_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
33
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/signals_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
//go:build darwin || dragonfly || freebsd || linux || netbsd || openbsd || solaris || aix || zos
|
||||
// +build darwin dragonfly freebsd linux netbsd openbsd solaris aix zos
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/signal"
|
||||
"syscall"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// listenForResize sends messages (or errors) when the terminal resizes.
|
||||
// Argument output should be the file descriptor for the terminal; usually
|
||||
// os.Stdout.
|
||||
func (p *Program) listenForResize(done chan struct{}) {
|
||||
sig := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
|
||||
signal.Notify(sig, syscall.SIGWINCH)
|
||||
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
signal.Stop(sig)
|
||||
close(done)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
return
|
||||
case <-sig:
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.checkResize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
10
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/signals_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
10
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/signals_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
//go:build windows
|
||||
// +build windows
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
// listenForResize is not available on windows because windows does not
|
||||
// implement syscall.SIGWINCH.
|
||||
func (p *Program) listenForResize(done chan struct{}) {
|
||||
close(done)
|
||||
}
|
||||
729
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/standard_renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
729
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/standard_renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,729 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/ansi/compressor"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// defaultFramerate specifies the maximum interval at which we should
|
||||
// update the view.
|
||||
defaultFPS = 60
|
||||
maxFPS = 120
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// standardRenderer is a framerate-based terminal renderer, updating the view
|
||||
// at a given framerate to avoid overloading the terminal emulator.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In cases where very high performance is needed the renderer can be told
|
||||
// to exclude ranges of lines, allowing them to be written to directly.
|
||||
type standardRenderer struct {
|
||||
mtx *sync.Mutex
|
||||
out io.Writer
|
||||
|
||||
buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
queuedMessageLines []string
|
||||
framerate time.Duration
|
||||
ticker *time.Ticker
|
||||
done chan struct{}
|
||||
lastRender string
|
||||
linesRendered int
|
||||
useANSICompressor bool
|
||||
once sync.Once
|
||||
|
||||
// cursor visibility state
|
||||
cursorHidden bool
|
||||
|
||||
// essentially whether or not we're using the full size of the terminal
|
||||
altScreenActive bool
|
||||
|
||||
// whether or not we're currently using bracketed paste
|
||||
bpActive bool
|
||||
|
||||
// renderer dimensions; usually the size of the window
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
|
||||
// lines explicitly set not to render
|
||||
ignoreLines map[int]struct{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newRenderer creates a new renderer. Normally you'll want to initialize it
|
||||
// with os.Stdout as the first argument.
|
||||
func newRenderer(out io.Writer, useANSICompressor bool, fps int) renderer {
|
||||
if fps < 1 {
|
||||
fps = defaultFPS
|
||||
} else if fps > maxFPS {
|
||||
fps = maxFPS
|
||||
}
|
||||
r := &standardRenderer{
|
||||
out: out,
|
||||
mtx: &sync.Mutex{},
|
||||
done: make(chan struct{}),
|
||||
framerate: time.Second / time.Duration(fps),
|
||||
useANSICompressor: useANSICompressor,
|
||||
queuedMessageLines: []string{},
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r.useANSICompressor {
|
||||
r.out = &compressor.Writer{Forward: out}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// start starts the renderer.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) start() {
|
||||
if r.ticker == nil {
|
||||
r.ticker = time.NewTicker(r.framerate)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// If the ticker already exists, it has been stopped and we need to
|
||||
// reset it.
|
||||
r.ticker.Reset(r.framerate)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Since the renderer can be restarted after a stop, we need to reset
|
||||
// the done channel and its corresponding sync.Once.
|
||||
r.once = sync.Once{}
|
||||
|
||||
go r.listen()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// stop permanently halts the renderer, rendering the final frame.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) stop() {
|
||||
// Stop the renderer before acquiring the mutex to avoid a deadlock.
|
||||
r.once.Do(func() {
|
||||
r.done <- struct{}{}
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// flush locks the mutex
|
||||
r.flush()
|
||||
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EraseEntireLine)
|
||||
// Move the cursor back to the beginning of the line
|
||||
r.execute("\r")
|
||||
|
||||
if r.useANSICompressor {
|
||||
if w, ok := r.out.(io.WriteCloser); ok {
|
||||
_ = w.Close()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// execute writes a sequence to the terminal.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) execute(seq string) {
|
||||
_, _ = io.WriteString(r.out, seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// kill halts the renderer. The final frame will not be rendered.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) kill() {
|
||||
// Stop the renderer before acquiring the mutex to avoid a deadlock.
|
||||
r.once.Do(func() {
|
||||
r.done <- struct{}{}
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EraseEntireLine)
|
||||
// Move the cursor back to the beginning of the line
|
||||
r.execute("\r")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// listen waits for ticks on the ticker, or a signal to stop the renderer.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) listen() {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-r.done:
|
||||
r.ticker.Stop()
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
case <-r.ticker.C:
|
||||
r.flush()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// flush renders the buffer.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) flush() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if r.buf.Len() == 0 || r.buf.String() == r.lastRender {
|
||||
// Nothing to do
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Output buffer
|
||||
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
|
||||
|
||||
newLines := strings.Split(r.buf.String(), "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
// If we know the output's height, we can use it to determine how many
|
||||
// lines we can render. We drop lines from the top of the render buffer if
|
||||
// necessary, as we can't navigate the cursor into the terminal's scrollback
|
||||
// buffer.
|
||||
if r.height > 0 && len(newLines) > r.height {
|
||||
newLines = newLines[len(newLines)-r.height:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
numLinesThisFlush := len(newLines)
|
||||
oldLines := strings.Split(r.lastRender, "\n")
|
||||
skipLines := make(map[int]struct{})
|
||||
flushQueuedMessages := len(r.queuedMessageLines) > 0 && !r.altScreenActive
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear any lines we painted in the last render.
|
||||
if r.linesRendered > 0 {
|
||||
for i := r.linesRendered - 1; i > 0; i-- {
|
||||
// if we are clearing queued messages, we want to clear all lines, since
|
||||
// printing messages allows for native terminal word-wrap, we
|
||||
// don't have control over the queued lines
|
||||
if flushQueuedMessages {
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.EraseEntireLine)
|
||||
} else if (len(newLines) <= len(oldLines)) && (len(newLines) > i && len(oldLines) > i) && (newLines[i] == oldLines[i]) {
|
||||
// If the number of lines we want to render hasn't increased and
|
||||
// new line is the same as the old line we can skip rendering for
|
||||
// this line as a performance optimization.
|
||||
skipLines[i] = struct{}{}
|
||||
} else if _, exists := r.ignoreLines[i]; !exists {
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.EraseEntireLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.CursorUp1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if _, exists := r.ignoreLines[0]; !exists {
|
||||
// We need to return to the start of the line here to properly
|
||||
// erase it. Going back the entire width of the terminal will
|
||||
// usually be farther than we need to go, but terminal emulators
|
||||
// will stop the cursor at the start of the line as a rule.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We use this sequence in particular because it's part of the ANSI
|
||||
// standard (whereas others are proprietary to, say, VT100/VT52).
|
||||
// If cursor previous line (ESC[ + <n> + F) were better supported
|
||||
// we could use that above to eliminate this step.
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.CursorLeft(r.width))
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.EraseEntireLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Merge the set of lines we're skipping as a rendering optimization with
|
||||
// the set of lines we've explicitly asked the renderer to ignore.
|
||||
for k, v := range r.ignoreLines {
|
||||
skipLines[k] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if flushQueuedMessages {
|
||||
// Dump the lines we've queued up for printing
|
||||
for _, line := range r.queuedMessageLines {
|
||||
_, _ = buf.WriteString(line)
|
||||
_, _ = buf.WriteString("\r\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// clear the queued message lines
|
||||
r.queuedMessageLines = []string{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint new lines
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(newLines); i++ {
|
||||
if _, skip := skipLines[i]; skip {
|
||||
// Unless this is the last line, move the cursor down.
|
||||
if i < len(newLines)-1 {
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.CursorDown1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if i == 0 && r.lastRender == "" {
|
||||
// On first render, reset the cursor to the start of the line
|
||||
// before writing anything.
|
||||
buf.WriteByte('\r')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
line := newLines[i]
|
||||
|
||||
// Truncate lines wider than the width of the window to avoid
|
||||
// wrapping, which will mess up rendering. If we don't have the
|
||||
// width of the window this will be ignored.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that on Windows we only get the width of the window on
|
||||
// program initialization, so after a resize this won't perform
|
||||
// correctly (signal SIGWINCH is not supported on Windows).
|
||||
if r.width > 0 {
|
||||
line = ansi.Truncate(line, r.width, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, _ = buf.WriteString(line)
|
||||
|
||||
if i < len(newLines)-1 {
|
||||
_, _ = buf.WriteString("\r\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.linesRendered = numLinesThisFlush
|
||||
|
||||
// Make sure the cursor is at the start of the last line to keep rendering
|
||||
// behavior consistent.
|
||||
if r.altScreenActive {
|
||||
// This case fixes a bug in macOS terminal. In other terminals the
|
||||
// other case seems to do the job regardless of whether or not we're
|
||||
// using the full terminal window.
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.MoveCursor(r.linesRendered, 0))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.CursorLeft(r.width))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, _ = r.out.Write(buf.Bytes())
|
||||
r.lastRender = r.buf.String()
|
||||
r.buf.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// write writes to the internal buffer. The buffer will be outputted via the
|
||||
// ticker which calls flush().
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) write(s string) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
r.buf.Reset()
|
||||
|
||||
// If an empty string was passed we should clear existing output and
|
||||
// rendering nothing. Rather than introduce additional state to manage
|
||||
// this, we render a single space as a simple (albeit less correct)
|
||||
// solution.
|
||||
if s == "" {
|
||||
s = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, _ = r.buf.WriteString(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) repaint() {
|
||||
r.lastRender = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) clearScreen() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EraseEntireDisplay)
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.MoveCursorOrigin)
|
||||
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) altScreen() bool {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return r.altScreenActive
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) enterAltScreen() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if r.altScreenActive {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r.altScreenActive = true
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EnableAltScreenBuffer)
|
||||
|
||||
// Ensure that the terminal is cleared, even when it doesn't support
|
||||
// alt screen (or alt screen support is disabled, like GNU screen by
|
||||
// default).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: we can't use r.clearScreen() here because the mutex is already
|
||||
// locked.
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EraseEntireDisplay)
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.MoveCursorOrigin)
|
||||
|
||||
// cmd.exe and other terminals keep separate cursor states for the AltScreen
|
||||
// and the main buffer. We have to explicitly reset the cursor visibility
|
||||
// whenever we enter AltScreen.
|
||||
if r.cursorHidden {
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.HideCursor)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.ShowCursor)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) exitAltScreen() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if !r.altScreenActive {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r.altScreenActive = false
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.DisableAltScreenBuffer)
|
||||
|
||||
// cmd.exe and other terminals keep separate cursor states for the AltScreen
|
||||
// and the main buffer. We have to explicitly reset the cursor visibility
|
||||
// whenever we exit AltScreen.
|
||||
if r.cursorHidden {
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.HideCursor)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.ShowCursor)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) showCursor() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.cursorHidden = false
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.ShowCursor)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) hideCursor() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.cursorHidden = true
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.HideCursor)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) enableMouseCellMotion() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EnableMouseCellMotion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) disableMouseCellMotion() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.DisableMouseCellMotion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) enableMouseAllMotion() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EnableMouseAllMotion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) disableMouseAllMotion() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.DisableMouseAllMotion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) enableMouseSGRMode() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EnableMouseSgrExt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) disableMouseSGRMode() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.DisableMouseSgrExt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) enableBracketedPaste() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.EnableBracketedPaste)
|
||||
r.bpActive = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) disableBracketedPaste() {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.DisableBracketedPaste)
|
||||
r.bpActive = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) bracketedPasteActive() bool {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return r.bpActive
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setWindowTitle sets the terminal window title.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) setWindowTitle(title string) {
|
||||
r.execute(ansi.SetWindowTitle(title))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setIgnoredLines specifies lines not to be touched by the standard Bubble Tea
|
||||
// renderer.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) setIgnoredLines(from int, to int) {
|
||||
// Lock if we're going to be clearing some lines since we don't want
|
||||
// anything jacking our cursor.
|
||||
if r.linesRendered > 0 {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if r.ignoreLines == nil {
|
||||
r.ignoreLines = make(map[int]struct{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := from; i < to; i++ {
|
||||
r.ignoreLines[i] = struct{}{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Erase ignored lines
|
||||
if r.linesRendered > 0 {
|
||||
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
|
||||
|
||||
for i := r.linesRendered - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if _, exists := r.ignoreLines[i]; exists {
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.EraseEntireLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.CursorUp1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.MoveCursor(r.linesRendered, 0)) // put cursor back
|
||||
_, _ = r.out.Write(buf.Bytes())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clearIgnoredLines returns control of any ignored lines to the standard
|
||||
// Bubble Tea renderer. That is, any lines previously set to be ignored can be
|
||||
// rendered to again.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) clearIgnoredLines() {
|
||||
r.ignoreLines = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// insertTop effectively scrolls up. It inserts lines at the top of a given
|
||||
// area designated to be a scrollable region, pushing everything else down.
|
||||
// This is roughly how ncurses does it.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To call this function use command ScrollUp().
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For this to work renderer.ignoreLines must be set to ignore the scrollable
|
||||
// region since we are bypassing the normal Bubble Tea renderer here.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because this method relies on the terminal dimensions, it's only valid for
|
||||
// full-window applications (generally those that use the alternate screen
|
||||
// buffer).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method bypasses the normal rendering buffer and is philosophically
|
||||
// different than the normal way we approach rendering in Bubble Tea. It's for
|
||||
// use in high-performance rendering, such as a pager that could potentially
|
||||
// be rendering very complicated ansi. In cases where the content is simpler
|
||||
// standard Bubble Tea rendering should suffice.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) insertTop(lines []string, topBoundary, bottomBoundary int) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.SetScrollingRegion(topBoundary, bottomBoundary))
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.MoveCursor(topBoundary, 0))
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.InsertLine(len(lines)))
|
||||
_, _ = buf.WriteString(strings.Join(lines, "\r\n"))
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.SetScrollingRegion(0, r.height))
|
||||
|
||||
// Move cursor back to where the main rendering routine expects it to be
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.MoveCursor(r.linesRendered, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
_, _ = r.out.Write(buf.Bytes())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// insertBottom effectively scrolls down. It inserts lines at the bottom of
|
||||
// a given area designated to be a scrollable region, pushing everything else
|
||||
// up. This is roughly how ncurses does it.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To call this function use the command ScrollDown().
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See note in insertTop() for caveats, how this function only makes sense for
|
||||
// full-window applications, and how it differs from the normal way we do
|
||||
// rendering in Bubble Tea.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) insertBottom(lines []string, topBoundary, bottomBoundary int) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.SetScrollingRegion(topBoundary, bottomBoundary))
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.MoveCursor(bottomBoundary, 0))
|
||||
_, _ = buf.WriteString("\r\n" + strings.Join(lines, "\r\n"))
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.SetScrollingRegion(0, r.height))
|
||||
|
||||
// Move cursor back to where the main rendering routine expects it to be
|
||||
buf.WriteString(ansi.MoveCursor(r.linesRendered, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
_, _ = r.out.Write(buf.Bytes())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// handleMessages handles internal messages for the renderer.
|
||||
func (r *standardRenderer) handleMessages(msg Msg) {
|
||||
switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
case repaintMsg:
|
||||
// Force a repaint by clearing the render cache as we slide into a
|
||||
// render.
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
case WindowSizeMsg:
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
r.width = msg.Width
|
||||
r.height = msg.Height
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
case clearScrollAreaMsg:
|
||||
r.clearIgnoredLines()
|
||||
|
||||
// Force a repaint on the area where the scrollable stuff was in this
|
||||
// update cycle
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
case syncScrollAreaMsg:
|
||||
// Re-render scrolling area
|
||||
r.clearIgnoredLines()
|
||||
r.setIgnoredLines(msg.topBoundary, msg.bottomBoundary)
|
||||
r.insertTop(msg.lines, msg.topBoundary, msg.bottomBoundary)
|
||||
|
||||
// Force non-scrolling stuff to repaint in this update cycle
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
case scrollUpMsg:
|
||||
r.insertTop(msg.lines, msg.topBoundary, msg.bottomBoundary)
|
||||
|
||||
case scrollDownMsg:
|
||||
r.insertBottom(msg.lines, msg.topBoundary, msg.bottomBoundary)
|
||||
|
||||
case printLineMessage:
|
||||
if !r.altScreenActive {
|
||||
lines := strings.Split(msg.messageBody, "\n")
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
r.queuedMessageLines = append(r.queuedMessageLines, lines...)
|
||||
r.repaint()
|
||||
r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HIGH-PERFORMANCE RENDERING STUFF
|
||||
|
||||
type syncScrollAreaMsg struct {
|
||||
lines []string
|
||||
topBoundary int
|
||||
bottomBoundary int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SyncScrollArea performs a paint of the entire region designated to be the
|
||||
// scrollable area. This is required to initialize the scrollable region and
|
||||
// should also be called on resize (WindowSizeMsg).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For high-performance, scroll-based rendering only.
|
||||
func SyncScrollArea(lines []string, topBoundary int, bottomBoundary int) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return syncScrollAreaMsg{
|
||||
lines: lines,
|
||||
topBoundary: topBoundary,
|
||||
bottomBoundary: bottomBoundary,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type clearScrollAreaMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearScrollArea deallocates the scrollable region and returns the control of
|
||||
// those lines to the main rendering routine.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For high-performance, scroll-based rendering only.
|
||||
func ClearScrollArea() Msg {
|
||||
return clearScrollAreaMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type scrollUpMsg struct {
|
||||
lines []string
|
||||
topBoundary int
|
||||
bottomBoundary int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollUp adds lines to the top of the scrollable region, pushing existing
|
||||
// lines below down. Lines that are pushed out the scrollable region disappear
|
||||
// from view.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For high-performance, scroll-based rendering only.
|
||||
func ScrollUp(newLines []string, topBoundary, bottomBoundary int) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return scrollUpMsg{
|
||||
lines: newLines,
|
||||
topBoundary: topBoundary,
|
||||
bottomBoundary: bottomBoundary,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type scrollDownMsg struct {
|
||||
lines []string
|
||||
topBoundary int
|
||||
bottomBoundary int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollDown adds lines to the bottom of the scrollable region, pushing
|
||||
// existing lines above up. Lines that are pushed out of the scrollable region
|
||||
// disappear from view.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For high-performance, scroll-based rendering only.
|
||||
func ScrollDown(newLines []string, topBoundary, bottomBoundary int) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return scrollDownMsg{
|
||||
lines: newLines,
|
||||
topBoundary: topBoundary,
|
||||
bottomBoundary: bottomBoundary,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type printLineMessage struct {
|
||||
messageBody string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Println prints above the Program. This output is unmanaged by the program and
|
||||
// will persist across renders by the Program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unlike fmt.Println (but similar to log.Println) the message will be print on
|
||||
// its own line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the altscreen is active no output will be printed.
|
||||
func Println(args ...interface{}) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return printLineMessage{
|
||||
messageBody: fmt.Sprint(args...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Printf prints above the Program. It takes a format template followed by
|
||||
// values similar to fmt.Printf. This output is unmanaged by the program and
|
||||
// will persist across renders by the Program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unlike fmt.Printf (but similar to log.Printf) the message will be print on
|
||||
// its own line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the altscreen is active no output will be printed.
|
||||
func Printf(template string, args ...interface{}) Cmd {
|
||||
return func() Msg {
|
||||
return printLineMessage{
|
||||
messageBody: fmt.Sprintf(template, args...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
758
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tea.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
758
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tea.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,758 @@
|
||||
// Package tea provides a framework for building rich terminal user interfaces
|
||||
// based on the paradigms of The Elm Architecture. It's well-suited for simple
|
||||
// and complex terminal applications, either inline, full-window, or a mix of
|
||||
// both. It's been battle-tested in several large projects and is
|
||||
// production-ready.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A tutorial is available at https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tree/master/tutorials
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example programs can be found at https://github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tree/master/examples
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/signal"
|
||||
"runtime/debug"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"sync/atomic"
|
||||
"syscall"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/term"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/cancelreader"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/sync/errgroup"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ErrProgramKilled is returned by [Program.Run] when the program got killed.
|
||||
var ErrProgramKilled = errors.New("program was killed")
|
||||
|
||||
// Msg contain data from the result of a IO operation. Msgs trigger the update
|
||||
// function and, henceforth, the UI.
|
||||
type Msg interface{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Model contains the program's state as well as its core functions.
|
||||
type Model interface {
|
||||
// Init is the first function that will be called. It returns an optional
|
||||
// initial command. To not perform an initial command return nil.
|
||||
Init() Cmd
|
||||
|
||||
// Update is called when a message is received. Use it to inspect messages
|
||||
// and, in response, update the model and/or send a command.
|
||||
Update(Msg) (Model, Cmd)
|
||||
|
||||
// View renders the program's UI, which is just a string. The view is
|
||||
// rendered after every Update.
|
||||
View() string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd is an IO operation that returns a message when it's complete. If it's
|
||||
// nil it's considered a no-op. Use it for things like HTTP requests, timers,
|
||||
// saving and loading from disk, and so on.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that there's almost never a reason to use a command to send a message
|
||||
// to another part of your program. That can almost always be done in the
|
||||
// update function.
|
||||
type Cmd func() Msg
|
||||
|
||||
type inputType int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
defaultInput inputType = iota
|
||||
ttyInput
|
||||
customInput
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements the stringer interface for [inputType]. It is inteded to
|
||||
// be used in testing.
|
||||
func (i inputType) String() string {
|
||||
return [...]string{
|
||||
"default input",
|
||||
"tty input",
|
||||
"custom input",
|
||||
}[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Options to customize the program during its initialization. These are
|
||||
// generally set with ProgramOptions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The options here are treated as bits.
|
||||
type startupOptions int16
|
||||
|
||||
func (s startupOptions) has(option startupOptions) bool {
|
||||
return s&option != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
withAltScreen startupOptions = 1 << iota
|
||||
withMouseCellMotion
|
||||
withMouseAllMotion
|
||||
withANSICompressor
|
||||
withoutSignalHandler
|
||||
// Catching panics is incredibly useful for restoring the terminal to a
|
||||
// usable state after a panic occurs. When this is set, Bubble Tea will
|
||||
// recover from panics, print the stack trace, and disable raw mode. This
|
||||
// feature is on by default.
|
||||
withoutCatchPanics
|
||||
withoutBracketedPaste
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// channelHandlers manages the series of channels returned by various processes.
|
||||
// It allows us to wait for those processes to terminate before exiting the
|
||||
// program.
|
||||
type channelHandlers []chan struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Adds a channel to the list of handlers. We wait for all handlers to terminate
|
||||
// gracefully on shutdown.
|
||||
func (h *channelHandlers) add(ch chan struct{}) {
|
||||
*h = append(*h, ch)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// shutdown waits for all handlers to terminate.
|
||||
func (h channelHandlers) shutdown() {
|
||||
var wg sync.WaitGroup
|
||||
for _, ch := range h {
|
||||
wg.Add(1)
|
||||
go func(ch chan struct{}) {
|
||||
<-ch
|
||||
wg.Done()
|
||||
}(ch)
|
||||
}
|
||||
wg.Wait()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Program is a terminal user interface.
|
||||
type Program struct {
|
||||
initialModel Model
|
||||
|
||||
// Configuration options that will set as the program is initializing,
|
||||
// treated as bits. These options can be set via various ProgramOptions.
|
||||
startupOptions startupOptions
|
||||
|
||||
// startupTitle is the title that will be set on the terminal when the
|
||||
// program starts.
|
||||
startupTitle string
|
||||
|
||||
inputType inputType
|
||||
|
||||
ctx context.Context
|
||||
cancel context.CancelFunc
|
||||
|
||||
msgs chan Msg
|
||||
errs chan error
|
||||
finished chan struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// where to send output, this will usually be os.Stdout.
|
||||
output io.Writer
|
||||
// ttyOutput is null if output is not a TTY.
|
||||
ttyOutput term.File
|
||||
previousOutputState *term.State
|
||||
renderer renderer
|
||||
|
||||
// the environment variables for the program, defaults to os.Environ().
|
||||
environ []string
|
||||
|
||||
// where to read inputs from, this will usually be os.Stdin.
|
||||
input io.Reader
|
||||
// ttyInput is null if input is not a TTY.
|
||||
ttyInput term.File
|
||||
previousTtyInputState *term.State
|
||||
cancelReader cancelreader.CancelReader
|
||||
readLoopDone chan struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// was the altscreen active before releasing the terminal?
|
||||
altScreenWasActive bool
|
||||
ignoreSignals uint32
|
||||
|
||||
bpWasActive bool // was the bracketed paste mode active before releasing the terminal?
|
||||
|
||||
filter func(Model, Msg) Msg
|
||||
|
||||
// fps is the frames per second we should set on the renderer, if
|
||||
// applicable,
|
||||
fps int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Quit is a special command that tells the Bubble Tea program to exit.
|
||||
func Quit() Msg {
|
||||
return QuitMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// QuitMsg signals that the program should quit. You can send a QuitMsg with
|
||||
// Quit.
|
||||
type QuitMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Suspend is a special command that tells the Bubble Tea program to suspend.
|
||||
func Suspend() Msg {
|
||||
return SuspendMsg{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SuspendMsg signals the program should suspend.
|
||||
// This usually happens when ctrl+z is pressed on common programs, but since
|
||||
// bubbletea puts the terminal in raw mode, we need to handle it in a
|
||||
// per-program basis.
|
||||
// You can send this message with Suspend.
|
||||
type SuspendMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResumeMsg can be listen to to do something once a program is resumed back
|
||||
// from a suspend state.
|
||||
type ResumeMsg struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewProgram creates a new Program.
|
||||
func NewProgram(model Model, opts ...ProgramOption) *Program {
|
||||
p := &Program{
|
||||
initialModel: model,
|
||||
msgs: make(chan Msg),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply all options to the program.
|
||||
for _, opt := range opts {
|
||||
opt(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A context can be provided with a ProgramOption, but if none was provided
|
||||
// we'll use the default background context.
|
||||
if p.ctx == nil {
|
||||
p.ctx = context.Background()
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Initialize context and teardown channel.
|
||||
p.ctx, p.cancel = context.WithCancel(p.ctx)
|
||||
|
||||
// if no output was set, set it to stdout
|
||||
if p.output == nil {
|
||||
p.output = os.Stdout
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// if no environment was set, set it to os.Environ()
|
||||
if p.environ == nil {
|
||||
p.environ = os.Environ()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Program) handleSignals() chan struct{} {
|
||||
ch := make(chan struct{})
|
||||
|
||||
// Listen for SIGINT and SIGTERM.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In most cases ^C will not send an interrupt because the terminal will be
|
||||
// in raw mode and ^C will be captured as a keystroke and sent along to
|
||||
// Program.Update as a KeyMsg. When input is not a TTY, however, ^C will be
|
||||
// caught here.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// SIGTERM is sent by unix utilities (like kill) to terminate a process.
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
sig := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
|
||||
signal.Notify(sig, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
signal.Stop(sig)
|
||||
close(ch)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
case <-sig:
|
||||
if atomic.LoadUint32(&p.ignoreSignals) == 0 {
|
||||
p.msgs <- QuitMsg{}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
return ch
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// handleResize handles terminal resize events.
|
||||
func (p *Program) handleResize() chan struct{} {
|
||||
ch := make(chan struct{})
|
||||
|
||||
if p.ttyOutput != nil {
|
||||
// Get the initial terminal size and send it to the program.
|
||||
go p.checkResize()
|
||||
|
||||
// Listen for window resizes.
|
||||
go p.listenForResize(ch)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
close(ch)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ch
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// handleCommands runs commands in a goroutine and sends the result to the
|
||||
// program's message channel.
|
||||
func (p *Program) handleCommands(cmds chan Cmd) chan struct{} {
|
||||
ch := make(chan struct{})
|
||||
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
defer close(ch)
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
case cmd := <-cmds:
|
||||
if cmd == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Don't wait on these goroutines, otherwise the shutdown
|
||||
// latency would get too large as a Cmd can run for some time
|
||||
// (e.g. tick commands that sleep for half a second). It's not
|
||||
// possible to cancel them so we'll have to leak the goroutine
|
||||
// until Cmd returns.
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
msg := cmd() // this can be long.
|
||||
p.Send(msg)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
return ch
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Program) disableMouse() {
|
||||
p.renderer.disableMouseCellMotion()
|
||||
p.renderer.disableMouseAllMotion()
|
||||
p.renderer.disableMouseSGRMode()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// eventLoop is the central message loop. It receives and handles the default
|
||||
// Bubble Tea messages, update the model and triggers redraws.
|
||||
func (p *Program) eventLoop(model Model, cmds chan Cmd) (Model, error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
return model, nil
|
||||
|
||||
case err := <-p.errs:
|
||||
return model, err
|
||||
|
||||
case msg := <-p.msgs:
|
||||
// Filter messages.
|
||||
if p.filter != nil {
|
||||
msg = p.filter(model, msg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if msg == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle special internal messages.
|
||||
switch msg := msg.(type) {
|
||||
case QuitMsg:
|
||||
return model, nil
|
||||
|
||||
case SuspendMsg:
|
||||
if suspendSupported {
|
||||
p.suspend()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case clearScreenMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.clearScreen()
|
||||
|
||||
case enterAltScreenMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.enterAltScreen()
|
||||
|
||||
case exitAltScreenMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.exitAltScreen()
|
||||
|
||||
case enableMouseCellMotionMsg, enableMouseAllMotionMsg:
|
||||
switch msg.(type) {
|
||||
case enableMouseCellMotionMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseCellMotion()
|
||||
case enableMouseAllMotionMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseAllMotion()
|
||||
}
|
||||
// mouse mode (1006) is a no-op if the terminal doesn't support it.
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseSGRMode()
|
||||
|
||||
case disableMouseMsg:
|
||||
p.disableMouse()
|
||||
|
||||
case showCursorMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.showCursor()
|
||||
|
||||
case hideCursorMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.hideCursor()
|
||||
|
||||
case enableBracketedPasteMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.enableBracketedPaste()
|
||||
|
||||
case disableBracketedPasteMsg:
|
||||
p.renderer.disableBracketedPaste()
|
||||
|
||||
case execMsg:
|
||||
// NB: this blocks.
|
||||
p.exec(msg.cmd, msg.fn)
|
||||
|
||||
case BatchMsg:
|
||||
for _, cmd := range msg {
|
||||
cmds <- cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
case sequenceMsg:
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
// Execute commands one at a time, in order.
|
||||
for _, cmd := range msg {
|
||||
if cmd == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
msg := cmd()
|
||||
if batchMsg, ok := msg.(BatchMsg); ok {
|
||||
g, _ := errgroup.WithContext(p.ctx)
|
||||
for _, cmd := range batchMsg {
|
||||
cmd := cmd
|
||||
g.Go(func() error {
|
||||
p.Send(cmd())
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//nolint:errcheck
|
||||
g.Wait() // wait for all commands from batch msg to finish
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.Send(msg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
case setWindowTitleMsg:
|
||||
p.SetWindowTitle(string(msg))
|
||||
|
||||
case windowSizeMsg:
|
||||
go p.checkResize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Process internal messages for the renderer.
|
||||
if r, ok := p.renderer.(*standardRenderer); ok {
|
||||
r.handleMessages(msg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var cmd Cmd
|
||||
model, cmd = model.Update(msg) // run update
|
||||
cmds <- cmd // process command (if any)
|
||||
p.renderer.write(model.View()) // send view to renderer
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run initializes the program and runs its event loops, blocking until it gets
|
||||
// terminated by either [Program.Quit], [Program.Kill], or its signal handler.
|
||||
// Returns the final model.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Run() (Model, error) {
|
||||
handlers := channelHandlers{}
|
||||
cmds := make(chan Cmd)
|
||||
p.errs = make(chan error)
|
||||
p.finished = make(chan struct{}, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
defer p.cancel()
|
||||
|
||||
switch p.inputType {
|
||||
case defaultInput:
|
||||
p.input = os.Stdin
|
||||
|
||||
// The user has not set a custom input, so we need to check whether or
|
||||
// not standard input is a terminal. If it's not, we open a new TTY for
|
||||
// input. This will allow things to "just work" in cases where data was
|
||||
// piped in or redirected to the application.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To disable input entirely pass nil to the [WithInput] program option.
|
||||
f, isFile := p.input.(term.File)
|
||||
if !isFile {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if term.IsTerminal(f.Fd()) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f, err := openInputTTY()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return p.initialModel, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close() //nolint:errcheck
|
||||
p.input = f
|
||||
|
||||
case ttyInput:
|
||||
// Open a new TTY, by request
|
||||
f, err := openInputTTY()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return p.initialModel, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close() //nolint:errcheck
|
||||
p.input = f
|
||||
|
||||
case customInput:
|
||||
// (There is nothing extra to do.)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle signals.
|
||||
if !p.startupOptions.has(withoutSignalHandler) {
|
||||
handlers.add(p.handleSignals())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Recover from panics.
|
||||
if !p.startupOptions.has(withoutCatchPanics) {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if r := recover(); r != nil {
|
||||
p.shutdown(true)
|
||||
fmt.Printf("Caught panic:\n\n%s\n\nRestoring terminal...\n\n", r)
|
||||
debug.PrintStack()
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If no renderer is set use the standard one.
|
||||
if p.renderer == nil {
|
||||
p.renderer = newRenderer(p.output, p.startupOptions.has(withANSICompressor), p.fps)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if output is a TTY before entering raw mode, hiding the cursor and
|
||||
// so on.
|
||||
if err := p.initTerminal(); err != nil {
|
||||
return p.initialModel, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Honor program startup options.
|
||||
if p.startupTitle != "" {
|
||||
p.renderer.setWindowTitle(p.startupTitle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.startupOptions&withAltScreen != 0 {
|
||||
p.renderer.enterAltScreen()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.startupOptions&withoutBracketedPaste == 0 {
|
||||
p.renderer.enableBracketedPaste()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.startupOptions&withMouseCellMotion != 0 {
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseCellMotion()
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseSGRMode()
|
||||
} else if p.startupOptions&withMouseAllMotion != 0 {
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseAllMotion()
|
||||
p.renderer.enableMouseSGRMode()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Start the renderer.
|
||||
p.renderer.start()
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize the program.
|
||||
model := p.initialModel
|
||||
if initCmd := model.Init(); initCmd != nil {
|
||||
ch := make(chan struct{})
|
||||
handlers.add(ch)
|
||||
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
defer close(ch)
|
||||
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case cmds <- initCmd:
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render the initial view.
|
||||
p.renderer.write(model.View())
|
||||
|
||||
// Subscribe to user input.
|
||||
if p.input != nil {
|
||||
if err := p.initCancelReader(); err != nil {
|
||||
return model, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle resize events.
|
||||
handlers.add(p.handleResize())
|
||||
|
||||
// Process commands.
|
||||
handlers.add(p.handleCommands(cmds))
|
||||
|
||||
// Run event loop, handle updates and draw.
|
||||
model, err := p.eventLoop(model, cmds)
|
||||
killed := p.ctx.Err() != nil
|
||||
if killed {
|
||||
err = fmt.Errorf("%w: %s", ErrProgramKilled, p.ctx.Err())
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Ensure we rendered the final state of the model.
|
||||
p.renderer.write(model.View())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tear down.
|
||||
p.cancel()
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if the cancel reader has been setup before waiting and closing.
|
||||
if p.cancelReader != nil {
|
||||
// Wait for input loop to finish.
|
||||
if p.cancelReader.Cancel() {
|
||||
p.waitForReadLoop()
|
||||
}
|
||||
_ = p.cancelReader.Close()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Wait for all handlers to finish.
|
||||
handlers.shutdown()
|
||||
|
||||
// Restore terminal state.
|
||||
p.shutdown(killed)
|
||||
|
||||
return model, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StartReturningModel initializes the program and runs its event loops,
|
||||
// blocking until it gets terminated by either [Program.Quit], [Program.Kill],
|
||||
// or its signal handler. Returns the final model.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: please use [Program.Run] instead.
|
||||
func (p *Program) StartReturningModel() (Model, error) {
|
||||
return p.Run()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Start initializes the program and runs its event loops, blocking until it
|
||||
// gets terminated by either [Program.Quit], [Program.Kill], or its signal
|
||||
// handler.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: please use [Program.Run] instead.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Start() error {
|
||||
_, err := p.Run()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Send sends a message to the main update function, effectively allowing
|
||||
// messages to be injected from outside the program for interoperability
|
||||
// purposes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the program hasn't started yet this will be a blocking operation.
|
||||
// If the program has already been terminated this will be a no-op, so it's safe
|
||||
// to send messages after the program has exited.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Send(msg Msg) {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
case p.msgs <- msg:
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Quit is a convenience function for quitting Bubble Tea programs. Use it
|
||||
// when you need to shut down a Bubble Tea program from the outside.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you wish to quit from within a Bubble Tea program use the Quit command.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the program is not running this will be a no-op, so it's safe to call
|
||||
// if the program is unstarted or has already exited.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Quit() {
|
||||
p.Send(Quit())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Kill stops the program immediately and restores the former terminal state.
|
||||
// The final render that you would normally see when quitting will be skipped.
|
||||
// [program.Run] returns a [ErrProgramKilled] error.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Kill() {
|
||||
p.cancel()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Wait waits/blocks until the underlying Program finished shutting down.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Wait() {
|
||||
<-p.finished
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// shutdown performs operations to free up resources and restore the terminal
|
||||
// to its original state.
|
||||
func (p *Program) shutdown(kill bool) {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
if kill {
|
||||
p.renderer.kill()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.renderer.stop()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_ = p.restoreTerminalState()
|
||||
p.finished <- struct{}{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReleaseTerminal restores the original terminal state and cancels the input
|
||||
// reader. You can return control to the Program with RestoreTerminal.
|
||||
func (p *Program) ReleaseTerminal() error {
|
||||
atomic.StoreUint32(&p.ignoreSignals, 1)
|
||||
if p.cancelReader != nil {
|
||||
p.cancelReader.Cancel()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.waitForReadLoop()
|
||||
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.stop()
|
||||
p.altScreenWasActive = p.renderer.altScreen()
|
||||
p.bpWasActive = p.renderer.bracketedPasteActive()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return p.restoreTerminalState()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreTerminal reinitializes the Program's input reader, restores the
|
||||
// terminal to the former state when the program was running, and repaints.
|
||||
// Use it to reinitialize a Program after running ReleaseTerminal.
|
||||
func (p *Program) RestoreTerminal() error {
|
||||
atomic.StoreUint32(&p.ignoreSignals, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
if err := p.initTerminal(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := p.initCancelReader(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.altScreenWasActive {
|
||||
p.renderer.enterAltScreen()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// entering alt screen already causes a repaint.
|
||||
go p.Send(repaintMsg{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.start()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.bpWasActive {
|
||||
p.renderer.enableBracketedPaste()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If the output is a terminal, it may have been resized while another
|
||||
// process was at the foreground, in which case we may not have received
|
||||
// SIGWINCH. Detect any size change now and propagate the new size as
|
||||
// needed.
|
||||
go p.checkResize()
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Println prints above the Program. This output is unmanaged by the program
|
||||
// and will persist across renders by the Program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the altscreen is active no output will be printed.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Println(args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
p.msgs <- printLineMessage{
|
||||
messageBody: fmt.Sprint(args...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Printf prints above the Program. It takes a format template followed by
|
||||
// values similar to fmt.Printf. This output is unmanaged by the program and
|
||||
// will persist across renders by the Program.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unlike fmt.Printf (but similar to log.Printf) the message will be print on
|
||||
// its own line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the altscreen is active no output will be printed.
|
||||
func (p *Program) Printf(template string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
p.msgs <- printLineMessage{
|
||||
messageBody: fmt.Sprintf(template, args...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
127
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tty.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
127
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tty.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/term"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/cancelreader"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Program) suspend() {
|
||||
if err := p.ReleaseTerminal(); err != nil {
|
||||
// If we can't release input, abort.
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
suspendProcess()
|
||||
|
||||
_ = p.RestoreTerminal()
|
||||
go p.Send(ResumeMsg{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Program) initTerminal() error {
|
||||
if err := p.initInput(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.renderer.hideCursor()
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// restoreTerminalState restores the terminal to the state prior to running the
|
||||
// Bubble Tea program.
|
||||
func (p *Program) restoreTerminalState() error {
|
||||
if p.renderer != nil {
|
||||
p.renderer.disableBracketedPaste()
|
||||
p.renderer.showCursor()
|
||||
p.disableMouse()
|
||||
|
||||
if p.renderer.altScreen() {
|
||||
p.renderer.exitAltScreen()
|
||||
|
||||
// give the terminal a moment to catch up
|
||||
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 10) //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return p.restoreInput()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// restoreInput restores the tty input to its original state.
|
||||
func (p *Program) restoreInput() error {
|
||||
if p.ttyInput != nil && p.previousTtyInputState != nil {
|
||||
if err := term.Restore(p.ttyInput.Fd(), p.previousTtyInputState); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error restoring console: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.ttyOutput != nil && p.previousOutputState != nil {
|
||||
if err := term.Restore(p.ttyOutput.Fd(), p.previousOutputState); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error restoring console: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// initCancelReader (re)commences reading inputs.
|
||||
func (p *Program) initCancelReader() error {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
p.cancelReader, err = newInputReader(p.input)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating cancelreader: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.readLoopDone = make(chan struct{})
|
||||
go p.readLoop()
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Program) readLoop() {
|
||||
defer close(p.readLoopDone)
|
||||
|
||||
err := readInputs(p.ctx, p.msgs, p.cancelReader)
|
||||
if !errors.Is(err, io.EOF) && !errors.Is(err, cancelreader.ErrCanceled) {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
case p.errs <- err:
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// waitForReadLoop waits for the cancelReader to finish its read loop.
|
||||
func (p *Program) waitForReadLoop() {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.readLoopDone:
|
||||
case <-time.After(500 * time.Millisecond): //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
// The read loop hangs, which means the input
|
||||
// cancelReader's cancel function has returned true even
|
||||
// though it was not able to cancel the read.
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// checkResize detects the current size of the output and informs the program
|
||||
// via a WindowSizeMsg.
|
||||
func (p *Program) checkResize() {
|
||||
if p.ttyOutput == nil {
|
||||
// can't query window size
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
w, h, err := term.GetSize(p.ttyOutput.Fd())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-p.ctx.Done():
|
||||
case p.errs <- err:
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.Send(WindowSizeMsg{
|
||||
Width: w,
|
||||
Height: h,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
49
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tty_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
49
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tty_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
//go:build darwin || dragonfly || freebsd || linux || netbsd || openbsd || solaris || aix || zos
|
||||
// +build darwin dragonfly freebsd linux netbsd openbsd solaris aix zos
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/signal"
|
||||
"syscall"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/term"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Program) initInput() (err error) {
|
||||
// Check if input is a terminal
|
||||
if f, ok := p.input.(term.File); ok && term.IsTerminal(f.Fd()) {
|
||||
p.ttyInput = f
|
||||
p.previousTtyInputState, err = term.MakeRaw(p.ttyInput.Fd())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error entering raw mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if f, ok := p.output.(term.File); ok && term.IsTerminal(f.Fd()) {
|
||||
p.ttyOutput = f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func openInputTTY() (*os.File, error) {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open("/dev/tty")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not open a new TTY: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const suspendSupported = true
|
||||
|
||||
// Send SIGTSTP to the entire process group.
|
||||
func suspendProcess() {
|
||||
c := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
|
||||
signal.Notify(c, syscall.SIGCONT)
|
||||
_ = syscall.Kill(0, syscall.SIGTSTP)
|
||||
// blocks until a CONT happens...
|
||||
<-c
|
||||
}
|
||||
68
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tty_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
68
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea/tty_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
//go:build windows
|
||||
// +build windows
|
||||
|
||||
package tea
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/term"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/sys/windows"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Program) initInput() (err error) {
|
||||
// Save stdin state and enable VT input
|
||||
// We also need to enable VT
|
||||
// input here.
|
||||
if f, ok := p.input.(term.File); ok && term.IsTerminal(f.Fd()) {
|
||||
p.ttyInput = f
|
||||
p.previousTtyInputState, err = term.MakeRaw(p.ttyInput.Fd())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Enable VT input
|
||||
var mode uint32
|
||||
if err := windows.GetConsoleMode(windows.Handle(p.ttyInput.Fd()), &mode); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error getting console mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err := windows.SetConsoleMode(windows.Handle(p.ttyInput.Fd()), mode|windows.ENABLE_VIRTUAL_TERMINAL_INPUT); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error setting console mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Save output screen buffer state and enable VT processing.
|
||||
if f, ok := p.output.(term.File); ok && term.IsTerminal(f.Fd()) {
|
||||
p.ttyOutput = f
|
||||
p.previousOutputState, err = term.GetState(f.Fd())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var mode uint32
|
||||
if err := windows.GetConsoleMode(windows.Handle(p.ttyOutput.Fd()), &mode); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error getting console mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err := windows.SetConsoleMode(windows.Handle(p.ttyOutput.Fd()), mode|windows.ENABLE_VIRTUAL_TERMINAL_PROCESSING); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error setting console mode: %w", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open the Windows equivalent of a TTY.
|
||||
func openInputTTY() (*os.File, error) {
|
||||
f, err := os.OpenFile("CONIN$", os.O_RDWR, 0o644)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const suspendSupported = false
|
||||
|
||||
func suspendProcess() {}
|
||||
1
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
1
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
ssh_example_ed25519*
|
||||
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
run:
|
||||
tests: false
|
||||
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- EXC0001
|
||||
- EXC0005
|
||||
- EXC0011
|
||||
- EXC0012
|
||||
- EXC0013
|
||||
|
||||
max-issues-per-linter: 0
|
||||
max-same-issues: 0
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
# - dupl
|
||||
- exhaustive
|
||||
# - exhaustivestruct
|
||||
- goconst
|
||||
- godot
|
||||
- godox
|
||||
- gomnd
|
||||
- gomoddirectives
|
||||
- goprintffuncname
|
||||
# - lll
|
||||
- misspell
|
||||
- nakedret
|
||||
- nestif
|
||||
- noctx
|
||||
- nolintlint
|
||||
- prealloc
|
||||
- wrapcheck
|
||||
|
||||
# disable default linters, they are already enabled in .golangci.yml
|
||||
disable:
|
||||
- deadcode
|
||||
- errcheck
|
||||
- gosimple
|
||||
- govet
|
||||
- ineffassign
|
||||
- staticcheck
|
||||
- structcheck
|
||||
- typecheck
|
||||
- unused
|
||||
- varcheck
|
||||
30
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
30
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
run:
|
||||
tests: false
|
||||
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- EXC0001
|
||||
- EXC0005
|
||||
- EXC0011
|
||||
- EXC0012
|
||||
- EXC0013
|
||||
|
||||
max-issues-per-linter: 0
|
||||
max-same-issues: 0
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
- bodyclose
|
||||
- exportloopref
|
||||
- gofumpt
|
||||
- goimports
|
||||
- gosec
|
||||
- nilerr
|
||||
- predeclared
|
||||
- revive
|
||||
- rowserrcheck
|
||||
- sqlclosecheck
|
||||
- tparallel
|
||||
- unconvert
|
||||
- unparam
|
||||
- whitespace
|
||||
5
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
5
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
includes:
|
||||
- from_url:
|
||||
url: charmbracelet/meta/main/goreleaser-lib.yaml
|
||||
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://goreleaser.com/static/schema-pro.json
|
||||
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2021-2023 Charmbracelet, Inc
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
658
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
658
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,658 @@
|
||||
# Lip Gloss
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<a href="https://stuff.charm.sh/lipgloss/lipgloss-mascot-2k.png"><img width="340" alt="Lip Gloss title treatment" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/25087/147cadb1-4254-43ec-ae6b-8d6ca7b029a1"></a><br>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/charmbracelet/lipgloss.svg" alt="Latest Release"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss?tab=doc"><img src="https://godoc.org/github.com/golang/gddo?status.svg" alt="GoDoc"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/actions"><img src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/workflows/build/badge.svg" alt="Build Status"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://www.phorm.ai/query?projectId=a0e324b6-b706-4546-b951-6671ea60c13f"><img src="https://stuff.charm.sh/misc/phorm-badge.svg" alt="phorm.ai"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Style definitions for nice terminal layouts. Built with TUIs in mind.
|
||||
|
||||
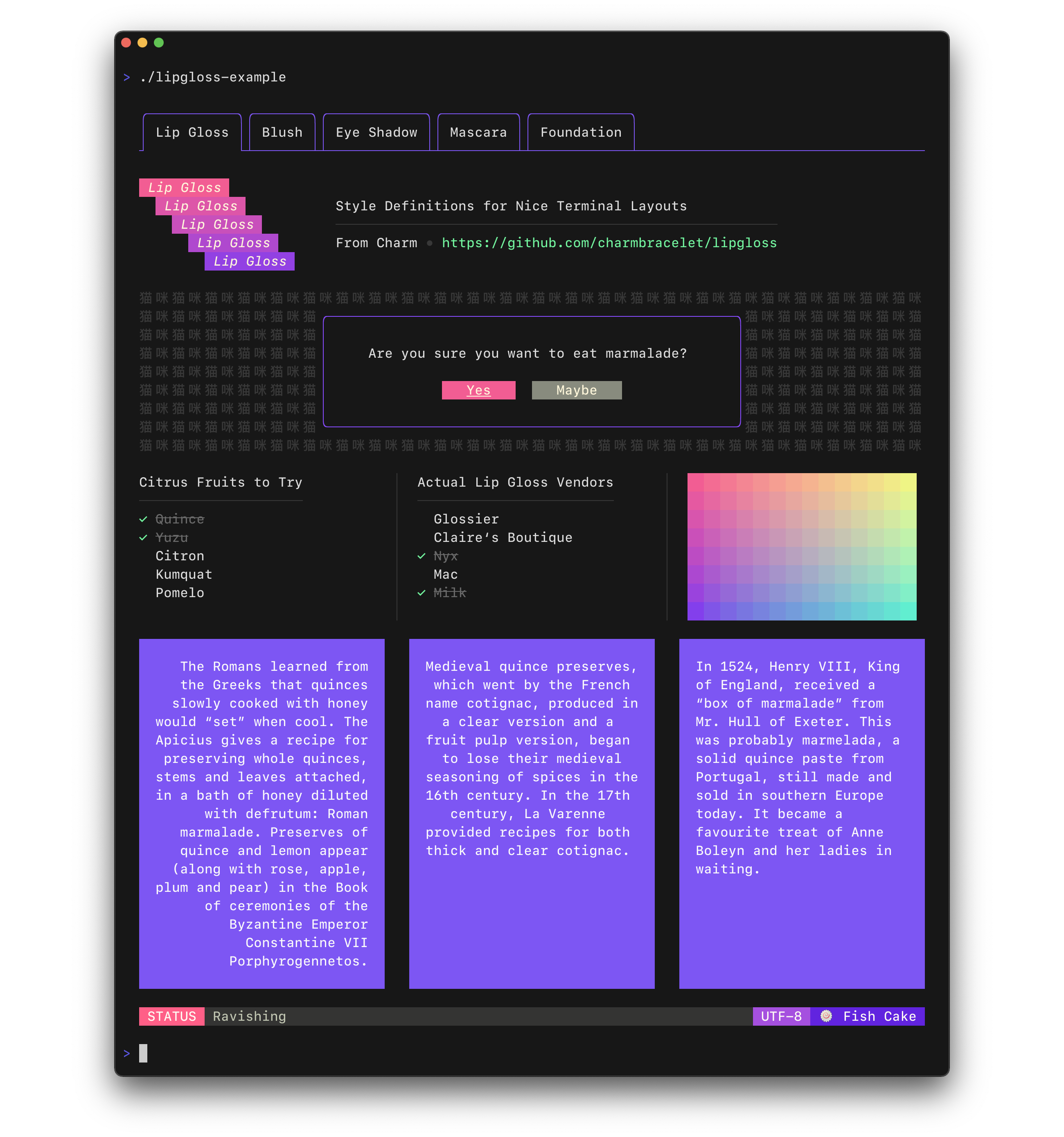
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss takes an expressive, declarative approach to terminal rendering.
|
||||
Users familiar with CSS will feel at home with Lip Gloss.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("#FAFAFA")).
|
||||
Background(lipgloss.Color("#7D56F4")).
|
||||
PaddingTop(2).
|
||||
PaddingLeft(4).
|
||||
Width(22)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(style.Render("Hello, kitty"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Colors
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss supports the following color profiles:
|
||||
|
||||
### ANSI 16 colors (4-bit)
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("5") // magenta
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("9") // red
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("12") // light blue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### ANSI 256 Colors (8-bit)
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("86") // aqua
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("201") // hot pink
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("202") // orange
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### True Color (16,777,216 colors; 24-bit)
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("#0000FF") // good ol' 100% blue
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("#04B575") // a green
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("#3C3C3C") // a dark gray
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...as well as a 1-bit ASCII profile, which is black and white only.
|
||||
|
||||
The terminal's color profile will be automatically detected, and colors outside
|
||||
the gamut of the current palette will be automatically coerced to their closest
|
||||
available value.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adaptive Colors
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify color options for light and dark backgrounds:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{Light: "236", Dark: "248"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The terminal's background color will automatically be detected and the
|
||||
appropriate color will be chosen at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete Colors
|
||||
|
||||
CompleteColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
profiles.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.CompleteColor{True: "#0000FF", ANSI256: "86", ANSI: "5"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Automatic color degradation will not be performed in this case and it will be
|
||||
based on the color specified.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete Adaptive Colors
|
||||
|
||||
You can use CompleteColor with AdaptiveColor to specify the exact values for
|
||||
light and dark backgrounds without automatic color degradation.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.CompleteAdaptiveColor{
|
||||
Light: CompleteColor{TrueColor: "#d7ffae", ANSI256: "193", ANSI: "11"},
|
||||
Dark: CompleteColor{TrueColor: "#d75fee", ANSI256: "163", ANSI: "5"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inline Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss supports the usual ANSI text formatting options:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
Italic(true).
|
||||
Faint(true).
|
||||
Blink(true).
|
||||
Strikethrough(true).
|
||||
Underline(true).
|
||||
Reverse(true)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Block-Level Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss also supports rules for block-level formatting:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Padding
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
PaddingTop(2).
|
||||
PaddingRight(4).
|
||||
PaddingBottom(2).
|
||||
PaddingLeft(4)
|
||||
|
||||
// Margins
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
MarginTop(2).
|
||||
MarginRight(4).
|
||||
MarginBottom(2).
|
||||
MarginLeft(4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There is also shorthand syntax for margins and padding, which follows the same
|
||||
format as CSS:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// 2 cells on all sides
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Padding(2)
|
||||
|
||||
// 2 cells on the top and bottom, 4 cells on the left and right
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Margin(2, 4)
|
||||
|
||||
// 1 cell on the top, 4 cells on the sides, 2 cells on the bottom
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Padding(1, 4, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
// Clockwise, starting from the top: 2 cells on the top, 4 on the right, 3 on
|
||||
// the bottom, and 1 on the left
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Margin(2, 4, 3, 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Aligning Text
|
||||
|
||||
You can align paragraphs of text to the left, right, or center.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Width(24).
|
||||
Align(lipgloss.Left). // align it left
|
||||
Align(lipgloss.Right). // no wait, align it right
|
||||
Align(lipgloss.Center) // just kidding, align it in the center
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Width and Height
|
||||
|
||||
Setting a minimum width and height is simple and straightforward.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString("What’s for lunch?").
|
||||
Width(24).
|
||||
Height(32).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("63"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Borders
|
||||
|
||||
Adding borders is easy:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Add a purple, rectangular border
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
BorderStyle(lipgloss.NormalBorder()).
|
||||
BorderForeground(lipgloss.Color("63"))
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a rounded, yellow-on-purple border to the top and left
|
||||
var anotherStyle = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
BorderStyle(lipgloss.RoundedBorder()).
|
||||
BorderForeground(lipgloss.Color("228")).
|
||||
BorderBackground(lipgloss.Color("63")).
|
||||
BorderTop(true).
|
||||
BorderLeft(true)
|
||||
|
||||
// Make your own border
|
||||
var myCuteBorder = lipgloss.Border{
|
||||
Top: "._.:*:",
|
||||
Bottom: "._.:*:",
|
||||
Left: "|*",
|
||||
Right: "|*",
|
||||
TopLeft: "*",
|
||||
TopRight: "*",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "*",
|
||||
BottomRight: "*",
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are also shorthand functions for defining borders, which follow a similar
|
||||
pattern to the margin and padding shorthand functions.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Add a thick border to the top and bottom
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Border(lipgloss.ThickBorder(), true, false)
|
||||
|
||||
// Add a double border to the top and left sides. Rules are set clockwise
|
||||
// from top.
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Border(lipgloss.DoubleBorder(), true, false, false, true)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more on borders see [the docs][docs].
|
||||
|
||||
## Copying Styles
|
||||
|
||||
Just use assignment:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("219"))
|
||||
|
||||
copiedStyle := style // this is a true copy
|
||||
|
||||
wildStyle := style.Blink(true) // this is also true copy, with blink added
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since `Style` data structures contains only primitive types, assigning a style
|
||||
to another effectively creates a new copy of the style without mutating the
|
||||
original.
|
||||
|
||||
## Inheritance
|
||||
|
||||
Styles can inherit rules from other styles. When inheriting, only unset rules
|
||||
on the receiver are inherited.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var styleA = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("229")).
|
||||
Background(lipgloss.Color("63"))
|
||||
|
||||
// Only the background color will be inherited here, because the foreground
|
||||
// color will have been already set:
|
||||
var styleB = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("201")).
|
||||
Inherit(styleA)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Unsetting Rules
|
||||
|
||||
All rules can be unset:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Bold(true). // make it bold
|
||||
UnsetBold(). // jk don't make it bold
|
||||
Background(lipgloss.Color("227")). // yellow background
|
||||
UnsetBackground() // never mind
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When a rule is unset, it won't be inherited or copied.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforcing Rules
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes, such as when developing a component, you want to make sure style
|
||||
definitions respect their intended purpose in the UI. This is where `Inline`
|
||||
and `MaxWidth`, and `MaxHeight` come in:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Force rendering onto a single line, ignoring margins, padding, and borders.
|
||||
someStyle.Inline(true).Render("yadda yadda")
|
||||
|
||||
// Also limit rendering to five cells
|
||||
someStyle.Inline(true).MaxWidth(5).Render("yadda yadda")
|
||||
|
||||
// Limit rendering to a 5x5 cell block
|
||||
someStyle.MaxWidth(5).MaxHeight(5).Render("yadda yadda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Tabs
|
||||
|
||||
The tab character (`\t`) is rendered differently in different terminals (often
|
||||
as 8 spaces, sometimes 4). Because of this inconsistency, Lip Gloss converts
|
||||
tabs to 4 spaces at render time. This behavior can be changed on a per-style
|
||||
basis, however:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style := lipgloss.NewStyle() // tabs will render as 4 spaces, the default
|
||||
style = style.TabWidth(2) // render tabs as 2 spaces
|
||||
style = style.TabWidth(0) // remove tabs entirely
|
||||
style = style.TabWidth(lipgloss.NoTabConversion) // leave tabs intact
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, you just call the `Render(string...)` method on a `lipgloss.Style`:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style := lipgloss.NewStyle().Bold(true).SetString("Hello,")
|
||||
fmt.Println(style.Render("kitty.")) // Hello, kitty.
|
||||
fmt.Println(style.Render("puppy.")) // Hello, puppy.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But you could also use the Stringer interface:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().SetString("你好,猫咪。").Bold(true)
|
||||
fmt.Println(style) // 你好,猫咪。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Renderers
|
||||
|
||||
Custom renderers allow you to render to a specific outputs. This is
|
||||
particularly important when you want to render to different outputs and
|
||||
correctly detect the color profile and dark background status for each, such as
|
||||
in a server-client situation.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func myLittleHandler(sess ssh.Session) {
|
||||
// Create a renderer for the client.
|
||||
renderer := lipgloss.NewRenderer(sess)
|
||||
|
||||
// Create a new style on the renderer.
|
||||
style := renderer.NewStyle().Background(lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{Light: "63", Dark: "228"})
|
||||
|
||||
// Render. The color profile and dark background state will be correctly detected.
|
||||
io.WriteString(sess, style.Render("Heyyyyyyy"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For an example on using a custom renderer over SSH with [Wish][wish] see the
|
||||
[SSH example][ssh-example].
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to pure styling, Lip Gloss also ships with some utilities to help
|
||||
assemble your layouts.
|
||||
|
||||
### Joining Paragraphs
|
||||
|
||||
Horizontally and vertically joining paragraphs is a cinch.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Horizontally join three paragraphs along their bottom edges
|
||||
lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Bottom, paragraphA, paragraphB, paragraphC)
|
||||
|
||||
// Vertically join two paragraphs along their center axes
|
||||
lipgloss.JoinVertical(lipgloss.Center, paragraphA, paragraphB)
|
||||
|
||||
// Horizontally join three paragraphs, with the shorter ones aligning 20%
|
||||
// from the top of the tallest
|
||||
lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(0.2, paragraphA, paragraphB, paragraphC)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Measuring Width and Height
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you’ll want to know the width and height of text blocks when building
|
||||
your layouts.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Render a block of text.
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Width(40).
|
||||
Padding(2)
|
||||
var block string = style.Render(someLongString)
|
||||
|
||||
// Get the actual, physical dimensions of the text block.
|
||||
width := lipgloss.Width(block)
|
||||
height := lipgloss.Height(block)
|
||||
|
||||
// Here's a shorthand function.
|
||||
w, h := lipgloss.Size(block)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Placing Text in Whitespace
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you’ll simply want to place a block of text in whitespace.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Center a paragraph horizontally in a space 80 cells wide. The height of
|
||||
// the block returned will be as tall as the input paragraph.
|
||||
block := lipgloss.PlaceHorizontal(80, lipgloss.Center, fancyStyledParagraph)
|
||||
|
||||
// Place a paragraph at the bottom of a space 30 cells tall. The width of
|
||||
// the text block returned will be as wide as the input paragraph.
|
||||
block := lipgloss.PlaceVertical(30, lipgloss.Bottom, fancyStyledParagraph)
|
||||
|
||||
// Place a paragraph in the bottom right corner of a 30x80 cell space.
|
||||
block := lipgloss.Place(30, 80, lipgloss.Right, lipgloss.Bottom, fancyStyledParagraph)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also style the whitespace. For details, see [the docs][docs].
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering Tables
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a table rendering sub-package.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define some rows of data.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
rows := [][]string{
|
||||
{"Chinese", "您好", "你好"},
|
||||
{"Japanese", "こんにちは", "やあ"},
|
||||
{"Arabic", "أهلين", "أهلا"},
|
||||
{"Russian", "Здравствуйте", "Привет"},
|
||||
{"Spanish", "Hola", "¿Qué tal?"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use the table package to style and render the table.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := table.New().
|
||||
Border(lipgloss.NormalBorder()).
|
||||
BorderStyle(lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("99"))).
|
||||
StyleFunc(func(row, col int) lipgloss.Style {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case row == 0:
|
||||
return HeaderStyle
|
||||
case row%2 == 0:
|
||||
return EvenRowStyle
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return OddRowStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
}).
|
||||
Headers("LANGUAGE", "FORMAL", "INFORMAL").
|
||||
Rows(rows...)
|
||||
|
||||
// You can also add tables row-by-row
|
||||
t.Row("English", "You look absolutely fabulous.", "How's it going?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the table.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(t)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For more on tables see [the docs](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss?tab=doc) and [examples](https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/tree/master/examples/table).
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Lists
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a list rendering sub-package.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/list"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define a new list.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New("A", "B", "C")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(l)
|
||||
|
||||
// • A
|
||||
// • B
|
||||
// • C
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Lists have the ability to nest.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New(
|
||||
"A", list.New("Artichoke"),
|
||||
"B", list.New("Baking Flour", "Bananas", "Barley", "Bean Sprouts"),
|
||||
"C", list.New("Cashew Apple", "Cashews", "Coconut Milk", "Curry Paste", "Currywurst"),
|
||||
"D", list.New("Dill", "Dragonfruit", "Dried Shrimp"),
|
||||
"E", list.New("Eggs"),
|
||||
"F", list.New("Fish Cake", "Furikake"),
|
||||
"J", list.New("Jicama"),
|
||||
"K", list.New("Kohlrabi"),
|
||||
"L", list.New("Leeks", "Lentils", "Licorice Root"),
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(l)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="600" alt="image" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/42545625/0dc9f440-0748-4151-a3b0-7dcf29dfcdb0">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Lists can be customized via their enumeration function as well as using
|
||||
`lipgloss.Style`s.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
enumeratorStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("99")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
itemStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("212")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
|
||||
l := list.New(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
"Nyx",
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
Enumerator(list.Roman).
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(enumeratorStyle).
|
||||
ItemStyle(itemStyle)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="600" alt="List example" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/42545625/360494f1-57fb-4e13-bc19-0006efe01561">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the predefined enumerators (`Arabic`, `Alphabet`, `Roman`, `Bullet`, `Tree`),
|
||||
you may also define your own custom enumerator:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New("Duck", "Duck", "Duck", "Duck", "Goose", "Duck", "Duck")
|
||||
|
||||
func DuckDuckGooseEnumerator(l list.Items, i int) string {
|
||||
if l.At(i).Value() == "Goose" {
|
||||
return "Honk →"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
l = l.Enumerator(DuckDuckGooseEnumerator)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="600" alt="image" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/42545625/157aaf30-140d-4948-9bb4-dfba46e5b87e">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
If you need, you can also build lists incrementally:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New()
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < repeat; i++ {
|
||||
l.Item("Lip Gloss")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
Why are things misaligning? Why are borders at the wrong widths?
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
<p>This is most likely due to your locale and encoding, particularly with
|
||||
regard to Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (for example, <code>zh_CN.UTF-8</code>
|
||||
or <code>ja_JP.UTF-8</code>). The most direct way to fix this is to set
|
||||
<code>RUNEWIDTH_EASTASIAN=0</code> in your environment.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>For details see <a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/issues/40">https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/issues/40.</a></p>
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
Why isn't Lip Gloss displaying colors?
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
<p>Lip Gloss automatically degrades colors to the best available option in the
|
||||
given terminal, and if output's not a TTY it will remove color output entirely.
|
||||
This is common when running tests, CI, or when piping output elsewhere.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>If necessary, you can force a color profile in your tests with
|
||||
<a href="https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss#SetColorProfile"><code>SetColorProfile</code></a>.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
lipgloss.SetColorProfile(termenv.TrueColor)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
_Note:_ this option limits the flexibility of your application and can cause
|
||||
ANSI escape codes to be output in cases where that might not be desired. Take
|
||||
careful note of your use case and environment before choosing to force a color
|
||||
profile.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## What about [Bubble Tea][tea]?
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss doesn’t replace Bubble Tea. Rather, it is an excellent Bubble Tea
|
||||
companion. It was designed to make assembling terminal user interface views as
|
||||
simple and fun as possible so that you can focus on building your application
|
||||
instead of concerning yourself with low-level layout details.
|
||||
|
||||
In simple terms, you can use Lip Gloss to help build your Bubble Tea views.
|
||||
|
||||
[tea]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/tea
|
||||
|
||||
## Under the Hood
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss is built on the excellent [Termenv][termenv] and [Reflow][reflow]
|
||||
libraries which deal with color and ANSI-aware text operations, respectively.
|
||||
For many use cases Termenv and Reflow will be sufficient for your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
[termenv]: https://github.com/muesli/termenv
|
||||
[reflow]: https://github.com/muesli/reflow
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Markdown
|
||||
|
||||
For a more document-centric rendering solution with support for things like
|
||||
lists, tables, and syntax-highlighted code have a look at [Glamour][glamour],
|
||||
the stylesheet-based Markdown renderer.
|
||||
|
||||
[glamour]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/glamour
|
||||
|
||||
## Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
We’d love to hear your thoughts on this project. Feel free to drop us a note!
|
||||
|
||||
- [Twitter](https://twitter.com/charmcli)
|
||||
- [The Fediverse](https://mastodon.social/@charmcli)
|
||||
- [Discord](https://charm.sh/chat)
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
[MIT](https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/raw/master/LICENSE)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Part of [Charm](https://charm.sh).
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://charm.sh/"><img alt="The Charm logo" src="https://stuff.charm.sh/charm-badge.jpg" width="400"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Charm热爱开源 • Charm loves open source
|
||||
|
||||
[docs]: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss?tab=doc
|
||||
[wish]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/wish
|
||||
[ssh-example]: examples/ssh
|
||||
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/align.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/align.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Perform text alignment. If the string is multi-lined, we also make all lines
|
||||
// the same width by padding them with spaces. If a termenv style is passed,
|
||||
// use that to style the spaces added.
|
||||
func alignTextHorizontal(str string, pos Position, width int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
lines, widestLine := getLines(str)
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
for i, l := range lines {
|
||||
lineWidth := ansi.StringWidth(l)
|
||||
|
||||
shortAmount := widestLine - lineWidth // difference from the widest line
|
||||
shortAmount += max(0, width-(shortAmount+lineWidth)) // difference from the total width, if set
|
||||
|
||||
if shortAmount > 0 {
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Right:
|
||||
s := strings.Repeat(" ", shortAmount)
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
s = style.Styled(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l = s + l
|
||||
case Center:
|
||||
// Note: remainder goes on the right.
|
||||
left := shortAmount / 2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
right := left + shortAmount%2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
|
||||
leftSpaces := strings.Repeat(" ", left)
|
||||
rightSpaces := strings.Repeat(" ", right)
|
||||
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
leftSpaces = style.Styled(leftSpaces)
|
||||
rightSpaces = style.Styled(rightSpaces)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l = leftSpaces + l + rightSpaces
|
||||
default: // Left
|
||||
s := strings.Repeat(" ", shortAmount)
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
s = style.Styled(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l += s
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
if i < len(lines)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func alignTextVertical(str string, pos Position, height int, _ *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
strHeight := strings.Count(str, "\n") + 1
|
||||
if height < strHeight {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos {
|
||||
case Top:
|
||||
return str + strings.Repeat("\n", height-strHeight)
|
||||
case Center:
|
||||
topPadding, bottomPadding := (height-strHeight)/2, (height-strHeight)/2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
if strHeight+topPadding+bottomPadding > height {
|
||||
topPadding--
|
||||
} else if strHeight+topPadding+bottomPadding < height {
|
||||
bottomPadding++
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strings.Repeat("\n", topPadding) + str + strings.Repeat("\n", bottomPadding)
|
||||
case Bottom:
|
||||
return strings.Repeat("\n", height-strHeight) + str
|
||||
}
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
//go:build !windows
|
||||
// +build !windows
|
||||
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
// enableLegacyWindowsANSI is only needed on Windows.
|
||||
func enableLegacyWindowsANSI() {}
|
||||
22
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
22
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
//go:build windows
|
||||
// +build windows
|
||||
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var enableANSI sync.Once
|
||||
|
||||
// enableANSIColors enables support for ANSI color sequences in the Windows
|
||||
// default console (cmd.exe and the PowerShell application). Note that this
|
||||
// only works with Windows 10. Also note that Windows Terminal supports colors
|
||||
// by default.
|
||||
func enableLegacyWindowsANSI() {
|
||||
enableANSI.Do(func() {
|
||||
_, _ = termenv.EnableWindowsANSIConsole()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
443
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/borders.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
443
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/borders.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,443 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
"github.com/rivo/uniseg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Border contains a series of values which comprise the various parts of a
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
type Border struct {
|
||||
Top string
|
||||
Bottom string
|
||||
Left string
|
||||
Right string
|
||||
TopLeft string
|
||||
TopRight string
|
||||
BottomLeft string
|
||||
BottomRight string
|
||||
MiddleLeft string
|
||||
MiddleRight string
|
||||
Middle string
|
||||
MiddleTop string
|
||||
MiddleBottom string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetTopSize returns the width of the top border. If borders contain runes of
|
||||
// varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on the top
|
||||
// edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetTopSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.TopLeft, b.Top, b.TopRight)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetRightSize returns the width of the right border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the right edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetRightSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.TopRight, b.Right, b.BottomRight)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBottomSize returns the width of the bottom border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the bottom edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetBottomSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.BottomLeft, b.Bottom, b.BottomRight)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetLeftSize returns the width of the left border. If borders contain runes
|
||||
// of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on the
|
||||
// left edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetLeftSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.TopLeft, b.Left, b.BottomLeft)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getBorderEdgeWidth(borderParts ...string) (maxWidth int) {
|
||||
for _, piece := range borderParts {
|
||||
w := maxRuneWidth(piece)
|
||||
if w > maxWidth {
|
||||
maxWidth = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return maxWidth
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
noBorder = Border{}
|
||||
|
||||
normalBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "─",
|
||||
Bottom: "─",
|
||||
Left: "│",
|
||||
Right: "│",
|
||||
TopLeft: "┌",
|
||||
TopRight: "┐",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "└",
|
||||
BottomRight: "┘",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "├",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "┤",
|
||||
Middle: "┼",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "┬",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "┴",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
roundedBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "─",
|
||||
Bottom: "─",
|
||||
Left: "│",
|
||||
Right: "│",
|
||||
TopLeft: "╭",
|
||||
TopRight: "╮",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "╰",
|
||||
BottomRight: "╯",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "├",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "┤",
|
||||
Middle: "┼",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "┬",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "┴",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
blockBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "█",
|
||||
Bottom: "█",
|
||||
Left: "█",
|
||||
Right: "█",
|
||||
TopLeft: "█",
|
||||
TopRight: "█",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "█",
|
||||
BottomRight: "█",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
outerHalfBlockBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "▀",
|
||||
Bottom: "▄",
|
||||
Left: "▌",
|
||||
Right: "▐",
|
||||
TopLeft: "▛",
|
||||
TopRight: "▜",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "▙",
|
||||
BottomRight: "▟",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
innerHalfBlockBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "▄",
|
||||
Bottom: "▀",
|
||||
Left: "▐",
|
||||
Right: "▌",
|
||||
TopLeft: "▗",
|
||||
TopRight: "▖",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "▝",
|
||||
BottomRight: "▘",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
thickBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "━",
|
||||
Bottom: "━",
|
||||
Left: "┃",
|
||||
Right: "┃",
|
||||
TopLeft: "┏",
|
||||
TopRight: "┓",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "┗",
|
||||
BottomRight: "┛",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "┣",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "┫",
|
||||
Middle: "╋",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "┳",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "┻",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
doubleBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "═",
|
||||
Bottom: "═",
|
||||
Left: "║",
|
||||
Right: "║",
|
||||
TopLeft: "╔",
|
||||
TopRight: "╗",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "╚",
|
||||
BottomRight: "╝",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "╠",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "╣",
|
||||
Middle: "╬",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "╦",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "╩",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
hiddenBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: " ",
|
||||
Bottom: " ",
|
||||
Left: " ",
|
||||
Right: " ",
|
||||
TopLeft: " ",
|
||||
TopRight: " ",
|
||||
BottomLeft: " ",
|
||||
BottomRight: " ",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: " ",
|
||||
MiddleRight: " ",
|
||||
Middle: " ",
|
||||
MiddleTop: " ",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: " ",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// NormalBorder returns a standard-type border with a normal weight and 90
|
||||
// degree corners.
|
||||
func NormalBorder() Border {
|
||||
return normalBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RoundedBorder returns a border with rounded corners.
|
||||
func RoundedBorder() Border {
|
||||
return roundedBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BlockBorder returns a border that takes the whole block.
|
||||
func BlockBorder() Border {
|
||||
return blockBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OuterHalfBlockBorder returns a half-block border that sits outside the frame.
|
||||
func OuterHalfBlockBorder() Border {
|
||||
return outerHalfBlockBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InnerHalfBlockBorder returns a half-block border that sits inside the frame.
|
||||
func InnerHalfBlockBorder() Border {
|
||||
return innerHalfBlockBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ThickBorder returns a border that's thicker than the one returned by
|
||||
// NormalBorder.
|
||||
func ThickBorder() Border {
|
||||
return thickBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DoubleBorder returns a border comprised of two thin strokes.
|
||||
func DoubleBorder() Border {
|
||||
return doubleBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HiddenBorder returns a border that renders as a series of single-cell
|
||||
// spaces. It's useful for cases when you want to remove a standard border but
|
||||
// maintain layout positioning. This said, you can still apply a background
|
||||
// color to a hidden border.
|
||||
func HiddenBorder() Border {
|
||||
return hiddenBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) applyBorder(str string) string {
|
||||
var (
|
||||
topSet = s.isSet(borderTopKey)
|
||||
rightSet = s.isSet(borderRightKey)
|
||||
bottomSet = s.isSet(borderBottomKey)
|
||||
leftSet = s.isSet(borderLeftKey)
|
||||
|
||||
border = s.getBorderStyle()
|
||||
hasTop = s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false)
|
||||
hasRight = s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false)
|
||||
hasBottom = s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false)
|
||||
hasLeft = s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false)
|
||||
|
||||
topFG = s.getAsColor(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
rightFG = s.getAsColor(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
bottomFG = s.getAsColor(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
leftFG = s.getAsColor(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
|
||||
topBG = s.getAsColor(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
rightBG = s.getAsColor(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
bottomBG = s.getAsColor(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
leftBG = s.getAsColor(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// If a border is set and no sides have been specifically turned on or off
|
||||
// render borders on all sides.
|
||||
if border != noBorder && !(topSet || rightSet || bottomSet || leftSet) {
|
||||
hasTop = true
|
||||
hasRight = true
|
||||
hasBottom = true
|
||||
hasLeft = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If no border is set or all borders are been disabled, abort.
|
||||
if border == noBorder || (!hasTop && !hasRight && !hasBottom && !hasLeft) {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lines, width := getLines(str)
|
||||
|
||||
if hasLeft {
|
||||
if border.Left == "" {
|
||||
border.Left = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
width += maxRuneWidth(border.Left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if hasRight && border.Right == "" {
|
||||
border.Right = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If corners should be rendered but are set with the empty string, fill them
|
||||
// with a single space.
|
||||
if hasTop && hasLeft && border.TopLeft == "" {
|
||||
border.TopLeft = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasTop && hasRight && border.TopRight == "" {
|
||||
border.TopRight = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasBottom && hasLeft && border.BottomLeft == "" {
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasBottom && hasRight && border.BottomRight == "" {
|
||||
border.BottomRight = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Figure out which corners we should actually be using based on which
|
||||
// sides are set to show.
|
||||
if hasTop {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case !hasLeft && !hasRight:
|
||||
border.TopLeft = ""
|
||||
border.TopRight = ""
|
||||
case !hasLeft:
|
||||
border.TopLeft = ""
|
||||
case !hasRight:
|
||||
border.TopRight = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasBottom {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case !hasLeft && !hasRight:
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = ""
|
||||
border.BottomRight = ""
|
||||
case !hasLeft:
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = ""
|
||||
case !hasRight:
|
||||
border.BottomRight = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// For now, limit corners to one rune.
|
||||
border.TopLeft = getFirstRuneAsString(border.TopLeft)
|
||||
border.TopRight = getFirstRuneAsString(border.TopRight)
|
||||
border.BottomRight = getFirstRuneAsString(border.BottomRight)
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = getFirstRuneAsString(border.BottomLeft)
|
||||
|
||||
var out strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
// Render top
|
||||
if hasTop {
|
||||
top := renderHorizontalEdge(border.TopLeft, border.Top, border.TopRight, width)
|
||||
top = s.styleBorder(top, topFG, topBG)
|
||||
out.WriteString(top)
|
||||
out.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
leftRunes := []rune(border.Left)
|
||||
leftIndex := 0
|
||||
|
||||
rightRunes := []rune(border.Right)
|
||||
rightIndex := 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Render sides
|
||||
for i, l := range lines {
|
||||
if hasLeft {
|
||||
r := string(leftRunes[leftIndex])
|
||||
leftIndex++
|
||||
if leftIndex >= len(leftRunes) {
|
||||
leftIndex = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(s.styleBorder(r, leftFG, leftBG))
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(l)
|
||||
if hasRight {
|
||||
r := string(rightRunes[rightIndex])
|
||||
rightIndex++
|
||||
if rightIndex >= len(rightRunes) {
|
||||
rightIndex = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(s.styleBorder(r, rightFG, rightBG))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(lines)-1 {
|
||||
out.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render bottom
|
||||
if hasBottom {
|
||||
bottom := renderHorizontalEdge(border.BottomLeft, border.Bottom, border.BottomRight, width)
|
||||
bottom = s.styleBorder(bottom, bottomFG, bottomBG)
|
||||
out.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
out.WriteString(bottom)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return out.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render the horizontal (top or bottom) portion of a border.
|
||||
func renderHorizontalEdge(left, middle, right string, width int) string {
|
||||
if middle == "" {
|
||||
middle = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
leftWidth := ansi.StringWidth(left)
|
||||
rightWidth := ansi.StringWidth(right)
|
||||
|
||||
runes := []rune(middle)
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
|
||||
out := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
out.WriteString(left)
|
||||
for i := leftWidth + rightWidth; i < width+rightWidth; {
|
||||
out.WriteRune(runes[j])
|
||||
j++
|
||||
if j >= len(runes) {
|
||||
j = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += ansi.StringWidth(string(runes[j]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(right)
|
||||
|
||||
return out.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply foreground and background styling to a border.
|
||||
func (s Style) styleBorder(border string, fg, bg TerminalColor) string {
|
||||
if fg == noColor && bg == noColor {
|
||||
return border
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
style := termenv.Style{}
|
||||
|
||||
if fg != noColor {
|
||||
style = style.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bg != noColor {
|
||||
style = style.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return style.Styled(border)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func maxRuneWidth(str string) int {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
|
||||
state := -1
|
||||
for len(str) > 0 {
|
||||
var w int
|
||||
_, str, w, state = uniseg.FirstGraphemeClusterInString(str, state)
|
||||
if w > width {
|
||||
width = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return width
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getFirstRuneAsString(str string) string {
|
||||
if str == "" {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
r := []rune(str)
|
||||
return string(r[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
172
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
172
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,172 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TerminalColor is a color intended to be rendered in the terminal.
|
||||
type TerminalColor interface {
|
||||
color(*Renderer) termenv.Color
|
||||
RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var noColor = NoColor{}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoColor is used to specify the absence of color styling. When this is active
|
||||
// foreground colors will be rendered with the terminal's default text color,
|
||||
// and background colors will not be drawn at all.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var style = someStyle.Background(lipgloss.NoColor{})
|
||||
type NoColor struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (NoColor) color(*Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
return termenv.NoColor{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. Because we have to return
|
||||
// something, despite this color being the absence of color, we're returning
|
||||
// black with 100% opacity.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (n NoColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0xFFFF //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Color specifies a color by hex or ANSI value. For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ansiColor := lipgloss.Color("21")
|
||||
// hexColor := lipgloss.Color("#0000ff")
|
||||
type Color string
|
||||
|
||||
func (c Color) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
return r.ColorProfile().Color(string(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (c Color) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(c.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ANSIColor is a color specified by an ANSI color value. It's merely syntactic
|
||||
// sugar for the more general Color function. Invalid colors will render as
|
||||
// black.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // These two statements are equivalent.
|
||||
// colorA := lipgloss.ANSIColor(21)
|
||||
// colorB := lipgloss.Color("21")
|
||||
type ANSIColor uint
|
||||
|
||||
func (ac ANSIColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
return Color(strconv.FormatUint(uint64(ac), 10)).color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (ac ANSIColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
cf := Color(strconv.FormatUint(uint64(ac), 10))
|
||||
return cf.RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AdaptiveColor provides color options for light and dark backgrounds. The
|
||||
// appropriate color will be returned at runtime based on the darkness of the
|
||||
// terminal background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// color := lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{Light: "#0000ff", Dark: "#000099"}
|
||||
type AdaptiveColor struct {
|
||||
Light string
|
||||
Dark string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (ac AdaptiveColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
if r.HasDarkBackground() {
|
||||
return Color(ac.Dark).color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Color(ac.Light).color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (ac AdaptiveColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(ac.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CompleteColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
// profiles. Automatic color degradation will not be performed.
|
||||
type CompleteColor struct {
|
||||
TrueColor string
|
||||
ANSI256 string
|
||||
ANSI string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CompleteColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
p := r.ColorProfile()
|
||||
switch p { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case termenv.TrueColor:
|
||||
return p.Color(c.TrueColor)
|
||||
case termenv.ANSI256:
|
||||
return p.Color(c.ANSI256)
|
||||
case termenv.ANSI:
|
||||
return p.Color(c.ANSI)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return termenv.NoColor{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
// CompleteAdaptiveColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (c CompleteColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(c.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CompleteAdaptiveColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
// profiles, with separate options for light and dark backgrounds. Automatic
|
||||
// color degradation will not be performed.
|
||||
type CompleteAdaptiveColor struct {
|
||||
Light CompleteColor
|
||||
Dark CompleteColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (cac CompleteAdaptiveColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
if r.HasDarkBackground() {
|
||||
return cac.Dark.color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cac.Light.color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (cac CompleteAdaptiveColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(cac.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
542
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/get.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
542
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/get.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,542 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBold returns the style's bold value. If no value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBold() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(boldKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetItalic returns the style's italic value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetItalic() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(italicKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetUnderline returns the style's underline value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetUnderline() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(underlineKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetStrikethrough returns the style's strikethrough value. If no value is set false
|
||||
// is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetStrikethrough() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(strikethroughKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetReverse returns the style's reverse value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetReverse() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(reverseKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBlink returns the style's blink value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBlink() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(blinkKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetFaint returns the style's faint value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetFaint() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(faintKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetForeground returns the style's foreground color. If no value is set
|
||||
// NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(foregroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBackground returns the style's background color. If no value is set
|
||||
// NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(backgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetWidth returns the style's width setting. If no width is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(widthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHeight returns the style's height setting. If no height is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHeight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(heightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetAlign returns the style's implicit horizontal alignment setting.
|
||||
// If no alignment is set Position.Left is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetAlign() Position {
|
||||
v := s.getAsPosition(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
if v == Position(0) {
|
||||
return Left
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetAlignHorizontal returns the style's implicit horizontal alignment setting.
|
||||
// If no alignment is set Position.Left is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetAlignHorizontal() Position {
|
||||
v := s.getAsPosition(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
if v == Position(0) {
|
||||
return Left
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetAlignVertical returns the style's implicit vertical alignment setting.
|
||||
// If no alignment is set Position.Top is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetAlignVertical() Position {
|
||||
v := s.getAsPosition(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
if v == Position(0) {
|
||||
return Top
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPadding returns the style's top, right, bottom, and left padding values,
|
||||
// in that order. 0 is returned for unset values.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPadding() (top, right, bottom, left int) {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingTop returns the style's top padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingTop() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingRight returns the style's right padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingRight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingBottom returns the style's bottom padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingBottom() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingLeft returns the style's left padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingLeft() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalPadding returns the style's left and right padding. Unset
|
||||
// values are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalPadding() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey) + s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalPadding returns the style's top and bottom padding. Unset values
|
||||
// are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalPadding() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey) + s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetColorWhitespace returns the style's whitespace coloring setting. If no
|
||||
// value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetColorWhitespace() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(colorWhitespaceKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMargin returns the style's top, right, bottom, and left margins, in that
|
||||
// order. 0 is returned for unset values.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMargin() (top, right, bottom, left int) {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginTopKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(marginRightKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginTop returns the style's top margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginTop() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginTopKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginRight returns the style's right margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginRight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginBottom returns the style's bottom margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginBottom() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginLeft returns the style's left margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginLeft() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalMargins returns the style's left and right margins. Unset
|
||||
// values are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalMargins() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey) + s.getAsInt(marginRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalMargins returns the style's top and bottom margins. Unset values
|
||||
// are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalMargins() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginTopKey) + s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorder returns the style's border style (type Border) and value for the
|
||||
// top, right, bottom, and left in that order. If no value is set for the
|
||||
// border style, Border{} is returned. For all other unset values false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorder() (b Border, top, right, bottom, left bool) {
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle(),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderStyle returns the style's border style (type Border). If no value
|
||||
// is set Border{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderStyle() Border {
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTop returns the style's top border setting. If no value is set
|
||||
// false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTop() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRight returns the style's right border setting. If no value is set
|
||||
// false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRight() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottom returns the style's bottom border setting. If no value is
|
||||
// set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottom() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeft returns the style's left border setting. If no value is
|
||||
// set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeft() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopForeground returns the style's border top foreground color. If
|
||||
// no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRightForeground returns the style's border right foreground color.
|
||||
// If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRightForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottomForeground returns the style's border bottom foreground
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottomForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeftForeground returns the style's border left foreground
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeftForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopBackground returns the style's border top background color. If
|
||||
// no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRightBackground returns the style's border right background color.
|
||||
// If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRightBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottomBackground returns the style's border bottom background
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottomBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeftBackground returns the style's border left background
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeftBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopWidth returns the width of the top border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the top edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: This function simply calls Style.GetBorderTopSize.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.GetBorderTopSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopSize returns the width of the top border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the top edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetTopSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeftSize returns the width of the left border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the left edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeftSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetLeftSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottomSize returns the width of the bottom border. If borders
|
||||
// contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border
|
||||
// exists on the left edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottomSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetBottomSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRightSize returns the width of the right border. If borders
|
||||
// contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border
|
||||
// exists on the right edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRightSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetRightSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalBorderSize returns the width of the horizontal borders. If
|
||||
// borders contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no
|
||||
// border exists on the horizontal edges, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalBorderSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetBorderLeftSize() + s.GetBorderRightSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalBorderSize returns the width of the vertical borders. If
|
||||
// borders contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no
|
||||
// border exists on the vertical edges, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalBorderSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetBorderTopSize() + s.GetBorderBottomSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetInline returns the style's inline setting. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetInline() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(inlineKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMaxWidth returns the style's max width setting. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMaxWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(maxWidthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMaxHeight returns the style's max height setting. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMaxHeight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(maxHeightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetTabWidth returns the style's tab width setting. If no value is set 4 is
|
||||
// returned which is the implicit default.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetTabWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(tabWidthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetUnderlineSpaces returns whether or not the style is set to underline
|
||||
// spaces. If not value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetUnderlineSpaces() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(underlineSpacesKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetStrikethroughSpaces returns whether or not the style is set to strikethrough
|
||||
// spaces. If not value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetStrikethroughSpaces() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(strikethroughSpacesKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalFrameSize returns the sum of the style's horizontal margins, padding
|
||||
// and border widths.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Provisional: this method may be renamed.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalFrameSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetHorizontalMargins() + s.GetHorizontalPadding() + s.GetHorizontalBorderSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalFrameSize returns the sum of the style's vertical margins, padding
|
||||
// and border widths.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Provisional: this method may be renamed.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalFrameSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetVerticalMargins() + s.GetVerticalPadding() + s.GetVerticalBorderSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetFrameSize returns the sum of the margins, padding and border width for
|
||||
// both the horizontal and vertical margins.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetFrameSize() (x, y int) {
|
||||
return s.GetHorizontalFrameSize(), s.GetVerticalFrameSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetTransform returns the transform set on the style. If no transform is set
|
||||
// nil is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetTransform() func(string) string {
|
||||
return s.getAsTransform(transformKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns whether or not the given property is set.
|
||||
func (s Style) isSet(k propKey) bool {
|
||||
return s.props.has(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsBool(k propKey, defaultVal bool) bool {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return defaultVal
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.attrs&int(k) != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsColor(k propKey) TerminalColor {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return noColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var c TerminalColor
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case foregroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.fgColor
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.bgColor
|
||||
case marginBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.marginBgColor
|
||||
case borderTopForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderTopFgColor
|
||||
case borderRightForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderRightFgColor
|
||||
case borderBottomForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderBottomFgColor
|
||||
case borderLeftForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderLeftFgColor
|
||||
case borderTopBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderTopBgColor
|
||||
case borderRightBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderRightBgColor
|
||||
case borderBottomBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderBottomBgColor
|
||||
case borderLeftBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderLeftBgColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c != nil {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return noColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsInt(k propKey) int {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case widthKey:
|
||||
return s.width
|
||||
case heightKey:
|
||||
return s.height
|
||||
case paddingTopKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingTop
|
||||
case paddingRightKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingRight
|
||||
case paddingBottomKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingBottom
|
||||
case paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingLeft
|
||||
case marginTopKey:
|
||||
return s.marginTop
|
||||
case marginRightKey:
|
||||
return s.marginRight
|
||||
case marginBottomKey:
|
||||
return s.marginBottom
|
||||
case marginLeftKey:
|
||||
return s.marginLeft
|
||||
case maxWidthKey:
|
||||
return s.maxWidth
|
||||
case maxHeightKey:
|
||||
return s.maxHeight
|
||||
case tabWidthKey:
|
||||
return s.tabWidth
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsPosition(k propKey) Position {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return Position(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case alignHorizontalKey:
|
||||
return s.alignHorizontal
|
||||
case alignVerticalKey:
|
||||
return s.alignVertical
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Position(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getBorderStyle() Border {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(borderStyleKey) {
|
||||
return noBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.borderStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsTransform(propKey) func(string) string {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(transformKey) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.transform
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Split a string into lines, additionally returning the size of the widest
|
||||
// line.
|
||||
func getLines(s string) (lines []string, widest int) {
|
||||
lines = strings.Split(s, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
for _, l := range lines {
|
||||
w := ansi.StringWidth(l)
|
||||
if widest < w {
|
||||
widest = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lines, widest
|
||||
}
|
||||
175
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/join.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
175
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/join.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// JoinHorizontal is a utility function for horizontally joining two
|
||||
// potentially multi-lined strings along a vertical axis. The first argument is
|
||||
// the position, with 0 being all the way at the top and 1 being all the way
|
||||
// at the bottom.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you just want to align to the top, center or bottom you may as well just
|
||||
// use the helper constants Top, Center, and Bottom.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// blockB := "...\n...\n..."
|
||||
// blockA := "...\n...\n...\n...\n..."
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join 20% from the top
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(0.2, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join on the top edge
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Top, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
func JoinHorizontal(pos Position, strs ...string) string {
|
||||
if len(strs) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(strs) == 1 {
|
||||
return strs[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// Groups of strings broken into multiple lines
|
||||
blocks = make([][]string, len(strs))
|
||||
|
||||
// Max line widths for the above text blocks
|
||||
maxWidths = make([]int, len(strs))
|
||||
|
||||
// Height of the tallest block
|
||||
maxHeight int
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Break text blocks into lines and get max widths for each text block
|
||||
for i, str := range strs {
|
||||
blocks[i], maxWidths[i] = getLines(str)
|
||||
if len(blocks[i]) > maxHeight {
|
||||
maxHeight = len(blocks[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add extra lines to make each side the same height
|
||||
for i := range blocks {
|
||||
if len(blocks[i]) >= maxHeight {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
extraLines := make([]string, maxHeight-len(blocks[i]))
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Top:
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(blocks[i], extraLines...)
|
||||
|
||||
case Bottom:
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(extraLines, blocks[i]...)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // Somewhere in the middle
|
||||
n := len(extraLines)
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(n) * pos.value()))
|
||||
top := n - split
|
||||
bottom := n - top
|
||||
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(extraLines[top:], blocks[i]...)
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(blocks[i], extraLines[bottom:]...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Merge lines
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
for i := range blocks[0] { // remember, all blocks have the same number of members now
|
||||
for j, block := range blocks {
|
||||
b.WriteString(block[i])
|
||||
|
||||
// Also make lines the same length
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", maxWidths[j]-ansi.StringWidth(block[i])))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(blocks[0])-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// JoinVertical is a utility function for vertically joining two potentially
|
||||
// multi-lined strings along a horizontal axis. The first argument is the
|
||||
// position, with 0 being all the way to the left and 1 being all the way to
|
||||
// the right.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you just want to align to the left, right or center you may as well just
|
||||
// use the helper constants Left, Center, and Right.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// blockB := "...\n...\n..."
|
||||
// blockA := "...\n...\n...\n...\n..."
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join 20% from the top
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinVertical(0.2, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join on the right edge
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinVertical(lipgloss.Right, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
func JoinVertical(pos Position, strs ...string) string {
|
||||
if len(strs) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(strs) == 1 {
|
||||
return strs[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
blocks = make([][]string, len(strs))
|
||||
maxWidth int
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
for i := range strs {
|
||||
var w int
|
||||
blocks[i], w = getLines(strs[i])
|
||||
if w > maxWidth {
|
||||
maxWidth = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
for i, block := range blocks {
|
||||
for j, line := range block {
|
||||
w := maxWidth - ansi.StringWidth(line)
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Left:
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", w))
|
||||
|
||||
case Right:
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", w))
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // Somewhere in the middle
|
||||
if w < 1 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(w) * pos.value()))
|
||||
right := w - split
|
||||
left := w - right
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", left))
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", right))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write a newline as long as we're not on the last line of the
|
||||
// last block.
|
||||
if !(i == len(blocks)-1 && j == len(block)-1) {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
154
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/position.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
154
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/position.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Position represents a position along a horizontal or vertical axis. It's in
|
||||
// situations where an axis is involved, like alignment, joining, placement and
|
||||
// so on.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A value of 0 represents the start (the left or top) and 1 represents the end
|
||||
// (the right or bottom). 0.5 represents the center.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// There are constants Top, Bottom, Center, Left and Right in this package that
|
||||
// can be used to aid readability.
|
||||
type Position float64
|
||||
|
||||
func (p Position) value() float64 {
|
||||
return math.Min(1, math.Max(0, float64(p)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Position aliases.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Top Position = 0.0
|
||||
Bottom Position = 1.0
|
||||
Center Position = 0.5
|
||||
Left Position = 0.0
|
||||
Right Position = 1.0
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Place places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled box of a given
|
||||
// width or height.
|
||||
func Place(width, height int, hPos, vPos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return renderer.Place(width, height, hPos, vPos, str, opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Place places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled box of a given
|
||||
// width or height.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) Place(width, height int, hPos, vPos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return r.PlaceVertical(height, vPos, r.PlaceHorizontal(width, hPos, str, opts...), opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceHorizontal places a string or text block horizontally in an unstyled
|
||||
// block of a given width. If the given width is shorter than the max width of
|
||||
// the string (measured by its longest line) this will be a noop.
|
||||
func PlaceHorizontal(width int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return renderer.PlaceHorizontal(width, pos, str, opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceHorizontal places a string or text block horizontally in an unstyled
|
||||
// block of a given width. If the given width is shorter than the max width of
|
||||
// the string (measured by its longest line) this will be a noöp.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) PlaceHorizontal(width int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
lines, contentWidth := getLines(str)
|
||||
gap := width - contentWidth
|
||||
|
||||
if gap <= 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ws := newWhitespace(r, opts...)
|
||||
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
for i, l := range lines {
|
||||
// Is this line shorter than the longest line?
|
||||
short := max(0, contentWidth-ansi.StringWidth(l))
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Left:
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(gap + short))
|
||||
|
||||
case Right:
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(gap + short))
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // somewhere in the middle
|
||||
totalGap := gap + short
|
||||
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(totalGap) * pos.value()))
|
||||
left := totalGap - split
|
||||
right := totalGap - left
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(left))
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(right))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if i < len(lines)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceVertical places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled block
|
||||
// of a given height. If the given height is shorter than the height of the
|
||||
// string (measured by its newlines) then this will be a noop.
|
||||
func PlaceVertical(height int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return renderer.PlaceVertical(height, pos, str, opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceVertical places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled block
|
||||
// of a given height. If the given height is shorter than the height of the
|
||||
// string (measured by its newlines) then this will be a noöp.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) PlaceVertical(height int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
contentHeight := strings.Count(str, "\n") + 1
|
||||
gap := height - contentHeight
|
||||
|
||||
if gap <= 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ws := newWhitespace(r, opts...)
|
||||
|
||||
_, width := getLines(str)
|
||||
emptyLine := ws.render(width)
|
||||
b := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Top:
|
||||
b.WriteString(str)
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
for i := 0; i < gap; i++ {
|
||||
b.WriteString(emptyLine)
|
||||
if i < gap-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case Bottom:
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(emptyLine+"\n", gap))
|
||||
b.WriteString(str)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // Somewhere in the middle
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(gap) * pos.value()))
|
||||
top := gap - split
|
||||
bottom := gap - top
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(emptyLine+"\n", top))
|
||||
b.WriteString(str)
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < bottom; i++ {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
b.WriteString(emptyLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
181
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
181
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// We're manually creating the struct here to avoid initializing the output and
|
||||
// query the terminal multiple times.
|
||||
var renderer = &Renderer{
|
||||
output: termenv.DefaultOutput(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Renderer is a lipgloss terminal renderer.
|
||||
type Renderer struct {
|
||||
output *termenv.Output
|
||||
colorProfile termenv.Profile
|
||||
hasDarkBackground bool
|
||||
|
||||
getColorProfile sync.Once
|
||||
explicitColorProfile bool
|
||||
|
||||
getBackgroundColor sync.Once
|
||||
explicitBackgroundColor bool
|
||||
|
||||
mtx sync.RWMutex
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultRenderer returns the default renderer.
|
||||
func DefaultRenderer() *Renderer {
|
||||
return renderer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDefaultRenderer sets the default global renderer.
|
||||
func SetDefaultRenderer(r *Renderer) {
|
||||
renderer = r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewRenderer creates a new Renderer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// w will be used to determine the terminal's color capabilities.
|
||||
func NewRenderer(w io.Writer, opts ...termenv.OutputOption) *Renderer {
|
||||
r := &Renderer{
|
||||
output: termenv.NewOutput(w, opts...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Output returns the termenv output.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) Output() *termenv.Output {
|
||||
r.mtx.RLock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.RUnlock()
|
||||
return r.output
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetOutput sets the termenv output.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) SetOutput(o *termenv.Output) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
r.output = o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ColorProfile returns the detected termenv color profile.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) ColorProfile() termenv.Profile {
|
||||
r.mtx.RLock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if !r.explicitColorProfile {
|
||||
r.getColorProfile.Do(func() {
|
||||
// NOTE: we don't need to lock here because sync.Once provides its
|
||||
// own locking mechanism.
|
||||
r.colorProfile = r.output.EnvColorProfile()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return r.colorProfile
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ColorProfile returns the detected termenv color profile.
|
||||
func ColorProfile() termenv.Profile {
|
||||
return renderer.ColorProfile()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColorProfile sets the color profile on the renderer. This function exists
|
||||
// mostly for testing purposes so that you can assure you're testing against
|
||||
// a specific profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the color
|
||||
// profile will detect and cache the terminal's color capabilities and choose
|
||||
// the best available profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Available color profiles are:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// termenv.Ascii // no color, 1-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI //16 colors, 4-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI256 // 256 colors, 8-bit
|
||||
// termenv.TrueColor // 16,777,216 colors, 24-bit
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) SetColorProfile(p termenv.Profile) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.colorProfile = p
|
||||
r.explicitColorProfile = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColorProfile sets the color profile on the default renderer. This
|
||||
// function exists mostly for testing purposes so that you can assure you're
|
||||
// testing against a specific profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the color
|
||||
// profile will detect and cache the terminal's color capabilities and choose
|
||||
// the best available profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Available color profiles are:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// termenv.Ascii // no color, 1-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI //16 colors, 4-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI256 // 256 colors, 8-bit
|
||||
// termenv.TrueColor // 16,777,216 colors, 24-bit
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func SetColorProfile(p termenv.Profile) {
|
||||
renderer.SetColorProfile(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasDarkBackground returns whether or not the terminal has a dark background.
|
||||
func HasDarkBackground() bool {
|
||||
return renderer.HasDarkBackground()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasDarkBackground returns whether or not the renderer will render to a dark
|
||||
// background. A dark background can either be auto-detected, or set explicitly
|
||||
// on the renderer.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) HasDarkBackground() bool {
|
||||
r.mtx.RLock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if !r.explicitBackgroundColor {
|
||||
r.getBackgroundColor.Do(func() {
|
||||
// NOTE: we don't need to lock here because sync.Once provides its
|
||||
// own locking mechanism.
|
||||
r.hasDarkBackground = r.output.HasDarkBackground()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return r.hasDarkBackground
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHasDarkBackground sets the background color detection value for the
|
||||
// default renderer. This function exists mostly for testing purposes so that
|
||||
// you can assure you're testing against a specific background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the
|
||||
// backgrounds value will be automatically detected and cached against the
|
||||
// terminal's current background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func SetHasDarkBackground(b bool) {
|
||||
renderer.SetHasDarkBackground(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHasDarkBackground sets the background color detection value on the
|
||||
// renderer. This function exists mostly for testing purposes so that you can
|
||||
// assure you're testing against a specific background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the
|
||||
// backgrounds value will be automatically detected and cached against the
|
||||
// terminal's current background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) SetHasDarkBackground(b bool) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.hasDarkBackground = b
|
||||
r.explicitBackgroundColor = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
43
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/runes.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
43
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/runes.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// StyleRunes apply a given style to runes at the given indices in the string.
|
||||
// Note that you must provide styling options for both matched and unmatched
|
||||
// runes. Indices out of bounds will be ignored.
|
||||
func StyleRunes(str string, indices []int, matched, unmatched Style) string {
|
||||
// Convert slice of indices to a map for easier lookups
|
||||
m := make(map[int]struct{})
|
||||
for _, i := range indices {
|
||||
m[i] = struct{}{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
out strings.Builder
|
||||
group strings.Builder
|
||||
style Style
|
||||
runes = []rune(str)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
for i, r := range runes {
|
||||
group.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
|
||||
_, matches := m[i]
|
||||
_, nextMatches := m[i+1]
|
||||
|
||||
if matches != nextMatches || i == len(runes)-1 {
|
||||
// Flush
|
||||
if matches {
|
||||
style = matched
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
style = unmatched
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(style.Render(group.String()))
|
||||
group.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return out.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
799
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/set.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
799
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/set.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,799 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a value on the underlying rules map.
|
||||
func (s *Style) set(key propKey, value interface{}) {
|
||||
// We don't allow negative integers on any of our other values, so just keep
|
||||
// them at zero or above. We could use uints instead, but the
|
||||
// conversions are a little tedious, so we're sticking with ints for
|
||||
// sake of usability.
|
||||
switch key { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case foregroundKey:
|
||||
s.fgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
s.bgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case widthKey:
|
||||
s.width = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case heightKey:
|
||||
s.height = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case alignHorizontalKey:
|
||||
s.alignHorizontal = value.(Position)
|
||||
case alignVerticalKey:
|
||||
s.alignVertical = value.(Position)
|
||||
case paddingTopKey:
|
||||
s.paddingTop = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case paddingRightKey:
|
||||
s.paddingRight = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case paddingBottomKey:
|
||||
s.paddingBottom = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
s.paddingLeft = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginTopKey:
|
||||
s.marginTop = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginRightKey:
|
||||
s.marginRight = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginBottomKey:
|
||||
s.marginBottom = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginLeftKey:
|
||||
s.marginLeft = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.marginBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderStyleKey:
|
||||
s.borderStyle = value.(Border)
|
||||
case borderTopForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderTopFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderRightForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderRightFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderBottomForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderBottomFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderLeftForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderLeftFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderTopBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderTopBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderRightBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderRightBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderBottomBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderBottomBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderLeftBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderLeftBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case maxWidthKey:
|
||||
s.maxWidth = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case maxHeightKey:
|
||||
s.maxHeight = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case tabWidthKey:
|
||||
// TabWidth is the only property that may have a negative value (and
|
||||
// that negative value can be no less than -1).
|
||||
s.tabWidth = value.(int)
|
||||
case transformKey:
|
||||
s.transform = value.(func(string) string)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if v, ok := value.(bool); ok { //nolint:nestif
|
||||
if v {
|
||||
s.attrs |= int(key)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s.attrs &^= int(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if attrs, ok := value.(int); ok {
|
||||
// bool attrs
|
||||
if attrs&int(key) != 0 {
|
||||
s.attrs |= int(key)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s.attrs &^= int(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set the prop on
|
||||
s.props = s.props.set(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setFrom sets the property from another style.
|
||||
func (s *Style) setFrom(key propKey, i Style) {
|
||||
switch key { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case foregroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(foregroundKey, i.fgColor)
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(backgroundKey, i.bgColor)
|
||||
case widthKey:
|
||||
s.set(widthKey, i.width)
|
||||
case heightKey:
|
||||
s.set(heightKey, i.height)
|
||||
case alignHorizontalKey:
|
||||
s.set(alignHorizontalKey, i.alignHorizontal)
|
||||
case alignVerticalKey:
|
||||
s.set(alignVerticalKey, i.alignVertical)
|
||||
case paddingTopKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingTopKey, i.paddingTop)
|
||||
case paddingRightKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingRightKey, i.paddingRight)
|
||||
case paddingBottomKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingBottomKey, i.paddingBottom)
|
||||
case paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingLeftKey, i.paddingLeft)
|
||||
case marginTopKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginTopKey, i.marginTop)
|
||||
case marginRightKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginRightKey, i.marginRight)
|
||||
case marginBottomKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginBottomKey, i.marginBottom)
|
||||
case marginLeftKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginLeftKey, i.marginLeft)
|
||||
case marginBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginBackgroundKey, i.marginBgColor)
|
||||
case borderStyleKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderStyleKey, i.borderStyle)
|
||||
case borderTopForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderTopForegroundKey, i.borderTopFgColor)
|
||||
case borderRightForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderRightForegroundKey, i.borderRightFgColor)
|
||||
case borderBottomForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomForegroundKey, i.borderBottomFgColor)
|
||||
case borderLeftForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftForegroundKey, i.borderLeftFgColor)
|
||||
case borderTopBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderTopBackgroundKey, i.borderTopBgColor)
|
||||
case borderRightBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderRightBackgroundKey, i.borderRightBgColor)
|
||||
case borderBottomBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomBackgroundKey, i.borderBottomBgColor)
|
||||
case borderLeftBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftBackgroundKey, i.borderLeftBgColor)
|
||||
case maxWidthKey:
|
||||
s.set(maxWidthKey, i.maxWidth)
|
||||
case maxHeightKey:
|
||||
s.set(maxHeightKey, i.maxHeight)
|
||||
case tabWidthKey:
|
||||
s.set(tabWidthKey, i.tabWidth)
|
||||
case transformKey:
|
||||
s.set(transformKey, i.transform)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// Set attributes for set bool properties
|
||||
s.set(key, i.attrs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func colorOrNil(c interface{}) TerminalColor {
|
||||
if c, ok := c.(TerminalColor); ok {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bold sets a bold formatting rule.
|
||||
func (s Style) Bold(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(boldKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Italic sets an italic formatting rule. In some terminal emulators this will
|
||||
// render with "reverse" coloring if not italic font variant is available.
|
||||
func (s Style) Italic(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(italicKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Underline sets an underline rule. By default, underlines will not be drawn on
|
||||
// whitespace like margins and padding. To change this behavior set
|
||||
// UnderlineSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) Underline(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(underlineKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Strikethrough sets a strikethrough rule. By default, strikes will not be
|
||||
// drawn on whitespace like margins and padding. To change this behavior set
|
||||
// StrikethroughSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) Strikethrough(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(strikethroughKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reverse sets a rule for inverting foreground and background colors.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reverse(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(reverseKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Blink sets a rule for blinking foreground text.
|
||||
func (s Style) Blink(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(blinkKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Faint sets a rule for rendering the foreground color in a dimmer shade.
|
||||
func (s Style) Faint(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(faintKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Foreground sets a foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Sets the foreground to blue
|
||||
// s := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("#0000ff"))
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Removes the foreground color
|
||||
// s.Foreground(lipgloss.NoColor)
|
||||
func (s Style) Foreground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(foregroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Background sets a background color.
|
||||
func (s Style) Background(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(backgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Width sets the width of the block before applying margins. The width, if
|
||||
// set, also determines where text will wrap.
|
||||
func (s Style) Width(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(widthKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height sets the height of the block before applying margins. If the height of
|
||||
// the text block is less than this value after applying padding (or not), the
|
||||
// block will be set to this height.
|
||||
func (s Style) Height(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(heightKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Align is a shorthand method for setting horizontal and vertical alignment.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the position value is applied to the horizontal alignment.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the value is applied to the horizontal and vertical
|
||||
// alignments, in that order.
|
||||
func (s Style) Align(p ...Position) Style {
|
||||
if len(p) > 0 {
|
||||
s.set(alignHorizontalKey, p[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(p) > 1 {
|
||||
s.set(alignVerticalKey, p[1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AlignHorizontal sets a horizontal text alignment rule.
|
||||
func (s Style) AlignHorizontal(p Position) Style {
|
||||
s.set(alignHorizontalKey, p)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AlignVertical sets a vertical text alignment rule.
|
||||
func (s Style) AlignVertical(p Position) Style {
|
||||
s.set(alignVerticalKey, p)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Padding is a shorthand method for setting padding on all sides at once.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the value is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the value is applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the value is applied to the top side, the horizontal
|
||||
// sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the value is applied clockwise starting from the top
|
||||
// side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments no padding will be added.
|
||||
func (s Style) Padding(i ...int) Style {
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesInt(i...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(paddingTopKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(paddingRightKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(paddingBottomKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(paddingLeftKey, left)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingLeft adds padding on the left.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingLeft(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingLeftKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingRight adds padding on the right.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingRight(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingRightKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingTop adds padding to the top of the block.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingTop(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingTopKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingBottom adds padding to the bottom of the block.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingBottom(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingBottomKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ColorWhitespace determines whether or not the background color should be
|
||||
// applied to the padding. This is true by default as it's more than likely the
|
||||
// desired and expected behavior, but it can be disabled for certain graphic
|
||||
// effects.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Just use margins and padding.
|
||||
func (s Style) ColorWhitespace(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(colorWhitespaceKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Margin is a shorthand method for setting margins on all sides at once.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the value is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the value is applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the value is applied to the top side, the horizontal
|
||||
// sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the value is applied clockwise starting from the top
|
||||
// side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments no margin will be added.
|
||||
func (s Style) Margin(i ...int) Style {
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesInt(i...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(marginTopKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(marginRightKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(marginBottomKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(marginLeftKey, left)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginLeft sets the value of the left margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginLeft(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginLeftKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginRight sets the value of the right margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginRight(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginRightKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginTop sets the value of the top margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginTop(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginTopKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginBottom sets the value of the bottom margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginBottom(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginBottomKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginBackground sets the background color of the margin. Note that this is
|
||||
// also set when inheriting from a style with a background color. In that case
|
||||
// the background color on that style will set the margin color on this style.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Border is shorthand for setting the border style and which sides should
|
||||
// have a border at once. The variadic argument sides works as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one value, the value is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two values, the values are applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three values, the values are applied to the top side, the horizontal
|
||||
// sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four values, the values are applied clockwise starting from the top
|
||||
// side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments the border will be applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Applies borders to the top and bottom only
|
||||
// lipgloss.NewStyle().Border(lipgloss.NormalBorder(), true, false)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Applies rounded borders to the right and bottom only
|
||||
// lipgloss.NewStyle().Border(lipgloss.RoundedBorder(), false, true, true, false)
|
||||
func (s Style) Border(b Border, sides ...bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderStyleKey, b)
|
||||
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesBool(sides...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
top = true
|
||||
right = true
|
||||
bottom = true
|
||||
left = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(borderTopKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(borderRightKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftKey, left)
|
||||
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderStyle defines the Border on a style. A Border contains a series of
|
||||
// definitions for the sides and corners of a border.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that if border visibility has not been set for any sides when setting
|
||||
// the border style, the border will be enabled for all sides during rendering.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// You can define border characters as you'd like, though several default
|
||||
// styles are included: NormalBorder(), RoundedBorder(), BlockBorder(),
|
||||
// OuterHalfBlockBorder(), InnerHalfBlockBorder(), ThickBorder(),
|
||||
// and DoubleBorder().
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// lipgloss.NewStyle().BorderStyle(lipgloss.ThickBorder())
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderStyle(b Border) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderStyleKey, b)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderTop determines whether or not to draw a top border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderTop(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderTopKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRight determines whether or not to draw a right border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderRight(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderRightKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBottom determines whether or not to draw a bottom border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBottom(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderLeft determines whether or not to draw a left border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderLeft(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderForeground is a shorthand function for setting all of the
|
||||
// foreground colors of the borders at once. The arguments work as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the argument is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the arguments are applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the arguments are applied to the top side, the
|
||||
// horizontal sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the arguments are applied clockwise starting from the
|
||||
// top side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments nothing will be set.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderForeground(c ...TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
if len(c) == 0 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesColor(c...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(borderTopForegroundKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(borderRightForegroundKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomForegroundKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftForegroundKey, left)
|
||||
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderTopForeground set the foreground color for the top of the border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderTopForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderTopForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRightForeground sets the foreground color for the right side of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderRightForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderRightForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBottomForeground sets the foreground color for the bottom of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBottomForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderLeftForeground sets the foreground color for the left side of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderLeftForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBackground is a shorthand function for setting all of the
|
||||
// background colors of the borders at once. The arguments work as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the argument is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the arguments are applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the arguments are applied to the top side, the
|
||||
// horizontal sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the arguments are applied clockwise starting from the
|
||||
// top side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments nothing will be set.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBackground(c ...TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
if len(c) == 0 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesColor(c...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(borderTopBackgroundKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(borderRightBackgroundKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomBackgroundKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftBackgroundKey, left)
|
||||
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderTopBackground sets the background color of the top of the border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderTopBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderTopBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRightBackground sets the background color of right side the border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderRightBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderRightBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBottomBackground sets the background color of the bottom of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBottomBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderLeftBackground set the background color of the left side of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderLeftBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Inline makes rendering output one line and disables the rendering of
|
||||
// margins, padding and borders. This is useful when you need a style to apply
|
||||
// only to font rendering and don't want it to change any physical dimensions.
|
||||
// It works well with Style.MaxWidth.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because this in intended to be used at the time of render, this method will
|
||||
// not mutate the style and instead return a copy.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var userInput string = "..."
|
||||
// var userStyle = text.Style{ /* ... */ }
|
||||
// fmt.Println(userStyle.Inline(true).Render(userInput))
|
||||
func (s Style) Inline(v bool) Style {
|
||||
o := s // copy
|
||||
o.set(inlineKey, v)
|
||||
return o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxWidth applies a max width to a given style. This is useful in enforcing
|
||||
// a certain width at render time, particularly with arbitrary strings and
|
||||
// styles.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because this in intended to be used at the time of render, this method will
|
||||
// not mutate the style and instead return a copy.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var userInput string = "..."
|
||||
// var userStyle = text.Style{ /* ... */ }
|
||||
// fmt.Println(userStyle.MaxWidth(16).Render(userInput))
|
||||
func (s Style) MaxWidth(n int) Style {
|
||||
o := s // copy
|
||||
o.set(maxWidthKey, n)
|
||||
return o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxHeight applies a max height to a given style. This is useful in enforcing
|
||||
// a certain height at render time, particularly with arbitrary strings and
|
||||
// styles.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because this in intended to be used at the time of render, this method will
|
||||
// not mutate the style and instead returns a copy.
|
||||
func (s Style) MaxHeight(n int) Style {
|
||||
o := s // copy
|
||||
o.set(maxHeightKey, n)
|
||||
return o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoTabConversion can be passed to [Style.TabWidth] to disable the replacement
|
||||
// of tabs with spaces at render time.
|
||||
const NoTabConversion = -1
|
||||
|
||||
// TabWidth sets the number of spaces that a tab (/t) should be rendered as.
|
||||
// When set to 0, tabs will be removed. To disable the replacement of tabs with
|
||||
// spaces entirely, set this to [NoTabConversion].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// By default, tabs will be replaced with 4 spaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) TabWidth(n int) Style {
|
||||
if n <= -1 {
|
||||
n = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.set(tabWidthKey, n)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineSpaces determines whether to underline spaces between words. By
|
||||
// default, this is true. Spaces can also be underlined without underlining the
|
||||
// text itself.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnderlineSpaces(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(underlineSpacesKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StrikethroughSpaces determines whether to apply strikethroughs to spaces
|
||||
// between words. By default, this is true. Spaces can also be struck without
|
||||
// underlining the text itself.
|
||||
func (s Style) StrikethroughSpaces(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(strikethroughSpacesKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transform applies a given function to a string at render time, allowing for
|
||||
// the string being rendered to be manipuated.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// s := NewStyle().Transform(strings.ToUpper)
|
||||
// fmt.Println(s.Render("raow!") // "RAOW!"
|
||||
func (s Style) Transform(fn func(string) string) Style {
|
||||
s.set(transformKey, fn)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Renderer sets the renderer for the style. This is useful for changing the
|
||||
// renderer for a style that is being used in a different context.
|
||||
func (s Style) Renderer(r *Renderer) Style {
|
||||
s.r = r
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// whichSidesInt is a helper method for setting values on sides of a block based
|
||||
// on the number of arguments. It follows the CSS shorthand rules for blocks
|
||||
// like margin, padding. and borders. Here are how the rules work:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0 args: do nothing
|
||||
// 1 arg: all sides
|
||||
// 2 args: top -> bottom
|
||||
// 3 args: top -> horizontal -> bottom
|
||||
// 4 args: top -> right -> bottom -> left
|
||||
// 5+ args: do nothing.
|
||||
func whichSidesInt(i ...int) (top, right, bottom, left int, ok bool) {
|
||||
switch len(i) {
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[0]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 2: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 3: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 4: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
left = i[3]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return top, right, bottom, left, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// whichSidesBool is like whichSidesInt, except it operates on a series of
|
||||
// boolean values. See the comment on whichSidesInt for details on how this
|
||||
// works.
|
||||
func whichSidesBool(i ...bool) (top, right, bottom, left bool, ok bool) {
|
||||
switch len(i) {
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[0]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 2: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 3: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 4: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
left = i[3]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return top, right, bottom, left, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// whichSidesColor is like whichSides, except it operates on a series of
|
||||
// boolean values. See the comment on whichSidesInt for details on how this
|
||||
// works.
|
||||
func whichSidesColor(i ...TerminalColor) (top, right, bottom, left TerminalColor, ok bool) {
|
||||
switch len(i) {
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[0]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 2: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 3: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 4: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
left = i[3]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return top, right, bottom, left, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
41
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/size.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
41
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/size.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Width returns the cell width of characters in the string. ANSI sequences are
|
||||
// ignored and characters wider than one cell (such as Chinese characters and
|
||||
// emojis) are appropriately measured.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// You should use this instead of len(string) len([]rune(string) as neither
|
||||
// will give you accurate results.
|
||||
func Width(str string) (width int) {
|
||||
for _, l := range strings.Split(str, "\n") {
|
||||
w := ansi.StringWidth(l)
|
||||
if w > width {
|
||||
width = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return width
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height returns height of a string in cells. This is done simply by
|
||||
// counting \n characters. If your strings use \r\n for newlines you should
|
||||
// convert them to \n first, or simply write a separate function for measuring
|
||||
// height.
|
||||
func Height(str string) int {
|
||||
return strings.Count(str, "\n") + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Size returns the width and height of the string in cells. ANSI sequences are
|
||||
// ignored and characters wider than one cell (such as Chinese characters and
|
||||
// emojis) are appropriately measured.
|
||||
func Size(str string) (width, height int) {
|
||||
width = Width(str)
|
||||
height = Height(str)
|
||||
return width, height
|
||||
}
|
||||
587
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
587
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,587 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const tabWidthDefault = 4
|
||||
|
||||
// Property for a key.
|
||||
type propKey int64
|
||||
|
||||
// Available properties.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// Boolean props come first.
|
||||
boldKey propKey = 1 << iota
|
||||
italicKey
|
||||
underlineKey
|
||||
strikethroughKey
|
||||
reverseKey
|
||||
blinkKey
|
||||
faintKey
|
||||
underlineSpacesKey
|
||||
strikethroughSpacesKey
|
||||
colorWhitespaceKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Non-boolean props.
|
||||
foregroundKey
|
||||
backgroundKey
|
||||
widthKey
|
||||
heightKey
|
||||
alignHorizontalKey
|
||||
alignVerticalKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Padding.
|
||||
paddingTopKey
|
||||
paddingRightKey
|
||||
paddingBottomKey
|
||||
paddingLeftKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Margins.
|
||||
marginTopKey
|
||||
marginRightKey
|
||||
marginBottomKey
|
||||
marginLeftKey
|
||||
marginBackgroundKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border runes.
|
||||
borderStyleKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border edges.
|
||||
borderTopKey
|
||||
borderRightKey
|
||||
borderBottomKey
|
||||
borderLeftKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border foreground colors.
|
||||
borderTopForegroundKey
|
||||
borderRightForegroundKey
|
||||
borderBottomForegroundKey
|
||||
borderLeftForegroundKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border background colors.
|
||||
borderTopBackgroundKey
|
||||
borderRightBackgroundKey
|
||||
borderBottomBackgroundKey
|
||||
borderLeftBackgroundKey
|
||||
|
||||
inlineKey
|
||||
maxWidthKey
|
||||
maxHeightKey
|
||||
tabWidthKey
|
||||
|
||||
transformKey
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// props is a set of properties.
|
||||
type props int64
|
||||
|
||||
// set sets a property.
|
||||
func (p props) set(k propKey) props {
|
||||
return p | props(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unset unsets a property.
|
||||
func (p props) unset(k propKey) props {
|
||||
return p &^ props(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// has checks if a property is set.
|
||||
func (p props) has(k propKey) bool {
|
||||
return p&props(k) != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewStyle returns a new, empty Style. While it's syntactic sugar for the
|
||||
// Style{} primitive, it's recommended to use this function for creating styles
|
||||
// in case the underlying implementation changes. It takes an optional string
|
||||
// value to be set as the underlying string value for this style.
|
||||
func NewStyle() Style {
|
||||
return renderer.NewStyle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewStyle returns a new, empty Style. While it's syntactic sugar for the
|
||||
// Style{} primitive, it's recommended to use this function for creating styles
|
||||
// in case the underlying implementation changes. It takes an optional string
|
||||
// value to be set as the underlying string value for this style.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) NewStyle() Style {
|
||||
s := Style{r: r}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Style contains a set of rules that comprise a style as a whole.
|
||||
type Style struct {
|
||||
r *Renderer
|
||||
props props
|
||||
value string
|
||||
|
||||
// we store bool props values here
|
||||
attrs int
|
||||
|
||||
// props that have values
|
||||
fgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
bgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
|
||||
alignHorizontal Position
|
||||
alignVertical Position
|
||||
|
||||
paddingTop int
|
||||
paddingRight int
|
||||
paddingBottom int
|
||||
paddingLeft int
|
||||
|
||||
marginTop int
|
||||
marginRight int
|
||||
marginBottom int
|
||||
marginLeft int
|
||||
marginBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
|
||||
borderStyle Border
|
||||
borderTopFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderRightFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderBottomFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderLeftFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderTopBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderRightBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderBottomBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderLeftBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
|
||||
maxWidth int
|
||||
maxHeight int
|
||||
tabWidth int
|
||||
|
||||
transform func(string) string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// joinString joins a list of strings into a single string separated with a
|
||||
// space.
|
||||
func joinString(strs ...string) string {
|
||||
return strings.Join(strs, " ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetString sets the underlying string value for this style. To render once
|
||||
// the underlying string is set, use the Style.String. This method is
|
||||
// a convenience for cases when having a stringer implementation is handy, such
|
||||
// as when using fmt.Sprintf. You can also simply define a style and render out
|
||||
// strings directly with Style.Render.
|
||||
func (s Style) SetString(strs ...string) Style {
|
||||
s.value = joinString(strs...)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the raw, unformatted, underlying string value for this style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Value() string {
|
||||
return s.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements stringer for a Style, returning the rendered result based
|
||||
// on the rules in this style. An underlying string value must be set with
|
||||
// Style.SetString prior to using this method.
|
||||
func (s Style) String() string {
|
||||
return s.Render()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy returns a copy of this style, including any underlying string values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: to copy just use assignment (i.e. a := b). All methods also
|
||||
// return a new style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Copy() Style {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Inherit overlays the style in the argument onto this style by copying each explicitly
|
||||
// set value from the argument style onto this style if it is not already explicitly set.
|
||||
// Existing set values are kept intact and not overwritten.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Margins, padding, and underlying string values are not inherited.
|
||||
func (s Style) Inherit(i Style) Style {
|
||||
for k := boldKey; k <= transformKey; k <<= 1 {
|
||||
if !i.isSet(k) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case marginTopKey, marginRightKey, marginBottomKey, marginLeftKey:
|
||||
// Margins are not inherited
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case paddingTopKey, paddingRightKey, paddingBottomKey, paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
// Padding is not inherited
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
// The margins also inherit the background color
|
||||
if !s.isSet(marginBackgroundKey) && !i.isSet(marginBackgroundKey) {
|
||||
s.set(marginBackgroundKey, i.bgColor)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.setFrom(k, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render applies the defined style formatting to a given string.
|
||||
func (s Style) Render(strs ...string) string {
|
||||
if s.r == nil {
|
||||
s.r = renderer
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.value != "" {
|
||||
strs = append([]string{s.value}, strs...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
str = joinString(strs...)
|
||||
|
||||
p = s.r.ColorProfile()
|
||||
te = p.String()
|
||||
teSpace = p.String()
|
||||
teWhitespace = p.String()
|
||||
|
||||
bold = s.getAsBool(boldKey, false)
|
||||
italic = s.getAsBool(italicKey, false)
|
||||
underline = s.getAsBool(underlineKey, false)
|
||||
strikethrough = s.getAsBool(strikethroughKey, false)
|
||||
reverse = s.getAsBool(reverseKey, false)
|
||||
blink = s.getAsBool(blinkKey, false)
|
||||
faint = s.getAsBool(faintKey, false)
|
||||
|
||||
fg = s.getAsColor(foregroundKey)
|
||||
bg = s.getAsColor(backgroundKey)
|
||||
|
||||
width = s.getAsInt(widthKey)
|
||||
height = s.getAsInt(heightKey)
|
||||
horizontalAlign = s.getAsPosition(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
verticalAlign = s.getAsPosition(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
|
||||
topPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
rightPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
bottomPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
leftPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
|
||||
colorWhitespace = s.getAsBool(colorWhitespaceKey, true)
|
||||
inline = s.getAsBool(inlineKey, false)
|
||||
maxWidth = s.getAsInt(maxWidthKey)
|
||||
maxHeight = s.getAsInt(maxHeightKey)
|
||||
|
||||
underlineSpaces = s.getAsBool(underlineSpacesKey, false) || (underline && s.getAsBool(underlineSpacesKey, true))
|
||||
strikethroughSpaces = s.getAsBool(strikethroughSpacesKey, false) || (strikethrough && s.getAsBool(strikethroughSpacesKey, true))
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we need to style whitespace (padding and space outside
|
||||
// paragraphs) separately?
|
||||
styleWhitespace = reverse
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we need to style spaces separately?
|
||||
useSpaceStyler = (underline && !underlineSpaces) || (strikethrough && !strikethroughSpaces) || underlineSpaces || strikethroughSpaces
|
||||
|
||||
transform = s.getAsTransform(transformKey)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if transform != nil {
|
||||
str = transform(str)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if s.props == 0 {
|
||||
return s.maybeConvertTabs(str)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Enable support for ANSI on the legacy Windows cmd.exe console. This is a
|
||||
// no-op on non-Windows systems and on Windows runs only once.
|
||||
enableLegacyWindowsANSI()
|
||||
|
||||
if bold {
|
||||
te = te.Bold()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if italic {
|
||||
te = te.Italic()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if underline {
|
||||
te = te.Underline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if reverse {
|
||||
if reverse {
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Reverse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
te = te.Reverse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if blink {
|
||||
te = te.Blink()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if faint {
|
||||
te = te.Faint()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if fg != noColor {
|
||||
te = te.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
if styleWhitespace {
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if useSpaceStyler {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if bg != noColor {
|
||||
te = te.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
if colorWhitespace {
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if useSpaceStyler {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if underline {
|
||||
te = te.Underline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if strikethrough {
|
||||
te = te.CrossOut()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if underlineSpaces {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.Underline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if strikethroughSpaces {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.CrossOut()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Potentially convert tabs to spaces
|
||||
str = s.maybeConvertTabs(str)
|
||||
|
||||
// Strip newlines in single line mode
|
||||
if inline {
|
||||
str = strings.ReplaceAll(str, "\n", "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Word wrap
|
||||
if !inline && width > 0 {
|
||||
wrapAt := width - leftPadding - rightPadding
|
||||
str = ansi.Wrap(str, wrapAt, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render core text
|
||||
{
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
l := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
for i := range l {
|
||||
if useSpaceStyler {
|
||||
// Look for spaces and apply a different styler
|
||||
for _, r := range l[i] {
|
||||
if unicode.IsSpace(r) {
|
||||
b.WriteString(teSpace.Styled(string(r)))
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString(te.Styled(string(r)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteString(te.Styled(l[i]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i != len(l)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
str = b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Padding
|
||||
if !inline { //nolint:nestif
|
||||
if leftPadding > 0 {
|
||||
var st *termenv.Style
|
||||
if colorWhitespace || styleWhitespace {
|
||||
st = &teWhitespace
|
||||
}
|
||||
str = padLeft(str, leftPadding, st)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if rightPadding > 0 {
|
||||
var st *termenv.Style
|
||||
if colorWhitespace || styleWhitespace {
|
||||
st = &teWhitespace
|
||||
}
|
||||
str = padRight(str, rightPadding, st)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if topPadding > 0 {
|
||||
str = strings.Repeat("\n", topPadding) + str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if bottomPadding > 0 {
|
||||
str += strings.Repeat("\n", bottomPadding)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height
|
||||
if height > 0 {
|
||||
str = alignTextVertical(str, verticalAlign, height, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set alignment. This will also pad short lines with spaces so that all
|
||||
// lines are the same length, so we run it under a few different conditions
|
||||
// beyond alignment.
|
||||
{
|
||||
numLines := strings.Count(str, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
if !(numLines == 0 && width == 0) {
|
||||
var st *termenv.Style
|
||||
if colorWhitespace || styleWhitespace {
|
||||
st = &teWhitespace
|
||||
}
|
||||
str = alignTextHorizontal(str, horizontalAlign, width, st)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !inline {
|
||||
str = s.applyBorder(str)
|
||||
str = s.applyMargins(str, inline)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Truncate according to MaxWidth
|
||||
if maxWidth > 0 {
|
||||
lines := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
for i := range lines {
|
||||
lines[i] = ansi.Truncate(lines[i], maxWidth, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
str = strings.Join(lines, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Truncate according to MaxHeight
|
||||
if maxHeight > 0 {
|
||||
lines := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
height := min(maxHeight, len(lines))
|
||||
if len(lines) > 0 {
|
||||
str = strings.Join(lines[:height], "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) maybeConvertTabs(str string) string {
|
||||
tw := tabWidthDefault
|
||||
if s.isSet(tabWidthKey) {
|
||||
tw = s.getAsInt(tabWidthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch tw {
|
||||
case -1:
|
||||
return str
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return strings.ReplaceAll(str, "\t", "")
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return strings.ReplaceAll(str, "\t", strings.Repeat(" ", tw))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) applyMargins(str string, inline bool) string {
|
||||
var (
|
||||
topMargin = s.getAsInt(marginTopKey)
|
||||
rightMargin = s.getAsInt(marginRightKey)
|
||||
bottomMargin = s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
leftMargin = s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
|
||||
styler termenv.Style
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
bgc := s.getAsColor(marginBackgroundKey)
|
||||
if bgc != noColor {
|
||||
styler = styler.Background(bgc.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add left and right margin
|
||||
str = padLeft(str, leftMargin, &styler)
|
||||
str = padRight(str, rightMargin, &styler)
|
||||
|
||||
// Top/bottom margin
|
||||
if !inline {
|
||||
_, width := getLines(str)
|
||||
spaces := strings.Repeat(" ", width)
|
||||
|
||||
if topMargin > 0 {
|
||||
str = styler.Styled(strings.Repeat(spaces+"\n", topMargin)) + str
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bottomMargin > 0 {
|
||||
str += styler.Styled(strings.Repeat("\n"+spaces, bottomMargin))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply left padding.
|
||||
func padLeft(str string, n int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
return pad(str, -n, style)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply right padding.
|
||||
func padRight(str string, n int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
return pad(str, n, style)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pad adds padding to either the left or right side of a string.
|
||||
// Positive values add to the right side while negative values
|
||||
// add to the left side.
|
||||
func pad(str string, n int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sp := strings.Repeat(" ", abs(n))
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
sp = style.Styled(sp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
l := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
for i := range l {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
// pad right
|
||||
case n > 0:
|
||||
b.WriteString(l[i])
|
||||
b.WriteString(sp)
|
||||
// pad left
|
||||
default:
|
||||
b.WriteString(sp)
|
||||
b.WriteString(l[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if i != len(l)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int { //nolint:unparam
|
||||
if a > b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func abs(a int) int {
|
||||
if a < 0 {
|
||||
return -a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
331
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/unset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
331
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/unset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,331 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
// unset unsets a property from a style.
|
||||
func (s *Style) unset(key propKey) {
|
||||
s.props = s.props.unset(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBold removes the bold style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBold() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(boldKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetItalic removes the italic style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetItalic() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(italicKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetUnderline removes the underline style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetUnderline() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(underlineKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetStrikethrough removes the strikethrough style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetStrikethrough() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(strikethroughKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetReverse removes the reverse style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetReverse() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(reverseKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBlink removes the blink style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBlink() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(blinkKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetFaint removes the faint style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetFaint() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(faintKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetForeground removes the foreground style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(foregroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBackground removes the background style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(backgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetWidth removes the width style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetWidth() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(widthKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetHeight removes the height style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetHeight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(heightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetAlign removes the horizontal and vertical text alignment style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetAlign() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
s.unset(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetAlignHorizontal removes the horizontal text alignment style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetAlignHorizontal() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetAlignVertical removes the vertical text alignment style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetAlignVertical() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPadding removes all padding style rules.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPadding() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
s.unset(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
s.unset(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
s.unset(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingLeft removes the left padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingLeft() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingRight removes the right padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingRight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingTop removes the top padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingTop() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingBottom removes the bottom padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingBottom() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetColorWhitespace removes the rule for coloring padding, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetColorWhitespace() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(colorWhitespaceKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMargins removes all margin style rules.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMargins() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
s.unset(marginRightKey)
|
||||
s.unset(marginTopKey)
|
||||
s.unset(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginLeft removes the left margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginLeft() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginRight removes the right margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginRight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginRightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginTop removes the top margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginTop() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginTopKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginBottom removes the bottom margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginBottom() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginBackground removes the margin's background color. Note that the
|
||||
// margin's background color can be set from the background color of another
|
||||
// style during inheritance.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderStyle removes the border style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderStyle() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderStyleKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTop removes the border top style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTop() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderRight removes the border right style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderRight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBottom removes the border bottom style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBottom() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderLeft removes the border left style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderLeft() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderForeground removes all border foreground color styles, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTopForeground removes the top border foreground color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTopForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderRightForeground removes the right border foreground color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderRightForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBottomForeground removes the bottom border foreground color
|
||||
// rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBottomForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderLeftForeground removes the left border foreground color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderLeftForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBackground removes all border background color styles, if
|
||||
// set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTopBackgroundColor removes the top border background color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: This function simply calls Style.UnsetBorderTopBackground.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTopBackgroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return s.UnsetBorderTopBackground()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTopBackground removes the top border background color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTopBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderRightBackground removes the right border background color
|
||||
// rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderRightBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBottomBackground removes the bottom border background color
|
||||
// rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBottomBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderLeftBackground removes the left border color rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderLeftBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetInline removes the inline style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetInline() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(inlineKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMaxWidth removes the max width style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMaxWidth() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(maxWidthKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMaxHeight removes the max height style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMaxHeight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(maxHeightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetTabWidth removes the tab width style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetTabWidth() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(tabWidthKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetUnderlineSpaces removes the value set by UnderlineSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetUnderlineSpaces() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(underlineSpacesKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetStrikethroughSpaces removes the value set by StrikethroughSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetStrikethroughSpaces() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(strikethroughSpacesKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetTransform removes the value set by Transform.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetTransform() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(transformKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetString sets the underlying string value to the empty string.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetString() Style {
|
||||
s.value = ""
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/whitespace.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/whitespace.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// whitespace is a whitespace renderer.
|
||||
type whitespace struct {
|
||||
re *Renderer
|
||||
style termenv.Style
|
||||
chars string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newWhitespace creates a new whitespace renderer. The order of the options
|
||||
// matters, if you're using WithWhitespaceRenderer, make sure it comes first as
|
||||
// other options might depend on it.
|
||||
func newWhitespace(r *Renderer, opts ...WhitespaceOption) *whitespace {
|
||||
w := &whitespace{
|
||||
re: r,
|
||||
style: r.ColorProfile().String(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, opt := range opts {
|
||||
opt(w)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return w
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render whitespaces.
|
||||
func (w whitespace) render(width int) string {
|
||||
if w.chars == "" {
|
||||
w.chars = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r := []rune(w.chars)
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
b := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cycle through runes and print them into the whitespace.
|
||||
for i := 0; i < width; {
|
||||
b.WriteRune(r[j])
|
||||
j++
|
||||
if j >= len(r) {
|
||||
j = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += ansi.StringWidth(string(r[j]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill any extra gaps white spaces. This might be necessary if any runes
|
||||
// are more than one cell wide, which could leave a one-rune gap.
|
||||
short := width - ansi.StringWidth(b.String())
|
||||
if short > 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", short))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return w.style.Styled(b.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WhitespaceOption sets a styling rule for rendering whitespace.
|
||||
type WhitespaceOption func(*whitespace)
|
||||
|
||||
// WithWhitespaceForeground sets the color of the characters in the whitespace.
|
||||
func WithWhitespaceForeground(c TerminalColor) WhitespaceOption {
|
||||
return func(w *whitespace) {
|
||||
w.style = w.style.Foreground(c.color(w.re))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithWhitespaceBackground sets the background color of the whitespace.
|
||||
func WithWhitespaceBackground(c TerminalColor) WhitespaceOption {
|
||||
return func(w *whitespace) {
|
||||
w.style = w.style.Background(c.color(w.re))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithWhitespaceChars sets the characters to be rendered in the whitespace.
|
||||
func WithWhitespaceChars(s string) WhitespaceOption {
|
||||
return func(w *whitespace) {
|
||||
w.chars = s
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2023 Charmbracelet, Inc.
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
11
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ansi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
11
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ansi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "io"
|
||||
|
||||
// Execute is a function that "execute" the given escape sequence by writing it
|
||||
// to the provided output writter.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar over [io.WriteString].
|
||||
func Execute(w io.Writer, s string) (int, error) {
|
||||
return io.WriteString(w, s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
8
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ascii.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
8
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ascii.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// SP is the space character (Char: \x20).
|
||||
SP = 0x20
|
||||
// DEL is the delete character (Caret: ^?, Char: \x7f).
|
||||
DEL = 0x7F
|
||||
)
|
||||
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/background.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/background.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SetForegroundColor returns a sequence that sets the default terminal
|
||||
// foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 10 ; color ST
|
||||
// OSC 10 ; color BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where color is the encoded color number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetForegroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]10;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestForegroundColor is a sequence that requests the current default
|
||||
// terminal foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestForegroundColor = "\x1b]10;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBackgroundColor returns a sequence that sets the default terminal
|
||||
// background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 11 ; color ST
|
||||
// OSC 11 ; color BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where color is the encoded color number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetBackgroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]11;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestBackgroundColor is a sequence that requests the current default
|
||||
// terminal background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestBackgroundColor = "\x1b]11;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCursorColor returns a sequence that sets the terminal cursor color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 12 ; color ST
|
||||
// OSC 12 ; color BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where color is the encoded color number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetCursorColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]12;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestCursorColor is a sequence that requests the current terminal cursor
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestCursorColor = "\x1b]12;?\x07"
|
||||
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c0.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c0.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// C0 control characters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// These range from (0x00-0x1F) as defined in ISO 646 (ASCII).
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C0_and_C1_control_codes
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// NUL is the null character (Caret: ^@, Char: \0).
|
||||
NUL = 0x00
|
||||
// SOH is the start of heading character (Caret: ^A).
|
||||
SOH = 0x01
|
||||
// STX is the start of text character (Caret: ^B).
|
||||
STX = 0x02
|
||||
// ETX is the end of text character (Caret: ^C).
|
||||
ETX = 0x03
|
||||
// EOT is the end of transmission character (Caret: ^D).
|
||||
EOT = 0x04
|
||||
// ENQ is the enquiry character (Caret: ^E).
|
||||
ENQ = 0x05
|
||||
// ACK is the acknowledge character (Caret: ^F).
|
||||
ACK = 0x06
|
||||
// BEL is the bell character (Caret: ^G, Char: \a).
|
||||
BEL = 0x07
|
||||
// BS is the backspace character (Caret: ^H, Char: \b).
|
||||
BS = 0x08
|
||||
// HT is the horizontal tab character (Caret: ^I, Char: \t).
|
||||
HT = 0x09
|
||||
// LF is the line feed character (Caret: ^J, Char: \n).
|
||||
LF = 0x0A
|
||||
// VT is the vertical tab character (Caret: ^K, Char: \v).
|
||||
VT = 0x0B
|
||||
// FF is the form feed character (Caret: ^L, Char: \f).
|
||||
FF = 0x0C
|
||||
// CR is the carriage return character (Caret: ^M, Char: \r).
|
||||
CR = 0x0D
|
||||
// SO is the shift out character (Caret: ^N).
|
||||
SO = 0x0E
|
||||
// SI is the shift in character (Caret: ^O).
|
||||
SI = 0x0F
|
||||
// DLE is the data link escape character (Caret: ^P).
|
||||
DLE = 0x10
|
||||
// DC1 is the device control 1 character (Caret: ^Q).
|
||||
DC1 = 0x11
|
||||
// DC2 is the device control 2 character (Caret: ^R).
|
||||
DC2 = 0x12
|
||||
// DC3 is the device control 3 character (Caret: ^S).
|
||||
DC3 = 0x13
|
||||
// DC4 is the device control 4 character (Caret: ^T).
|
||||
DC4 = 0x14
|
||||
// NAK is the negative acknowledge character (Caret: ^U).
|
||||
NAK = 0x15
|
||||
// SYN is the synchronous idle character (Caret: ^V).
|
||||
SYN = 0x16
|
||||
// ETB is the end of transmission block character (Caret: ^W).
|
||||
ETB = 0x17
|
||||
// CAN is the cancel character (Caret: ^X).
|
||||
CAN = 0x18
|
||||
// EM is the end of medium character (Caret: ^Y).
|
||||
EM = 0x19
|
||||
// SUB is the substitute character (Caret: ^Z).
|
||||
SUB = 0x1A
|
||||
// ESC is the escape character (Caret: ^[, Char: \e).
|
||||
ESC = 0x1B
|
||||
// FS is the file separator character (Caret: ^\).
|
||||
FS = 0x1C
|
||||
// GS is the group separator character (Caret: ^]).
|
||||
GS = 0x1D
|
||||
// RS is the record separator character (Caret: ^^).
|
||||
RS = 0x1E
|
||||
// US is the unit separator character (Caret: ^_).
|
||||
US = 0x1F
|
||||
)
|
||||
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c1.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c1.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// C1 control characters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// These range from (0x80-0x9F) as defined in ISO 6429 (ECMA-48).
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C0_and_C1_control_codes
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// PAD is the padding character.
|
||||
PAD = 0x80
|
||||
// HOP is the high octet preset character.
|
||||
HOP = 0x81
|
||||
// BPH is the break permitted here character.
|
||||
BPH = 0x82
|
||||
// NBH is the no break here character.
|
||||
NBH = 0x83
|
||||
// IND is the index character.
|
||||
IND = 0x84
|
||||
// NEL is the next line character.
|
||||
NEL = 0x85
|
||||
// SSA is the start of selected area character.
|
||||
SSA = 0x86
|
||||
// ESA is the end of selected area character.
|
||||
ESA = 0x87
|
||||
// HTS is the horizontal tab set character.
|
||||
HTS = 0x88
|
||||
// HTJ is the horizontal tab with justification character.
|
||||
HTJ = 0x89
|
||||
// VTS is the vertical tab set character.
|
||||
VTS = 0x8A
|
||||
// PLD is the partial line forward character.
|
||||
PLD = 0x8B
|
||||
// PLU is the partial line backward character.
|
||||
PLU = 0x8C
|
||||
// RI is the reverse index character.
|
||||
RI = 0x8D
|
||||
// SS2 is the single shift 2 character.
|
||||
SS2 = 0x8E
|
||||
// SS3 is the single shift 3 character.
|
||||
SS3 = 0x8F
|
||||
// DCS is the device control string character.
|
||||
DCS = 0x90
|
||||
// PU1 is the private use 1 character.
|
||||
PU1 = 0x91
|
||||
// PU2 is the private use 2 character.
|
||||
PU2 = 0x92
|
||||
// STS is the set transmit state character.
|
||||
STS = 0x93
|
||||
// CCH is the cancel character.
|
||||
CCH = 0x94
|
||||
// MW is the message waiting character.
|
||||
MW = 0x95
|
||||
// SPA is the start of guarded area character.
|
||||
SPA = 0x96
|
||||
// EPA is the end of guarded area character.
|
||||
EPA = 0x97
|
||||
// SOS is the start of string character.
|
||||
SOS = 0x98
|
||||
// SGCI is the single graphic character introducer character.
|
||||
SGCI = 0x99
|
||||
// SCI is the single character introducer character.
|
||||
SCI = 0x9A
|
||||
// CSI is the control sequence introducer character.
|
||||
CSI = 0x9B
|
||||
// ST is the string terminator character.
|
||||
ST = 0x9C
|
||||
// OSC is the operating system command character.
|
||||
OSC = 0x9D
|
||||
// PM is the privacy message character.
|
||||
PM = 0x9E
|
||||
// APC is the application program command character.
|
||||
APC = 0x9F
|
||||
)
|
||||
75
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/clipboard.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
75
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/clipboard.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "encoding/base64"
|
||||
|
||||
// Clipboard names.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SystemClipboard = 'c'
|
||||
PrimaryClipboard = 'p'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SetClipboard returns a sequence for manipulating the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 52 ; Pc ; Pd ST
|
||||
// OSC 52 ; Pc ; Pd BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pc is the clipboard name and Pd is the base64 encoded data.
|
||||
// Empty data or invalid base64 data will reset the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetClipboard(c byte, d string) string {
|
||||
if d != "" {
|
||||
d = base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(d))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]52;" + string(c) + ";" + d + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetSystemClipboard returns a sequence for setting the system clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetClipboard(SystemClipboard, d).
|
||||
func SetSystemClipboard(d string) string {
|
||||
return SetClipboard(SystemClipboard, d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetPrimaryClipboard returns a sequence for setting the primary clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetClipboard(PrimaryClipboard, d).
|
||||
func SetPrimaryClipboard(d string) string {
|
||||
return SetClipboard(PrimaryClipboard, d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetClipboard returns a sequence for resetting the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetClipboard(c, "").
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func ResetClipboard(c byte) string {
|
||||
return SetClipboard(c, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetSystemClipboard is a sequence for resetting the system clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to ResetClipboard(SystemClipboard).
|
||||
const ResetSystemClipboard = "\x1b]52;c;\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetPrimaryClipboard is a sequence for resetting the primary clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to ResetClipboard(PrimaryClipboard).
|
||||
const ResetPrimaryClipboard = "\x1b]52;p;\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestClipboard returns a sequence for requesting the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func RequestClipboard(c byte) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]52;" + string(c) + ";?\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestSystemClipboard is a sequence for requesting the system clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to RequestClipboard(SystemClipboard).
|
||||
const RequestSystemClipboard = "\x1b]52;c;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestPrimaryClipboard is a sequence for requesting the primary clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to RequestClipboard(PrimaryClipboard).
|
||||
const RequestPrimaryClipboard = "\x1b]52;p;?\x07"
|
||||
196
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
196
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,196 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Technically speaking, the 16 basic ANSI colors are arbitrary and can be
|
||||
// customized at the terminal level. Given that, we're returning what we feel
|
||||
// are good defaults.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This could also be a slice, but we use a map to make the mappings very
|
||||
// explicit.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://www.ditig.com/publications/256-colors-cheat-sheet
|
||||
var lowANSI = map[uint32]uint32{
|
||||
0: 0x000000, // black
|
||||
1: 0x800000, // red
|
||||
2: 0x008000, // green
|
||||
3: 0x808000, // yellow
|
||||
4: 0x000080, // blue
|
||||
5: 0x800080, // magenta
|
||||
6: 0x008080, // cyan
|
||||
7: 0xc0c0c0, // white
|
||||
8: 0x808080, // bright black
|
||||
9: 0xff0000, // bright red
|
||||
10: 0x00ff00, // bright green
|
||||
11: 0xffff00, // bright yellow
|
||||
12: 0x0000ff, // bright blue
|
||||
13: 0xff00ff, // bright magenta
|
||||
14: 0x00ffff, // bright cyan
|
||||
15: 0xffffff, // bright white
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Color is a color that can be used in a terminal. ANSI (including
|
||||
// ANSI256) and 24-bit "true colors" fall under this category.
|
||||
type Color interface {
|
||||
color.Color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BasicColor is an ANSI 3-bit or 4-bit color with a value from 0 to 15.
|
||||
type BasicColor uint8
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Color = BasicColor(0)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// Black is the ANSI black color.
|
||||
Black BasicColor = iota
|
||||
|
||||
// Red is the ANSI red color.
|
||||
Red
|
||||
|
||||
// Green is the ANSI green color.
|
||||
Green
|
||||
|
||||
// Yellow is the ANSI yellow color.
|
||||
Yellow
|
||||
|
||||
// Blue is the ANSI blue color.
|
||||
Blue
|
||||
|
||||
// Magenta is the ANSI magenta color.
|
||||
Magenta
|
||||
|
||||
// Cyan is the ANSI cyan color.
|
||||
Cyan
|
||||
|
||||
// White is the ANSI white color.
|
||||
White
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightBlack is the ANSI bright black color.
|
||||
BrightBlack
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightRed is the ANSI bright red color.
|
||||
BrightRed
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightGreen is the ANSI bright green color.
|
||||
BrightGreen
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightYellow is the ANSI bright yellow color.
|
||||
BrightYellow
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightBlue is the ANSI bright blue color.
|
||||
BrightBlue
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightMagenta is the ANSI bright magenta color.
|
||||
BrightMagenta
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightCyan is the ANSI bright cyan color.
|
||||
BrightCyan
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightWhite is the ANSI bright white color.
|
||||
BrightWhite
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the red, green, blue and alpha components of the color. It
|
||||
// satisfies the color.Color interface.
|
||||
func (c BasicColor) RGBA() (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
ansi := uint32(c)
|
||||
if ansi > 15 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, 0, 0xffff
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, g, b := ansiToRGB(ansi)
|
||||
return toRGBA(r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExtendedColor is an ANSI 256 (8-bit) color with a value from 0 to 255.
|
||||
type ExtendedColor uint8
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Color = ExtendedColor(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the red, green, blue and alpha components of the color. It
|
||||
// satisfies the color.Color interface.
|
||||
func (c ExtendedColor) RGBA() (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
r, g, b := ansiToRGB(uint32(c))
|
||||
return toRGBA(r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TrueColor is a 24-bit color that can be used in the terminal.
|
||||
// This can be used to represent RGB colors.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example, the color red can be represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TrueColor(0xff0000)
|
||||
type TrueColor uint32
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Color = TrueColor(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the red, green, blue and alpha components of the color. It
|
||||
// satisfies the color.Color interface.
|
||||
func (c TrueColor) RGBA() (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
r, g, b := hexToRGB(uint32(c))
|
||||
return toRGBA(r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ansiToRGB converts an ANSI color to a 24-bit RGB color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// r, g, b := ansiToRGB(57)
|
||||
func ansiToRGB(ansi uint32) (uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
// For out-of-range values return black.
|
||||
if ansi > 255 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Low ANSI.
|
||||
if ansi < 16 {
|
||||
h, ok := lowANSI[ansi]
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return 0, 0, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, g, b := hexToRGB(h)
|
||||
return r, g, b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Grays.
|
||||
if ansi > 231 {
|
||||
s := (ansi-232)*10 + 8
|
||||
return s, s, s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ANSI256.
|
||||
n := ansi - 16
|
||||
b := n % 6
|
||||
g := (n - b) / 6 % 6
|
||||
r := (n - b - g*6) / 36 % 6
|
||||
for _, v := range []*uint32{&r, &g, &b} {
|
||||
if *v > 0 {
|
||||
c := *v*40 + 55
|
||||
*v = c
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return r, g, b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hexToRGB converts a number in hexadecimal format to red, green, and blue
|
||||
// values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// r, g, b := hexToRGB(0x0000FF)
|
||||
func hexToRGB(hex uint32) (uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
return hex >> 16, hex >> 8 & 0xff, hex & 0xff
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// toRGBA converts an RGB 8-bit color values to 32-bit color values suitable
|
||||
// for color.Color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// color.Color requires 16-bit color values, so we duplicate the 8-bit values
|
||||
// to fill the 16-bit values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This always returns 0xffff (opaque) for the alpha channel.
|
||||
func toRGBA(r, g, b uint32) (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
r |= r << 8
|
||||
g |= g << 8
|
||||
b |= b << 8
|
||||
return r, g, b, 0xffff
|
||||
}
|
||||
141
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/csi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
141
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/csi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CsiSequence represents a control sequence introducer (CSI) sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The sequence starts with a CSI sequence, CSI (0x9B) in a 8-bit environment
|
||||
// or ESC [ (0x1B 0x5B) in a 7-bit environment, followed by any number of
|
||||
// parameters in the range of 0x30-0x3F, then by any number of intermediate
|
||||
// byte in the range of 0x20-0x2F, then finally with a single final byte in the
|
||||
// range of 0x20-0x7E.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI P..P I..I F
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.4.
|
||||
type CsiSequence struct {
|
||||
// Params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is a slice of integers, where each integer is a 32-bit integer
|
||||
// containing the parameter value in the lower 31 bits and a flag in the
|
||||
// most significant bit indicating whether there are more sub-parameters.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command of the sequence.
|
||||
// The command is a 32-bit integer containing the CSI command byte in the
|
||||
// lower 8 bits, the private marker in the next 8 bits, and the intermediate
|
||||
// byte in the next 8 bits.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Is represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 'u' | '?' << 8
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = CsiSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
return parser.Marker(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
// An intermediate byte is in the range of 0x20-0x2F. This includes these
|
||||
// characters from ' ', '!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', ”', '(', ')', '*', '+',
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Param(i int) int {
|
||||
return parser.Param(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) HasMore(i int) bool {
|
||||
return parser.HasMore(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Subparams(i int) []int {
|
||||
return parser.Subparams(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Len() int {
|
||||
return parser.Len(s.Params)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Range(fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
parser.Range(s.Params, fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return CsiSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]int(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The string will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC [ P..P I..I F).
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns a buffer containing the sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b[")
|
||||
if m := s.Marker(); m != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(m))
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.Range(func(i, param int, hasMore bool) bool {
|
||||
if param >= 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(param))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(s.Params)-1 {
|
||||
if hasMore {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(':')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(';')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
if i := s.Intermediate(); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(s.Command()))
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The bytes will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC [ P..P I..I F).
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
17
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ctrl.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
17
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ctrl.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestXTVersion is a control sequence that requests the terminal's XTVERSION. It responds with a DSR sequence identifying the version.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > Ps q
|
||||
// DCS > | text ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-PC-Style-Function-Keys
|
||||
const RequestXTVersion = "\x1b[>0q"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestPrimaryDeviceAttributes is a control sequence that requests the
|
||||
// terminal's primary device attributes (DA1).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI c
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DA1.html
|
||||
const RequestPrimaryDeviceAttributes = "\x1b[c"
|
||||
190
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cursor.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
190
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cursor.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// SaveCursor (DECSC) is an escape sequence that saves the current cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC 7
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSC.html
|
||||
const SaveCursor = "\x1b7"
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreCursor (DECRC) is an escape sequence that restores the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC 8
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRC.html
|
||||
const RestoreCursor = "\x1b8"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestCursorPosition (CPR) is an escape sequence that requests the current
|
||||
// cursor position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI 6 n
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal will report the cursor position as a CSI sequence in the
|
||||
// following format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pl ; Pc R
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pl is the line number and Pc is the column number.
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CPR.html
|
||||
const RequestCursorPosition = "\x1b[6n"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestExtendedCursorPosition (DECXCPR) is a sequence for requesting the
|
||||
// cursor position report including the current page number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? 6 n
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal will report the cursor position as a CSI sequence in the
|
||||
// following format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pl ; Pc ; Pp R
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pl is the line number, Pc is the column number, and Pp is the page
|
||||
// number.
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECXCPR.html
|
||||
const RequestExtendedCursorPosition = "\x1b[?6n"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorUp (CUU) returns a sequence for moving the cursor up n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n A
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUU.html
|
||||
func CursorUp(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "A"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorUp1 is a sequence for moving the cursor up one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorUp(1).
|
||||
const CursorUp1 = "\x1b[A"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorDown (CUD) returns a sequence for moving the cursor down n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n B
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUD.html
|
||||
func CursorDown(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "B"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorDown1 is a sequence for moving the cursor down one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorDown(1).
|
||||
const CursorDown1 = "\x1b[B"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorRight (CUF) returns a sequence for moving the cursor right n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n C
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUF.html
|
||||
func CursorRight(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "C"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorRight1 is a sequence for moving the cursor right one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorRight(1).
|
||||
const CursorRight1 = "\x1b[C"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorLeft (CUB) returns a sequence for moving the cursor left n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n D
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUB.html
|
||||
func CursorLeft(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "D"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorLeft1 is a sequence for moving the cursor left one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorLeft(1).
|
||||
const CursorLeft1 = "\x1b[D"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorNextLine (CNL) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// beginning of the next line n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n E
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CNL.html
|
||||
func CursorNextLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "E"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorPreviousLine (CPL) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// beginning of the previous line n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n F
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CPL.html
|
||||
func CursorPreviousLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "F"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveCursor (CUP) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the given row
|
||||
// and column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n ; m H
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUP.html
|
||||
func MoveCursor(row, col int) string {
|
||||
if row < 0 {
|
||||
row = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if col < 0 {
|
||||
col = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(row) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(col) + "H"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveCursorOrigin is a sequence for moving the cursor to the upper left
|
||||
// corner of the screen. This is equivalent to MoveCursor(1, 1).
|
||||
const MoveCursorOrigin = "\x1b[1;1H"
|
||||
|
||||
// SaveCursorPosition (SCP or SCOSC) is a sequence for saving the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI s
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This acts like Save, except the page number where the cursor is located is
|
||||
// not saved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCOSC.html
|
||||
const SaveCursorPosition = "\x1b[s"
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreCursorPosition (RCP or SCORC) is a sequence for restoring the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This acts like Restore, except the cursor stays on the same page where the
|
||||
// cursor was saved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCORC.html
|
||||
const RestoreCursorPosition = "\x1b[u"
|
||||
148
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/dcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
148
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/dcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// DcsSequence represents a Device Control String (DCS) escape sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The DCS sequence is used to send device control strings to the terminal. The
|
||||
// sequence starts with the C1 control code character DCS (0x9B) or ESC P in
|
||||
// 7-bit environments, followed by parameter bytes, intermediate bytes, a
|
||||
// command byte, followed by data bytes, and ends with the C1 control code
|
||||
// character ST (0x9C) or ESC \ in 7-bit environments.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This follows the parameter string format.
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.4.1
|
||||
type DcsSequence struct {
|
||||
// Params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is a slice of integers, where each integer is a 32-bit integer
|
||||
// containing the parameter value in the lower 31 bits and a flag in the
|
||||
// most significant bit indicating whether there are more sub-parameters.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Data contains the string raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is the data between the final byte and the escape sequence terminator.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command of the sequence.
|
||||
// The command is a 32-bit integer containing the DCS command byte in the
|
||||
// lower 8 bits, the private marker in the next 8 bits, and the intermediate
|
||||
// byte in the next 8 bits.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS > 0 ; 1 $ r <data> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Is represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 'r' | '>' << 8 | '$' << 16
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = DcsSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
return parser.Marker(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
// An intermediate byte is in the range of 0x20-0x2F. This includes these
|
||||
// characters from ' ', '!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', ”', '(', ')', '*', '+',
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Param(i int) int {
|
||||
return parser.Param(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) HasMore(i int) bool {
|
||||
return parser.HasMore(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Subparams(i int) []int {
|
||||
return parser.Subparams(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Len() int {
|
||||
return parser.Len(s.Params)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Range(fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
parser.Range(s.Params, fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return DcsSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]int(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The string will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC P p..p i..i f <data> ESC \).
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns a buffer containing the sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1bP")
|
||||
if m := s.Marker(); m != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(m))
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.Range(func(i, param int, hasMore bool) bool {
|
||||
if param >= -1 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(param))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(s.Params)-1 {
|
||||
if hasMore {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(':')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(';')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
if i := s.Intermediate(); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(s.Command()))
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteByte(ESC)
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\\')
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The bytes will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC P p..p i..i F <data> ESC \).
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
// Package ansi defines common ANSI escape sequences based on the ECMA-48
|
||||
// specs.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All sequences use 7-bit C1 control codes, which are supported by most
|
||||
// terminal emulators. OSC sequences are terminated by a BEL for wider
|
||||
// compatibility with terminals.
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
28
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/hyperlink.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
28
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/hyperlink.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strings"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHyperlink returns a sequence for starting a hyperlink.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 8 ; Params ; Uri ST
|
||||
// OSC 8 ; Params ; Uri BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To reset the hyperlink, omit the URI.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://gist.github.com/egmontkob/eb114294efbcd5adb1944c9f3cb5feda
|
||||
func SetHyperlink(uri string, params ...string) string {
|
||||
var p string
|
||||
if len(params) > 0 {
|
||||
p = strings.Join(params, ":")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]8;" + p + ";" + uri + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetHyperlink returns a sequence for resetting the hyperlink.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetHyperlink("", params...).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://gist.github.com/egmontkob/eb114294efbcd5adb1944c9f3cb5feda
|
||||
func ResetHyperlink(params ...string) string {
|
||||
return SetHyperlink("", params...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
58
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/kitty.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
58
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/kitty.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// Kitty keyboard protocol progressive enhancement flags.
|
||||
// See: https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
const (
|
||||
KittyDisambiguateEscapeCodes = 1 << iota
|
||||
KittyReportEventTypes
|
||||
KittyReportAlternateKeys
|
||||
KittyReportAllKeys
|
||||
KittyReportAssociatedKeys
|
||||
|
||||
KittyAllFlags = KittyDisambiguateEscapeCodes | KittyReportEventTypes |
|
||||
KittyReportAlternateKeys | KittyReportAllKeys | KittyReportAssociatedKeys
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestKittyKeyboard is a sequence to request the terminal Kitty keyboard
|
||||
// protocol enabled flags.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/
|
||||
const RequestKittyKeyboard = "\x1b[?u"
|
||||
|
||||
// PushKittyKeyboard returns a sequence to push the given flags to the terminal
|
||||
// Kitty Keyboard stack.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > flags u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
func PushKittyKeyboard(flags int) string {
|
||||
var f string
|
||||
if flags > 0 {
|
||||
f = strconv.Itoa(flags)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return "\x1b[>" + f + "u"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableKittyKeyboard is a sequence to push zero into the terminal Kitty
|
||||
// Keyboard stack to disable the protocol.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to PushKittyKeyboard(0).
|
||||
const DisableKittyKeyboard = "\x1b[>0u"
|
||||
|
||||
// PopKittyKeyboard returns a sequence to pop n number of flags from the
|
||||
// terminal Kitty Keyboard stack.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI < flags u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
func PopKittyKeyboard(n int) string {
|
||||
var num string
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
num = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return "\x1b[<" + num + "u"
|
||||
}
|
||||
132
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
132
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// This file define uses multiple sequences to set (SM), reset (RM), and request
|
||||
// (DECRQM) different ANSI and DEC modes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SM.html
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/RM.html
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRQM.html
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal then responds to the request with a Report Mode function
|
||||
// (DECRPM) in the format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ANSI format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pa ; Ps ; $ y
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DEC format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pa ; Ps $ y
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pa is the mode number, and Ps is the mode value.
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRPM.html
|
||||
|
||||
// Application Cursor Keys (DECCKM) is a mode that determines whether the
|
||||
// cursor keys send ANSI cursor sequences or application sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECCKM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1h"
|
||||
DisableCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1l"
|
||||
RequestCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Text Cursor Enable Mode (DECTCEM) is a mode that shows/hides the cursor.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECTCEM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ShowCursor = "\x1b[?25h"
|
||||
HideCursor = "\x1b[?25l"
|
||||
RequestCursorVisibility = "\x1b[?25$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// VT Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button press and release.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouse = "\x1b[?1000h"
|
||||
DisableMouse = "\x1b[?1000l"
|
||||
RequestMouse = "\x1b[?1000$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// VT Hilite Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button presses, releases, and highlighted cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001h"
|
||||
DisableMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001l"
|
||||
RequestMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Cell Motion Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse
|
||||
// reports on button press, release, and motion events.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002h"
|
||||
DisableMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002l"
|
||||
RequestMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// All Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button press, release, motion, and highlight events.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003h"
|
||||
DisableMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003l"
|
||||
RequestMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR Mouse Extension is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports events
|
||||
// formatted with SGR parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006h"
|
||||
DisableMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006l"
|
||||
RequestMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Alternate Screen Buffer is a mode that determines whether the alternate screen
|
||||
// buffer is active.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-The-Alternate-Screen-Buffer
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049h"
|
||||
DisableAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049l"
|
||||
RequestAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Bracketed Paste Mode is a mode that determines whether pasted text is
|
||||
// bracketed with escape sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://cirw.in/blog/bracketed-paste
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Bracketed-Paste-Mode
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004h"
|
||||
DisableBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004l"
|
||||
RequestBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Synchronized Output Mode is a mode that determines whether output is
|
||||
// synchronized with the terminal.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://gist.github.com/christianparpart/d8a62cc1ab659194337d73e399004036
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026h"
|
||||
DisableSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026l"
|
||||
RequestSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Win32Input is a mode that determines whether input is processed by the
|
||||
// Win32 console and Conpty.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://github.com/microsoft/terminal/blob/main/doc/specs/%234999%20-%20Improved%20keyboard%20handling%20in%20Conpty.md
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001h"
|
||||
DisableWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001l"
|
||||
RequestWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
69
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/osc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
69
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/osc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// OscSequence represents an OSC sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The sequence starts with a OSC sequence, OSC (0x9D) in a 8-bit environment
|
||||
// or ESC ] (0x1B 0x5D) in a 7-bit environment, followed by positive integer identifier,
|
||||
// then by arbitrary data terminated by a ST (0x9C) in a 8-bit environment,
|
||||
// ESC \ (0x1B 0x5C) in a 7-bit environment, or BEL (0x07) for backwards compatibility.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC Ps ; Pt ST
|
||||
// OSC Ps ; Pt BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.7.
|
||||
type OscSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence including the identifier
|
||||
// command.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command of the sequence.
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = OscSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return s.Cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Params returns the parameters of the OSC sequence split by ';'.
|
||||
// The first element is the identifier command.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Params() []string {
|
||||
return strings.Split(string(s.Data), ";")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return OscSequence{
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
// To be more compatible with different terminal, this will always return a
|
||||
// 7-bit formatted sequence, terminated by BEL.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
// To be more compatible with different terminal, this will always return a
|
||||
// 7-bit formatted sequence, terminated by BEL.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b]")
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteByte(BEL)
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
45
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/params.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
45
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/params.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Params parses and returns a list of control sequence parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Parameters are positive integers separated by semicolons. Empty parameters
|
||||
// default to zero. Parameters can have sub-parameters separated by colons.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Any non-parameter bytes are ignored. This includes bytes that are not in the
|
||||
// range of 0x30-0x3B.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.4.1.
|
||||
func Params(p []byte) [][]uint {
|
||||
if len(p) == 0 {
|
||||
return [][]uint{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter out non-parameter bytes i.e. non 0x30-0x3B.
|
||||
p = bytes.TrimFunc(p, func(r rune) bool {
|
||||
return r < 0x30 || r > 0x3B
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
parts := bytes.Split(p, []byte{';'})
|
||||
params := make([][]uint, len(parts))
|
||||
for i, part := range parts {
|
||||
sparts := bytes.Split(part, []byte{':'})
|
||||
params[i] = make([]uint, len(sparts))
|
||||
for j, spart := range sparts {
|
||||
params[i][j] = bytesToUint16(spart)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return params
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func bytesToUint16(b []byte) uint {
|
||||
var n uint
|
||||
for _, c := range b {
|
||||
n = n*10 + uint(c-'0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
357
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
357
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,357 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ParserDispatcher is a function that dispatches a sequence.
|
||||
type ParserDispatcher func(Sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
// Parser represents a DEC ANSI compatible sequence parser.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It uses a state machine to parse ANSI escape sequences and control
|
||||
// characters. The parser is designed to be used with a terminal emulator or
|
||||
// similar application that needs to parse ANSI escape sequences and control
|
||||
// characters.
|
||||
// See package [parser] for more information.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:generate go run ./gen.go
|
||||
type Parser struct {
|
||||
// Params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// These parameters used when constructing CSI and DCS sequences.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
// These data used when constructing OSC, DCS, SOS, PM, and APC sequences.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// DataLen keeps track of the length of the data buffer.
|
||||
// If DataLen is -1, the data buffer is unlimited and will grow as needed.
|
||||
// Otherwise, DataLen is limited by the size of the Data buffer.
|
||||
DataLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// ParamsLen keeps track of the number of parameters.
|
||||
// This is limited by the size of the Params buffer.
|
||||
ParamsLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command along with the private marker and
|
||||
// intermediate bytes of the sequence.
|
||||
// The first lower byte contains the command byte, the next byte contains
|
||||
// the private marker, and the next byte contains the intermediate byte.
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
|
||||
// RuneLen keeps track of the number of bytes collected for a UTF-8 rune.
|
||||
RuneLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// RuneBuf contains the bytes collected for a UTF-8 rune.
|
||||
RuneBuf [utf8.MaxRune]byte
|
||||
|
||||
// State is the current state of the parser.
|
||||
State byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewParser returns a new parser with the given sizes allocated.
|
||||
// If dataSize is zero, the underlying data buffer will be unlimited and will
|
||||
// grow as needed.
|
||||
func NewParser(paramsSize, dataSize int) *Parser {
|
||||
s := &Parser{
|
||||
Params: make([]int, paramsSize),
|
||||
Data: make([]byte, dataSize),
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dataSize <= 0 {
|
||||
s.DataLen = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset resets the parser to its initial state.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Reset() {
|
||||
p.clear()
|
||||
p.State = parser.GroundState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clear clears the parser parameters and command.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) clear() {
|
||||
if len(p.Params) > 0 {
|
||||
p.Params[0] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.ParamsLen = 0
|
||||
p.Cmd = 0
|
||||
p.RuneLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StateName returns the name of the current state.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) StateName() string {
|
||||
return parser.StateNames[p.State]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses the given dispatcher and byte buffer.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Parse(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b []byte) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(b); i++ {
|
||||
p.Advance(dispatcher, b[i], i < len(b)-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Advance advances the parser with the given dispatcher and byte.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Advance(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b byte, more bool) parser.Action {
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.Utf8State:
|
||||
// We handle UTF-8 here.
|
||||
return p.advanceUtf8(dispatcher, b)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return p.advance(dispatcher, b, more)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) collectRune(b byte) {
|
||||
if p.RuneLen < utf8.UTFMax {
|
||||
p.RuneBuf[p.RuneLen] = b
|
||||
p.RuneLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advanceUtf8(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b byte) parser.Action {
|
||||
// Collect UTF-8 rune bytes.
|
||||
p.collectRune(b)
|
||||
rw := utf8ByteLen(p.RuneBuf[0])
|
||||
if rw == -1 {
|
||||
// We panic here because the first byte comes from the state machine,
|
||||
// if this panics, it means there is a bug in the state machine!
|
||||
panic("invalid rune") // unreachable
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p.RuneLen < rw {
|
||||
return parser.NoneAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We have enough bytes to decode the rune
|
||||
bts := p.RuneBuf[:rw]
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(bts)
|
||||
if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(Rune(r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.State = parser.GroundState
|
||||
p.RuneLen = 0
|
||||
|
||||
return parser.NoneAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advance(d ParserDispatcher, b byte, more bool) parser.Action {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(p.State, b)
|
||||
|
||||
// We need to clear the parser state if the state changes from EscapeState.
|
||||
// This is because when we enter the EscapeState, we don't get a chance to
|
||||
// clear the parser state. For example, when a sequence terminates with a
|
||||
// ST (\x1b\\ or \x9c), we dispatch the current sequence and transition to
|
||||
// EscapeState. However, the parser state is not cleared in this case and
|
||||
// we need to clear it here before dispatching the esc sequence.
|
||||
if p.State != state {
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.EscapeState:
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ClearAction, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if action == parser.PutAction &&
|
||||
p.State == parser.DcsEntryState && state == parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
// XXX: This is a special case where we need to start collecting
|
||||
// non-string parameterized data i.e. doesn't follow the ECMA-48 §
|
||||
// 5.4.1 string parameters format.
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.StartAction, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle special cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case b == ESC && p.State == parser.EscapeState:
|
||||
// Two ESCs in a row
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
if !more {
|
||||
// Two ESCs at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case b == ESC && !more:
|
||||
// Last byte is an ESC
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == 'P' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC P (DCS) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == 'X' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC X (SOS) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '[' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC [ (CSI) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == ']' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC ] (OSC) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '^' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC ^ (PM) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '_' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC _ (APC) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
p.performAction(d, action, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.State = state
|
||||
|
||||
return action
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) performAction(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, action parser.Action, b byte) {
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.IgnoreAction:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ClearAction:
|
||||
p.clear()
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b) > 1 {
|
||||
p.collectRune(b)
|
||||
} else if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(Rune(b))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(ControlCode(b))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.MarkerAction:
|
||||
// Collect private marker
|
||||
// we only store the last marker
|
||||
p.Cmd &^= 0xff << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b) << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.CollectAction:
|
||||
// Collect intermediate bytes
|
||||
// we only store the last intermediate byte
|
||||
p.Cmd &^= 0xff << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b) << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ParamAction:
|
||||
// Collect parameters
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen >= len(p.Params) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b >= '0' && b <= '9' {
|
||||
if p.Params[p.ParamsLen] == parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] *= 10
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] += int(b - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b == ':' {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] |= parser.HasMoreFlag
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b == ';' || b == ':' {
|
||||
p.ParamsLen++
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen < len(p.Params) {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.StartAction:
|
||||
if p.DataLen < 0 {
|
||||
p.Data = make([]byte, 0)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.DataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.State >= parser.DcsEntryState && p.State <= parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
// Collect the command byte for DCS
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.Cmd = parser.MissingCommand
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.PutAction:
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.OscStringState:
|
||||
if b == ';' && p.Cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
// Try to parse the command
|
||||
datalen := len(p.Data)
|
||||
if p.DataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
datalen = p.DataLen
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < datalen; i++ {
|
||||
d := p.Data[i]
|
||||
if d < '0' || d > '9' {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.Cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
p.Cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.Cmd *= 10
|
||||
p.Cmd += int(d - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p.DataLen < 0 {
|
||||
p.Data = append(p.Data, b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if p.DataLen < len(p.Data) {
|
||||
p.Data[p.DataLen] = b
|
||||
p.DataLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.DispatchAction:
|
||||
// Increment the last parameter
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen > 0 && p.ParamsLen < len(p.Params)-1 ||
|
||||
p.ParamsLen == 0 && len(p.Params) > 0 && p.Params[0] != parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.ParamsLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if dispatcher == nil {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var seq Sequence
|
||||
data := p.Data
|
||||
if p.DataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
data = data[:p.DataLen]
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.CsiEntryState, parser.CsiParamState, parser.CsiIntermediateState:
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = CsiSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Params: p.Params[:p.ParamsLen]}
|
||||
case parser.EscapeState, parser.EscapeIntermediateState:
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = EscSequence(p.Cmd)
|
||||
case parser.DcsEntryState, parser.DcsParamState, parser.DcsIntermediateState, parser.DcsStringState:
|
||||
seq = DcsSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Params: p.Params[:p.ParamsLen], Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.OscStringState:
|
||||
seq = OscSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.SosStringState:
|
||||
seq = SosSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.PmStringState:
|
||||
seq = PmSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.ApcStringState:
|
||||
seq = ApcSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dispatcher(seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func utf8ByteLen(b byte) int {
|
||||
if b <= 0b0111_1111 { // 0x00-0x7F
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
} else if b >= 0b1100_0000 && b <= 0b1101_1111 { // 0xC0-0xDF
|
||||
return 2
|
||||
} else if b >= 0b1110_0000 && b <= 0b1110_1111 { // 0xE0-0xEF
|
||||
return 3
|
||||
} else if b >= 0b1111_0000 && b <= 0b1111_0111 { // 0xF0-0xF7
|
||||
return 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
78
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/const.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
78
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/const.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
package parser
|
||||
|
||||
// Action is a DEC ANSI parser action.
|
||||
type Action = byte
|
||||
|
||||
// These are the actions that the parser can take.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
NoneAction Action = iota
|
||||
ClearAction
|
||||
CollectAction
|
||||
MarkerAction
|
||||
DispatchAction
|
||||
ExecuteAction
|
||||
StartAction // Start of a data string
|
||||
PutAction // Put into the data string
|
||||
ParamAction
|
||||
PrintAction
|
||||
|
||||
IgnoreAction = NoneAction
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// nolint: unused
|
||||
var ActionNames = []string{
|
||||
"NoneAction",
|
||||
"ClearAction",
|
||||
"CollectAction",
|
||||
"MarkerAction",
|
||||
"DispatchAction",
|
||||
"ExecuteAction",
|
||||
"StartAction",
|
||||
"PutAction",
|
||||
"ParamAction",
|
||||
"PrintAction",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// State is a DEC ANSI parser state.
|
||||
type State = byte
|
||||
|
||||
// These are the states that the parser can be in.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
GroundState State = iota
|
||||
CsiEntryState
|
||||
CsiIntermediateState
|
||||
CsiParamState
|
||||
DcsEntryState
|
||||
DcsIntermediateState
|
||||
DcsParamState
|
||||
DcsStringState
|
||||
EscapeState
|
||||
EscapeIntermediateState
|
||||
OscStringState
|
||||
SosStringState
|
||||
PmStringState
|
||||
ApcStringState
|
||||
|
||||
// Utf8State is not part of the DEC ANSI standard. It is used to handle
|
||||
// UTF-8 sequences.
|
||||
Utf8State
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// nolint: unused
|
||||
var StateNames = []string{
|
||||
"GroundState",
|
||||
"CsiEntryState",
|
||||
"CsiIntermediateState",
|
||||
"CsiParamState",
|
||||
"DcsEntryState",
|
||||
"DcsIntermediateState",
|
||||
"DcsParamState",
|
||||
"DcsStringState",
|
||||
"EscapeState",
|
||||
"EscapeIntermediateState",
|
||||
"OscStringState",
|
||||
"SosStringState",
|
||||
"PmStringState",
|
||||
"ApcStringState",
|
||||
"Utf8State",
|
||||
}
|
||||
136
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/seq.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
136
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/seq.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
package parser
|
||||
|
||||
import "math"
|
||||
|
||||
// Shift and masks for sequence parameters and intermediates.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MarkerShift = 8
|
||||
IntermedShift = 16
|
||||
CommandMask = 0xff
|
||||
HasMoreFlag = math.MinInt32
|
||||
ParamMask = ^HasMoreFlag
|
||||
MissingParam = ParamMask
|
||||
MissingCommand = MissingParam
|
||||
MaxParam = math.MaxUint16 // the maximum value a parameter can have
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// MaxParamsSize is the maximum number of parameters a sequence can have.
|
||||
MaxParamsSize = 32
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultParamValue is the default value used for missing parameters.
|
||||
DefaultParamValue = 0
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func Marker(cmd int) int {
|
||||
return (cmd >> MarkerShift) & CommandMask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the sequence.
|
||||
// An intermediate byte is in the range of 0x20-0x2F. This includes these
|
||||
// characters from ' ', '!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', ”', '(', ')', '*', '+',
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func Intermediate(cmd int) int {
|
||||
return (cmd >> IntermedShift) & CommandMask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func Command(cmd int) int {
|
||||
return cmd & CommandMask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func Param(params []int, i int) int {
|
||||
if len(params) == 0 || i < 0 || i >= len(params) {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p := params[i] & ParamMask
|
||||
if p == MissingParam {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func HasMore(params []int, i int) bool {
|
||||
if len(params) == 0 || i >= len(params) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return params[i]&HasMoreFlag != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func Subparams(params []int, i int) []int {
|
||||
if len(params) == 0 || i < 0 || i >= len(params) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Count the number of parameters before the given parameter index.
|
||||
var count int
|
||||
var j int
|
||||
for j = 0; j < len(params); j++ {
|
||||
if count == i {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !HasMore(params, j) {
|
||||
count++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if count > i || j >= len(params) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var subs []int
|
||||
for ; j < len(params); j++ {
|
||||
if !HasMore(params, j) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
p := Param(params, j)
|
||||
if p == -1 {
|
||||
p = DefaultParamValue
|
||||
}
|
||||
subs = append(subs, p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p := Param(params, j)
|
||||
if p == -1 {
|
||||
p = DefaultParamValue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return append(subs, p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func Len(params []int) int {
|
||||
var n int
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(params); i++ {
|
||||
if !HasMore(params, i) {
|
||||
n++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func Range(params []int, fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(params); i++ {
|
||||
if !fn(i, Param(params, i), HasMore(params, i)) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
269
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/transition_table.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
269
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/transition_table.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,269 @@
|
||||
package parser
|
||||
|
||||
// Table values are generated like this:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// index: currentState << IndexStateShift | charCode
|
||||
// value: action << TransitionActionShift | nextState
|
||||
const (
|
||||
TransitionActionShift = 4
|
||||
TransitionStateMask = 15
|
||||
IndexStateShift = 8
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultTableSize is the default size of the transition table.
|
||||
DefaultTableSize = 4096
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Table is a DEC ANSI transition table.
|
||||
var Table = GenerateTransitionTable()
|
||||
|
||||
// TransitionTable is a DEC ANSI transition table.
|
||||
// https://vt100.net/emu/dec_ansi_parser
|
||||
type TransitionTable []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTransitionTable returns a new DEC ANSI transition table.
|
||||
func NewTransitionTable(size int) TransitionTable {
|
||||
if size <= 0 {
|
||||
size = DefaultTableSize
|
||||
}
|
||||
return TransitionTable(make([]byte, size))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDefault sets default transition.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) SetDefault(action Action, state State) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(t); i++ {
|
||||
t[i] = action<<TransitionActionShift | state
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddOne adds a transition.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) AddOne(code byte, state State, action Action, next State) {
|
||||
idx := int(state)<<IndexStateShift | int(code)
|
||||
value := action<<TransitionActionShift | next
|
||||
t[idx] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddMany adds many transitions.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) AddMany(codes []byte, state State, action Action, next State) {
|
||||
for _, code := range codes {
|
||||
t.AddOne(code, state, action, next)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddRange adds a range of transitions.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) AddRange(start, end byte, state State, action Action, next State) {
|
||||
for i := int(start); i <= int(end); i++ {
|
||||
t.AddOne(byte(i), state, action, next)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transition returns the next state and action for the given state and byte.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) Transition(state State, code byte) (State, Action) {
|
||||
index := int(state)<<IndexStateShift | int(code)
|
||||
value := t[index]
|
||||
return value & TransitionStateMask, value >> TransitionActionShift
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// byte range macro
|
||||
func r(start, end byte) []byte {
|
||||
var a []byte
|
||||
for i := int(start); i <= int(end); i++ {
|
||||
a = append(a, byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GenerateTransitionTable generates a DEC ANSI transition table compatible
|
||||
// with the VT500-series of terminals. This implementation includes a few
|
||||
// modifications that include:
|
||||
// - A new Utf8State is introduced to handle UTF8 sequences.
|
||||
// - Osc and Dcs data accept UTF8 sequences by extending the printable range
|
||||
// to 0xFF and 0xFE respectively.
|
||||
// - We don't ignore 0x3A (':') when building Csi and Dcs parameters and
|
||||
// instead use it to denote sub-parameters.
|
||||
// - Support dispatching SosPmApc sequences.
|
||||
func GenerateTransitionTable() TransitionTable {
|
||||
table := NewTransitionTable(DefaultTableSize)
|
||||
table.SetDefault(NoneAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Anywhere
|
||||
for _, state := range r(GroundState, Utf8State) {
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1a, 0x99, 0x9a}, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x80, 0x8F, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x90, 0x97, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, state, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Escape
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, state, ClearAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> SosStringState
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x98, state, StartAction, SosStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> PmStringState
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9E, state, StartAction, PmStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> ApcStringState
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9F, state, StartAction, ApcStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> CsiEntry
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9B, state, ClearAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> DcsEntry
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x90, state, ClearAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> OscString
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9D, state, StartAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Utf8
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xC2, 0xDF, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 2 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xE0, 0xEF, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 3 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xF0, 0xF4, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 4 byte sequence
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7F, GroundState, PrintAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// EscapeIntermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, EscapeIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, EscapeIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, EscapeIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, EscapeIntermediateState, CollectAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, EscapeIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
// EscapeIntermediate -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x7E, EscapeIntermediateState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Escape
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, EscapeState, ExecuteAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, EscapeState, ExecuteAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, EscapeState, ExecuteAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, EscapeState, IgnoreAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x4F, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x51, 0x57, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x59, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x5A, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x5C, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x60, 0x7E, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Escape_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, EscapeState, CollectAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Sos_pm_apc_string
|
||||
table.AddOne('X', EscapeState, StartAction, SosStringState) // SOS
|
||||
table.AddOne('^', EscapeState, StartAction, PmStringState) // PM
|
||||
table.AddOne('_', EscapeState, StartAction, ApcStringState) // APC
|
||||
// Escape -> Dcs_entry
|
||||
table.AddOne('P', EscapeState, ClearAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Csi_entry
|
||||
table.AddOne('[', EscapeState, ClearAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Osc_string
|
||||
table.AddOne(']', EscapeState, StartAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Sos_pm_apc_string
|
||||
for _, state := range r(SosStringState, ApcStringState) {
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7F, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
// ESC, ST, CAN, and SUB terminate the sequence
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, state, DispatchAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, state, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1A}, state, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_entry
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x07, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x0E, 0x17, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
// Dcs_entry -> Dcs_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, DcsEntryState, CollectAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Dcs_entry -> Dcs_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, DcsEntryState, ParamAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, DcsEntryState, MarkerAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
// Dcs_entry -> Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x08, 0x0D, DcsEntryState, PutAction, DcsStringState) // Follows ECMA-48 § 8.3.27
|
||||
// XXX: allows passing ESC (not a ECMA-48 standard) this to allow for
|
||||
// passthrough of ANSI sequences like in Screen or Tmux passthrough mode.
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, DcsEntryState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, DcsEntryState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, DcsIntermediateState, CollectAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Dcs_intermediate -> Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3F, DcsIntermediateState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, DcsIntermediateState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, DcsParamState, ParamAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
// Dcs_param -> Dcs_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, DcsParamState, CollectAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Dcs_param -> Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, DcsParamState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7E, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsStringState, IgnoreAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x80, 0xFF, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState) // Allow Utf8 characters by extending the printable range from 0x7F to 0xFF
|
||||
// ST, CAN, SUB, and ESC terminate the sequence
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, DcsStringState, DispatchAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, DcsStringState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1A}, DcsStringState, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Csi_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, CsiParamState, ExecuteAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, CsiParamState, ExecuteAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, CsiParamState, ExecuteAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, CsiParamState, ParamAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, CsiParamState, IgnoreAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, CsiParamState, IgnoreAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
// Csi_param -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, CsiParamState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Csi_param -> Csi_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, CsiParamState, CollectAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Csi_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, CsiIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, CsiIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, CsiIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, CsiIntermediateState, CollectAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, CsiIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Csi_intermediate -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, CsiIntermediateState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Csi_intermediate -> Csi_ignore
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3F, CsiIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Csi_entry
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, CsiEntryState, ExecuteAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, CsiEntryState, ExecuteAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, CsiEntryState, ExecuteAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, CsiEntryState, IgnoreAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
// Csi_entry -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, CsiEntryState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Csi_entry -> Csi_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, CsiEntryState, CollectAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Csi_entry -> Csi_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, CsiEntryState, ParamAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, CsiEntryState, MarkerAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Osc_string
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x06, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x08, 0x17, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0xFF, OscStringState, PutAction, OscStringState) // Allow Utf8 characters by extending the printable range from 0x7F to 0xFF
|
||||
|
||||
// ST, CAN, SUB, ESC, and BEL terminate the sequence
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, OscStringState, DispatchAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x07, OscStringState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, OscStringState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1A}, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
return table
|
||||
}
|
||||
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/passthrough.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/passthrough.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ScreenPassthrough wraps the given ANSI sequence in a DCS passthrough
|
||||
// sequence to be sent to the outer terminal. This is used to send raw escape
|
||||
// sequences to the outer terminal when running inside GNU Screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS <data> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: Screen limits the length of string sequences to 768 bytes (since 2014).
|
||||
// Use zero to indicate no limit, otherwise, this will chunk the returned
|
||||
// string into limit sized chunks.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://www.gnu.org/software/screen/manual/screen.html#String-Escapes
|
||||
// See: https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/screen.git/tree/src/screen.h?id=c184c6ec27683ff1a860c45be5cf520d896fd2ef#n44
|
||||
func ScreenPassthrough(seq string, limit int) string {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1bP")
|
||||
if limit > 0 {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(seq); i += limit {
|
||||
end := i + limit
|
||||
if end > len(seq) {
|
||||
end = len(seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString(seq[i:end])
|
||||
if end < len(seq) {
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\\x1bP")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteString(seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TmuxPassthrough wraps the given ANSI sequence in a special DCS passthrough
|
||||
// sequence to be sent to the outer terminal. This is used to send raw escape
|
||||
// sequences to the outer terminal when running inside Tmux.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS tmux ; <escaped-data> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where <escaped-data> is the given sequence in which all occurrences of ESC
|
||||
// (0x1b) are doubled i.e. replaced with ESC ESC (0x1b 0x1b).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: this needs the `allow-passthrough` option to be set to `on`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://github.com/tmux/tmux/wiki/FAQ#what-is-the-passthrough-escape-sequence-and-how-do-i-use-it
|
||||
func TmuxPassthrough(seq string) string {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1bPtmux;")
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(seq); i++ {
|
||||
if seq[i] == ESC {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(ESC)
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(seq[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
126
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/screen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
126
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/screen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseDisplay (ED) clears the screen or parts of the screen. Possible values:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Clear from cursor to end of screen.
|
||||
// 1: Clear from cursor to beginning of the screen.
|
||||
// 2: Clear entire screen (and moves cursor to upper left on DOS).
|
||||
// 3: Clear entire screen and delete all lines saved in the scrollback buffer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> J
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/ED.html
|
||||
func EraseDisplay(n int) string {
|
||||
if n < 0 {
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(n) + "J"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseDisplay constants.
|
||||
// These are the possible values for the EraseDisplay function.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EraseDisplayRight = "\x1b[0J"
|
||||
EraseDisplayLeft = "\x1b[1J"
|
||||
EraseEntireDisplay = "\x1b[2J"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseLine (EL) clears the current line or parts of the line. Possible values:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Clear from cursor to end of line.
|
||||
// 1: Clear from cursor to beginning of the line.
|
||||
// 2: Clear entire line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The cursor position is not affected.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> K
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/EL.html
|
||||
func EraseLine(n int) string {
|
||||
if n < 0 {
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(n) + "K"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseLine constants.
|
||||
// These are the possible values for the EraseLine function.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EraseLineRight = "\x1b[0K"
|
||||
EraseLineLeft = "\x1b[1K"
|
||||
EraseEntireLine = "\x1b[2K"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollUp (SU) scrolls the screen up n lines. New lines are added at the
|
||||
// bottom of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> S
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SU.html
|
||||
func ScrollUp(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "S"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollDown (SD) scrolls the screen down n lines. New lines are added at the
|
||||
// top of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> T
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SD.html
|
||||
func ScrollDown(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "T"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InsertLine (IL) inserts n blank lines at the current cursor position.
|
||||
// Existing lines are moved down.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> L
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/IL.html
|
||||
func InsertLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "L"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DeleteLine (DL) deletes n lines at the current cursor position. Existing
|
||||
// lines are moved up.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> M
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DL.html
|
||||
func DeleteLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "M"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetScrollingRegion (DECSTBM) sets the top and bottom margins for the scrolling
|
||||
// region. The default is the entire screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <top> ; <bottom> r
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSTBM.html
|
||||
func SetScrollingRegion(t, b int) string {
|
||||
if t < 0 {
|
||||
t = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b < 0 {
|
||||
b = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(t) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(b) + "r"
|
||||
}
|
||||
199
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sequence.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
199
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sequence.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,199 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Sequence represents an ANSI sequence. This can be a control sequence, escape
|
||||
// sequence, a printable character, etc.
|
||||
type Sequence interface {
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
String() string
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the sequence.
|
||||
Bytes() []byte
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the sequence.
|
||||
Clone() Sequence
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rune represents a printable character.
|
||||
type Rune rune
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = Rune(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return []byte(string(r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) String() string {
|
||||
return string(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ControlCode represents a control code character. This is a character that
|
||||
// is not printable and is used to control the terminal. This would be a
|
||||
// character in the C0 or C1 set in the range of 0x00-0x1F and 0x80-0x9F.
|
||||
type ControlCode byte
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = ControlCode(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (c ControlCode) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return []byte{byte(c)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (c ControlCode) String() string {
|
||||
return string(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (c ControlCode) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EscSequence represents an escape sequence.
|
||||
type EscSequence int
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = EscSequence(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns the buffer of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
if i := parser.Intermediate(int(e)); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(e.Command()))
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return e.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return e.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return e
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(int(e))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(int(e))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SosSequence represents a SOS sequence.
|
||||
type SosSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &SosSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return SosSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
b.WriteByte('X')
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PmSequence represents a PM sequence.
|
||||
type PmSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &PmSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return PmSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns the buffer of the PM sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
b.WriteByte('^')
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApcSequence represents an APC sequence.
|
||||
type ApcSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &ApcSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return ApcSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns the buffer of the APC sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
b.WriteByte('_')
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
296
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
296
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,296 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetStyle is a SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style sequence that resets
|
||||
// all attributes.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
const ResetStyle = "\x1b[m"
|
||||
|
||||
// Attr is a SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style attribute.
|
||||
type Attr = string
|
||||
|
||||
// Style represents an ANSI SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style.
|
||||
type Style []Attr
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the ANSI SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style sequence for
|
||||
// the given style.
|
||||
func (s Style) String() string {
|
||||
if len(s) == 0 {
|
||||
return ResetStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strings.Join(s, ";") + "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Styled returns a styled string with the given style applied.
|
||||
func (s Style) Styled(str string) string {
|
||||
if len(s) == 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.String() + str + ResetStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset appends the reset style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reset() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ResetAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bold appends the bold style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Bold() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, BoldAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Faint appends the faint style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Faint() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, FaintAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Italic appends the italic style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Italic() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ItalicAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Underline appends the underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Underline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, UnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DoubleUnderline appends the double underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DoubleUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DoubleUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CurlyUnderline appends the curly underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) CurlyUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, CurlyUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DottedUnderline appends the dotted underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DottedUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DottedUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DashedUnderline appends the dashed underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DashedUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DashedUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SlowBlink appends the slow blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) SlowBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, SlowBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RapidBlink appends the rapid blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) RapidBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, RapidBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reverse appends the reverse style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reverse() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ReverseAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Conceal appends the conceal style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Conceal() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ConcealAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Strikethrough appends the strikethrough style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Strikethrough() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, StrikethroughAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoBold appends the no bold style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoBold() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoBoldAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NormalIntensity appends the normal intensity style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NormalIntensity() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NormalIntensityAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoItalic appends the no italic style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoItalic() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoItalicAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoUnderline appends the no underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoBlink appends the no blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoReverse appends the no reverse style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoReverse() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoReverseAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoConceal appends the no conceal style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoConceal() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoConcealAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoStrikethrough appends the no strikethrough style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoStrikethrough() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoStrikethroughAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultForegroundColor appends the default foreground color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultForegroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultForegroundColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultBackgroundColor appends the default background color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultBackgroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultBackgroundColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultUnderlineColor appends the default underline color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultUnderlineColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultUnderlineColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForegroundColor appends the foreground color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) ForegroundColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ForegroundColorAttr(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BackgroundColor appends the background color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) BackgroundColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, BackgroundColorAttr(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineColor appends the underline color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnderlineColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, UnderlineColorAttr(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style attributes.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ResetAttr Attr = "0"
|
||||
BoldAttr Attr = "1"
|
||||
FaintAttr Attr = "2"
|
||||
ItalicAttr Attr = "3"
|
||||
UnderlineAttr Attr = "4"
|
||||
DoubleUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:2"
|
||||
CurlyUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:3"
|
||||
DottedUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:4"
|
||||
DashedUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:5"
|
||||
SlowBlinkAttr Attr = "5"
|
||||
RapidBlinkAttr Attr = "6"
|
||||
ReverseAttr Attr = "7"
|
||||
ConcealAttr Attr = "8"
|
||||
StrikethroughAttr Attr = "9"
|
||||
NoBoldAttr Attr = "21" // Some terminals treat this as double underline.
|
||||
NormalIntensityAttr Attr = "22"
|
||||
NoItalicAttr Attr = "23"
|
||||
NoUnderlineAttr Attr = "24"
|
||||
NoBlinkAttr Attr = "25"
|
||||
NoReverseAttr Attr = "27"
|
||||
NoConcealAttr Attr = "28"
|
||||
NoStrikethroughAttr Attr = "29"
|
||||
DefaultForegroundColorAttr Attr = "39"
|
||||
DefaultBackgroundColorAttr Attr = "49"
|
||||
DefaultUnderlineColorAttr Attr = "59"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ForegroundColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given foreground
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func ForegroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
// 3-bit or 4-bit ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "3<n>" or "9<n>" where n is the color number from 0 to 7
|
||||
if c < 8 {
|
||||
return "3" + string('0'+c)
|
||||
} else if c < 16 {
|
||||
return "9" + string('0'+c-8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "38;5;<n>"
|
||||
return "38;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case TrueColor, color.Color:
|
||||
// 24-bit "true color" foreground
|
||||
// "38;2;<r>;<g>;<b>"
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
return "38;2;" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(r)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BackgroundColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given background
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func BackgroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
// 3-bit or 4-bit ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "4<n>" or "10<n>" where n is the color number from 0 to 7
|
||||
if c < 8 {
|
||||
return "4" + string('0'+c)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return "10" + string('0'+c-8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "48;5;<n>"
|
||||
return "48;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case TrueColor, color.Color:
|
||||
// 24-bit "true color" foreground
|
||||
// "38;2;<r>;<g>;<b>"
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
return "48;2;" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(r)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given underline
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func UnderlineColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
// NOTE: we can't use 3-bit and 4-bit ANSI color codes with underline
|
||||
// color, use 256-color instead.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI underline color
|
||||
// "58;5;<n>"
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
return "58;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
return "58;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case TrueColor, color.Color:
|
||||
// 24-bit "true color" foreground
|
||||
// "38;2;<r>;<g>;<b>"
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
return "58;2;" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(r)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultUnderlineColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func shift(v uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
if v > 0xff {
|
||||
return v >> 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
31
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/termcap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
31
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/termcap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/hex"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestTermcap (XTGETTCAP) requests Termcap/Terminfo strings.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS + q <Pt> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where <Pt> is a list of Termcap/Terminfo capabilities, encoded in 2-digit
|
||||
// hexadecimals, separated by semicolons.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/terminfo.5.html
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func RequestTermcap(caps ...string) string {
|
||||
if len(caps) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s := "\x1bP+q"
|
||||
for i, c := range caps {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
s += ";"
|
||||
}
|
||||
s += strings.ToUpper(hex.EncodeToString([]byte(c)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return s + "\x1b\\"
|
||||
}
|
||||
32
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/title.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
32
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/title.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// SetIconNameWindowTitle returns a sequence for setting the icon name and
|
||||
// window title.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 0 ; title ST
|
||||
// OSC 0 ; title BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetIconNameWindowTitle(s string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]0;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetIconName returns a sequence for setting the icon name.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 1 ; title ST
|
||||
// OSC 1 ; title BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetIconName(s string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]1;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetWindowTitle returns a sequence for setting the window title.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 2 ; title ST
|
||||
// OSC 2 ; title BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetWindowTitle(s string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]2;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
112
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/truncate.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
112
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/truncate.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
"github.com/rivo/uniseg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Truncate truncates a string to a given length, adding a tail to the
|
||||
// end if the string is longer than the given length.
|
||||
// This function is aware of ANSI escape codes and will not break them, and
|
||||
// accounts for wide-characters (such as East Asians and emojis).
|
||||
func Truncate(s string, length int, tail string) string {
|
||||
if sw := StringWidth(s); sw <= length {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tw := StringWidth(tail)
|
||||
length -= tw
|
||||
if length < 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var cluster []byte
|
||||
var buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth := 0
|
||||
ignoring := false
|
||||
gstate := -1
|
||||
pstate := parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b := []byte(s)
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Here we iterate over the bytes of the string and collect printable
|
||||
// characters and runes. We also keep track of the width of the string
|
||||
// in cells.
|
||||
// Once we reach the given length, we start ignoring characters and only
|
||||
// collect ANSI escape codes until we reach the end of string.
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
// This action happens when we transition to the Utf8State.
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
|
||||
// increment the index by the length of the cluster
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
// Are we ignoring? Skip to the next byte
|
||||
if ignoring {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this gonna be too wide?
|
||||
// If so write the tail and stop collecting.
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
for _, r := range cluster {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gstate = -1 // reset grapheme state otherwise, width calculation might be off
|
||||
// Done collecting, now we're back in the ground state.
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this gonna be too wide?
|
||||
// If so write the tail and stop collecting.
|
||||
if curWidth >= length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Skip to the next byte if we're ignoring
|
||||
if ignoring {
|
||||
i++
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// collects printable ASCII
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
default:
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transition to the next state.
|
||||
pstate = state
|
||||
|
||||
// Once we reach the given length, we start ignoring runes and write
|
||||
// the tail to the buffer.
|
||||
if curWidth > length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/util.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/util.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// colorToHexString returns a hex string representation of a color.
|
||||
func colorToHexString(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
if c == nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
shift := func(v uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
if v > 0xff {
|
||||
return v >> 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
r, g, b = shift(r), shift(g), shift(b)
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("#%02x%02x%02x", r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// rgbToHex converts red, green, and blue values to a hexadecimal value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// hex := rgbToHex(0, 0, 255) // 0x0000FF
|
||||
func rgbToHex(r, g, b uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
return r<<16 + g<<8 + b
|
||||
}
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user